Unit 5 Solving Equations
... Evaluate algebraic expressions by substituting a value into the expression. Given concrete models of linear growing patterns, create verbal, numerical, graphical, and algebraic models. Investigate why some relationships are described as “linear.” Substitute numbers into variable expressions. Evaluat ...
... Evaluate algebraic expressions by substituting a value into the expression. Given concrete models of linear growing patterns, create verbal, numerical, graphical, and algebraic models. Investigate why some relationships are described as “linear.” Substitute numbers into variable expressions. Evaluat ...
here - Core Math Seminars
... Algebra II are assumed to have mastered those concepts outlined in the Algebra I standards. A thorough treatment of advanced algebraic concepts is provided through the study of functions, “families of functions,” equations, inequalities, systems of equations and inequalities, polynomials, rational e ...
... Algebra II are assumed to have mastered those concepts outlined in the Algebra I standards. A thorough treatment of advanced algebraic concepts is provided through the study of functions, “families of functions,” equations, inequalities, systems of equations and inequalities, polynomials, rational e ...
tutorial 7 - WordPress.com
... If 1 kg of mix A costs $12.50 to produce, 1 kg of mix, B costs $12.40 and 1 kg of mix C costs $11.70, determine the cost per kilogram of each different kind of nut. Hence, find the cost per kg to produce a mix containing 400 gram of Cashews nuts, 200 gram of Macadamias nuts and 400 grams of Brazil n ...
... If 1 kg of mix A costs $12.50 to produce, 1 kg of mix, B costs $12.40 and 1 kg of mix C costs $11.70, determine the cost per kilogram of each different kind of nut. Hence, find the cost per kg to produce a mix containing 400 gram of Cashews nuts, 200 gram of Macadamias nuts and 400 grams of Brazil n ...
CA 6th HLR 6.3 Notes F15 (MS)
... Pat Summers wins $200,000 in the Louisiana state lottery. He invests part of the money in real estate with an annual return of 3% and another part in a money market account at 2.5% interest. He invests the rest, which amounts to $80,000 less than the sum of the other two parts, in certificates of de ...
... Pat Summers wins $200,000 in the Louisiana state lottery. He invests part of the money in real estate with an annual return of 3% and another part in a money market account at 2.5% interest. He invests the rest, which amounts to $80,000 less than the sum of the other two parts, in certificates of de ...
Compound Inequalities
... 2. Turn off Show solution. Graph the inequalities x ≤ –2 and x > 1 in the Gizmo. A. Do the graphs have any points in common? B. What do you think is the solution of the compound inequality x ≤ –2 and x > 1? Select Show solution to check your answer. C. In the Gizmo, flip the sign in x > 1 so the ine ...
... 2. Turn off Show solution. Graph the inequalities x ≤ –2 and x > 1 in the Gizmo. A. Do the graphs have any points in common? B. What do you think is the solution of the compound inequality x ≤ –2 and x > 1? Select Show solution to check your answer. C. In the Gizmo, flip the sign in x > 1 so the ine ...
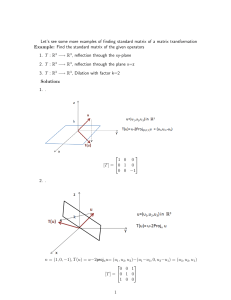
BASES, COORDINATES, LINEAR MAPS, AND MATRICES Math
... matrix CB B~ results in the coordinates of v relative to B. We know that if A is a matrix with n columns and if ej is the j th vector in the standard basis for Rn , then Aej is the jth column of A. Since [vj ] B = e j , equation (5) gives us (jth column of CB B~ ) = CB B~ ej = CB B~ [vj ] B = [vj ] ...
... matrix CB B~ results in the coordinates of v relative to B. We know that if A is a matrix with n columns and if ej is the j th vector in the standard basis for Rn , then Aej is the jth column of A. Since [vj ] B = e j , equation (5) gives us (jth column of CB B~ ) = CB B~ ej = CB B~ [vj ] B = [vj ] ...
Math 2142 Homework 4 Part 1: Due Friday March 11
... Therefore, the general solution to the homogeneous equation is c1 e−x + c2 e−2x . To guess a solution to the non-homogeneous equation, we try y = Ax2 + Bx + C. Calculating the derivatives, we have y 0 = 2Ax + B y 00 = 2A Plugging these values into the non-homogeneous equation gives us y 00 + 3y 0 + ...
... Therefore, the general solution to the homogeneous equation is c1 e−x + c2 e−2x . To guess a solution to the non-homogeneous equation, we try y = Ax2 + Bx + C. Calculating the derivatives, we have y 0 = 2Ax + B y 00 = 2A Plugging these values into the non-homogeneous equation gives us y 00 + 3y 0 + ...