matlab basics - University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila
... • Array: A collection of data values organized into rows and columns, and known by a single name. Row 1 Row 2 Row 3 arr(3,2) ...
... • Array: A collection of data values organized into rows and columns, and known by a single name. Row 1 Row 2 Row 3 arr(3,2) ...
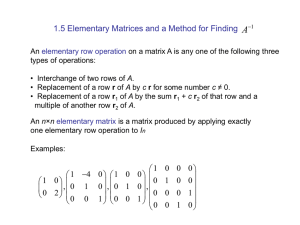
Chapter 5 Real Vector Space
... Definition: If S={v1,v2,...,vr} is a set of vectors in a vector space V, then the subspace W of V consisting of all linear combinations of the vectors in S is called the space spanned by v1,v2,...,vr, and we say that the vectors v1,v2,...,vr span W. To indicate that W is the space spanned by the vec ...
... Definition: If S={v1,v2,...,vr} is a set of vectors in a vector space V, then the subspace W of V consisting of all linear combinations of the vectors in S is called the space spanned by v1,v2,...,vr, and we say that the vectors v1,v2,...,vr span W. To indicate that W is the space spanned by the vec ...
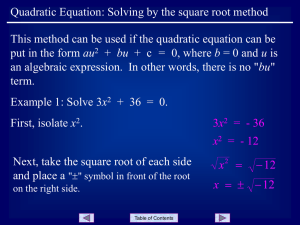
Intermediate Algebra
... Multiplying or dividing all parts of an inequality by the same NEGATIVE number and changing the sense (direction) of the inequality symbol gives an equivalent inequality Divide by - 2 ...
... Multiplying or dividing all parts of an inequality by the same NEGATIVE number and changing the sense (direction) of the inequality symbol gives an equivalent inequality Divide by - 2 ...
Document
... choose any real number for z and written: (z + 2, z + 1, z) put it in to get the x and y that go with it and these will solve the equation. You will get as many solutions as there are values of z to put in (infinitely many). ...
... choose any real number for z and written: (z + 2, z + 1, z) put it in to get the x and y that go with it and these will solve the equation. You will get as many solutions as there are values of z to put in (infinitely many). ...
SS2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
... Example: Form an equivalent equation by adding the opposite of the constant term on the left. 9 + x = 12 We’ll use the additive property of equality to move all variables to one side of the equation (for simplicity, in the beginning, we will move variables to the left) and all numbers to the other ...
... Example: Form an equivalent equation by adding the opposite of the constant term on the left. 9 + x = 12 We’ll use the additive property of equality to move all variables to one side of the equation (for simplicity, in the beginning, we will move variables to the left) and all numbers to the other ...