Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions
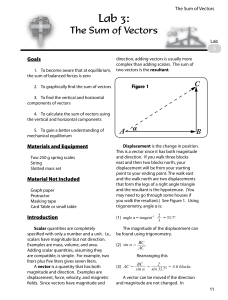
... A displacement vector has a magnitude of 175 m and points at an angle of 50.0 degrees relative to the x axis. Find the x and y components of this vector. ...
... A displacement vector has a magnitude of 175 m and points at an angle of 50.0 degrees relative to the x axis. Find the x and y components of this vector. ...
Lecture 16 (Feb 29) - West Virginia University
... 20 m/s. After the collisions both cars stick together and the resulting wreckage propagates at a common speed. Find the magnitude and the direction of of the velocity of the wreckage. Neglect Friction, i.e. any external forces. ...
... 20 m/s. After the collisions both cars stick together and the resulting wreckage propagates at a common speed. Find the magnitude and the direction of of the velocity of the wreckage. Neglect Friction, i.e. any external forces. ...
Mechanics
... A set of generalized coordinates can be used to replace the Cartesian coordinates. qm = qm(x11,…, xN3, t) xil = xil(q1, …, qf, t) Generalized coordinates need not be distances ...
... A set of generalized coordinates can be used to replace the Cartesian coordinates. qm = qm(x11,…, xN3, t) xil = xil(q1, …, qf, t) Generalized coordinates need not be distances ...