electromagnetism
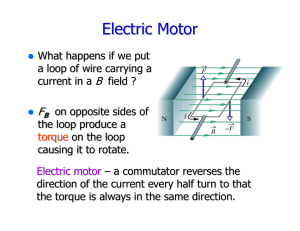
... direction of the current every half turn to that the torque is always in the same direction. ...
... direction of the current every half turn to that the torque is always in the same direction. ...
Chapter 6
... • Laws of magnetic attraction and repulsion – Like magnetic poles repel each other – Unlike magnetic poles attract each other – The closer together the magnets, the greater the attraction or repulsion ...
... • Laws of magnetic attraction and repulsion – Like magnetic poles repel each other – Unlike magnetic poles attract each other – The closer together the magnets, the greater the attraction or repulsion ...
Sea-Floor spreading
... Magnetic Stripes Alignment pattern of magnetic grains in the sea-floor crust that change over time based on the Polar direction (N v S) Every 100 K years the magnetic poles change direction (magnetic reversal) ...
... Magnetic Stripes Alignment pattern of magnetic grains in the sea-floor crust that change over time based on the Polar direction (N v S) Every 100 K years the magnetic poles change direction (magnetic reversal) ...
Condensed_Magnetism in solids
... Langevin gave a satisfactory explanation of diamagnetism on the basis of electron theory the basic principle of which ia Lenz’s law in electromagnetic induction which states that when a magnetic flux linked with electric current due to revolving electrons is changed, an induced current is set up in ...
... Langevin gave a satisfactory explanation of diamagnetism on the basis of electron theory the basic principle of which ia Lenz’s law in electromagnetic induction which states that when a magnetic flux linked with electric current due to revolving electrons is changed, an induced current is set up in ...
Earth`s Interior
... diagram of Earth’s interior and answer the questions. Use the Internet to search for any unknown information. Your challenge will be to demonstrate your understanding (to the teacher) at the end of this activity, by describing or illustrating Earth’s interior. You may wish to incorporate an egg. ...
... diagram of Earth’s interior and answer the questions. Use the Internet to search for any unknown information. Your challenge will be to demonstrate your understanding (to the teacher) at the end of this activity, by describing or illustrating Earth’s interior. You may wish to incorporate an egg. ...
Layers of Earth
... Earth as a magnet • Magnetic versus geographic poles – The geographic poles of the Earth are located where the axis of rotation intersects the planet – The magnetic poles of the Earth are near the geographic poles – The magnetic poles wander over time – They also reverse from time to time (about ev ...
... Earth as a magnet • Magnetic versus geographic poles – The geographic poles of the Earth are located where the axis of rotation intersects the planet – The magnetic poles of the Earth are near the geographic poles – The magnetic poles wander over time – They also reverse from time to time (about ev ...
Magnetic Fields
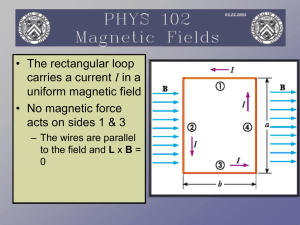
... is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop • The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop • τ = IA x B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the loop ...
... is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop • The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop • τ = IA x B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the loop ...
MAGNETISM Time Allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 (a) All
... the amount of work done in rotating it from stable to unstable equilibrium Q.5> A solenoid of length 2m and area 2x10-2m2 has 2000 turns and carries a current of 10A. Find the magnetic field at its centre. What is the direction of this field? Q.6> A bar magnet of moment 2Am2 is cut along transverse ...
... the amount of work done in rotating it from stable to unstable equilibrium Q.5> A solenoid of length 2m and area 2x10-2m2 has 2000 turns and carries a current of 10A. Find the magnetic field at its centre. What is the direction of this field? Q.6> A bar magnet of moment 2Am2 is cut along transverse ...
Electromagnetic Induction(EMI)
... The U-shaped conductor lies perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B with magnitude B = 0.60 T, directed into the page. We lay a metal rod with length L = 0.10 m across the two arms of the conductor, forming a conducting loop, and move the rod to the right with constant speed v = 2.5 m/s. What is ...
... The U-shaped conductor lies perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B with magnitude B = 0.60 T, directed into the page. We lay a metal rod with length L = 0.10 m across the two arms of the conductor, forming a conducting loop, and move the rod to the right with constant speed v = 2.5 m/s. What is ...
Conversations with the Earth
... • Based upon the study of lava flows of basalt throughout the world, it has been proposed that the Earth's magnetic field reverses at intervals, ranging from tens of thousands to many millions of years ...
... • Based upon the study of lava flows of basalt throughout the world, it has been proposed that the Earth's magnetic field reverses at intervals, ranging from tens of thousands to many millions of years ...
Earth Science Vocab
... Tectonic plate- one of the large, moving pieces into which Earth’s lithosphere is broken and which commonly carries both oceanic and continental crust ...
... Tectonic plate- one of the large, moving pieces into which Earth’s lithosphere is broken and which commonly carries both oceanic and continental crust ...
Title of PAPER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Earth and the constraints this will cause on the resources available, there has been much talk of moving to other planets. Mars is a prime target for future expansion due to its location in the solar system. However, Mars’ magnetosphere is currently too weak to provide protection to an atmosphere fr ...
... Earth and the constraints this will cause on the resources available, there has been much talk of moving to other planets. Mars is a prime target for future expansion due to its location in the solar system. However, Mars’ magnetosphere is currently too weak to provide protection to an atmosphere fr ...
Laboratory 3
... EGN 100 Introduction to Engineering Magnetic Fields Lab In magnetism, direction is defined by naming one pole of a magnet the north pole and the other the south pole. The magnetic field of the earth was known in early times, in that a magnetite (a mineral, naturally occurring material) needle floati ...
... EGN 100 Introduction to Engineering Magnetic Fields Lab In magnetism, direction is defined by naming one pole of a magnet the north pole and the other the south pole. The magnetic field of the earth was known in early times, in that a magnetite (a mineral, naturally occurring material) needle floati ...
EVOLUTION OF EARTH
... Continents circulated around the globe, a result of plate motions, and continued volcanic activity. Life originated in the early oceans. The geologic cycle was established: erosion by water, wind, and ice, new crust formed by volcanic activity, mountain-building where plates collided. Earth’ ...
... Continents circulated around the globe, a result of plate motions, and continued volcanic activity. Life originated in the early oceans. The geologic cycle was established: erosion by water, wind, and ice, new crust formed by volcanic activity, mountain-building where plates collided. Earth’ ...
Earth*s Layers - Madison County Schools
... The continents of Earth look as if they could fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. A German scientist named Alfred Wegener came up with the Continental Drift Theory. This theory says that all the continents used to be together, but drifted apart over millions of years. ...
... The continents of Earth look as if they could fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. A German scientist named Alfred Wegener came up with the Continental Drift Theory. This theory says that all the continents used to be together, but drifted apart over millions of years. ...
Ch 29 Magnetic Fields due to Currents
... Biot-Savart law Ampere’s law The magnetic dipole field ...
... Biot-Savart law Ampere’s law The magnetic dipole field ...
Key Concept Review (Answers to in-text “Concept Checks”) Chapter
... demanded explanation, and researchers redoubled their efforts to discover the links after the conclusion of the Second World War. 17. Radiometric dating allowed rock sequences to be dated and their relative positions through time determined. Radiometric studies also solidified understanding of Eart ...
... demanded explanation, and researchers redoubled their efforts to discover the links after the conclusion of the Second World War. 17. Radiometric dating allowed rock sequences to be dated and their relative positions through time determined. Radiometric studies also solidified understanding of Eart ...
The World`s Simplest Motor
... magnetic field as another wire, as long as the same size current runs through it. But, if there are multiple loops of wire, then each loop creates its own field and the magnetic field is very strong as compared to a single loop with the same size current. In the World’s Simplest Motor, the coil of w ...
... magnetic field as another wire, as long as the same size current runs through it. But, if there are multiple loops of wire, then each loop creates its own field and the magnetic field is very strong as compared to a single loop with the same size current. In the World’s Simplest Motor, the coil of w ...
Problem Set 9
... The energy of each strip is minimal when it is aligned with the field. This causes all filings to turn where they are and face (preferentially) the local direction of the field, which will already create a picture of the field. The filings now interact with each other and are therefore attracted o ...
... The energy of each strip is minimal when it is aligned with the field. This causes all filings to turn where they are and face (preferentially) the local direction of the field, which will already create a picture of the field. The filings now interact with each other and are therefore attracted o ...
Evidence Sheet 2 Locations of past glaciers
... measure it within those rocks. Think about a lava flow erupting from a volcano. The hot, molten lava has no crystal structure. As it cools, little crystals of a mineral called magnetite start to form and the rock becomes solid at the solidus temperature, about 900ºC. Because of the great heat energy ...
... measure it within those rocks. Think about a lava flow erupting from a volcano. The hot, molten lava has no crystal structure. As it cools, little crystals of a mineral called magnetite start to form and the rock becomes solid at the solidus temperature, about 900ºC. Because of the great heat energy ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.