Body System1 Cardiovascular System
... Though pressure is higher in the lower “tube,” the flow rates in the pair of tubes is identical because they both have the same pressure difference (90 mm Hg) between points P1 and P2. ...
... Though pressure is higher in the lower “tube,” the flow rates in the pair of tubes is identical because they both have the same pressure difference (90 mm Hg) between points P1 and P2. ...
Atacand (Chronic Heart Failure) - Forecast and Market Analysis to... Brochure
... in a trial for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HF-REF), but if clinical trial data continue to demonstrate the drug’s efficacy in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HF -PEF), and it gains approval for use in this population, it will be the first ...
... in a trial for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HF-REF), but if clinical trial data continue to demonstrate the drug’s efficacy in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HF -PEF), and it gains approval for use in this population, it will be the first ...
Adult Congenital Heart Disease - STA HealthCare Communications
... Congenital heart disease (CHD) has an incidence of 0.8% in North America, which does not take into account bicuspid aortic valve (1 to 2% incidence) and mitral valve prolapse. This translates into a prevalence of 4 per 1,000 adults,1 compared to a prevalence of about 6% for ischemic heart disease2 i ...
... Congenital heart disease (CHD) has an incidence of 0.8% in North America, which does not take into account bicuspid aortic valve (1 to 2% incidence) and mitral valve prolapse. This translates into a prevalence of 4 per 1,000 adults,1 compared to a prevalence of about 6% for ischemic heart disease2 i ...
Lab 4 Toad Heart Lab Protocol.pages
... Studies of isolated organs were pioneered in the late 19th century when scientists such as Sidney Ringer (1835–1910) developed a perfusion solution (Ringer’s solution) that could sustain an isolated organ from a pithed animal. A classic example of this phenomenon is the frog heart, which will contin ...
... Studies of isolated organs were pioneered in the late 19th century when scientists such as Sidney Ringer (1835–1910) developed a perfusion solution (Ringer’s solution) that could sustain an isolated organ from a pithed animal. A classic example of this phenomenon is the frog heart, which will contin ...
The heart is an extraordinary organ that has incredible endurance
... Simultaneous contraction of the atria and then the ventricles pumps blood through the heart ...
... Simultaneous contraction of the atria and then the ventricles pumps blood through the heart ...
Acetylcholine
... Hypothesis: Nicotine binds to the nicotine subtype of acetylcholine receptors causing the release of epinephrine. This would indicate a likely increase in heart rate. Results: According to the data, Daphnia treated with nicotine in fact had higher heart rates than the control. This agrees with the h ...
... Hypothesis: Nicotine binds to the nicotine subtype of acetylcholine receptors causing the release of epinephrine. This would indicate a likely increase in heart rate. Results: According to the data, Daphnia treated with nicotine in fact had higher heart rates than the control. This agrees with the h ...
Machine Learning Based Identification of Pathological Heart Sounds
... cycles. Data from recording training-a/a0011 ...
... cycles. Data from recording training-a/a0011 ...
Cardiac implantable devices - Royal Academy of Engineering
... very sophisticated and contain microprocessors and dedicated integrated circuits. They can be programmed in situ by a hand-held programmer that can also receive diagnostic information from the device. There are three basic types of these pacemakers: single chamber, dual chamber and rate responsive. ...
... very sophisticated and contain microprocessors and dedicated integrated circuits. They can be programmed in situ by a hand-held programmer that can also receive diagnostic information from the device. There are three basic types of these pacemakers: single chamber, dual chamber and rate responsive. ...
The Circulatory System I
... “This week, we’re going to be talking about the circulatory system. Who can tell me what makes up the circulatory system? The heart and blood vessels. There are actually two circulatory systems—does anyone know what they are?” 1. Pulmonary Circulation: Pulmonary means “having to do with the lungs. T ...
... “This week, we’re going to be talking about the circulatory system. Who can tell me what makes up the circulatory system? The heart and blood vessels. There are actually two circulatory systems—does anyone know what they are?” 1. Pulmonary Circulation: Pulmonary means “having to do with the lungs. T ...
What Causes Heart Attacks - Foundation for Alternative and
... circulation, and by creating spasms in the coronary arteries through the injection of heavy dye under high pressure – is notoriously inaccurate at assessing the amount of stenosis in the vessels as well as the true blood flow in the heart. To this day, most of the bypasses, stents, and angioplasties ...
... circulation, and by creating spasms in the coronary arteries through the injection of heavy dye under high pressure – is notoriously inaccurate at assessing the amount of stenosis in the vessels as well as the true blood flow in the heart. To this day, most of the bypasses, stents, and angioplasties ...
Your Personal Virtual Heart
... decision based on the patient’s ejection fraction—the proportion of blood that is pumped out of the heart with every beat. If this number is below 35 percent, then doctors advise the patient to undergo the implantation procedure. Lots of patients are getting implants based on this strategy, but in t ...
... decision based on the patient’s ejection fraction—the proportion of blood that is pumped out of the heart with every beat. If this number is below 35 percent, then doctors advise the patient to undergo the implantation procedure. Lots of patients are getting implants based on this strategy, but in t ...
Powerpoint - Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology
... Cardiac tracings (left) and fluoroscopic images (right) exhibiting the successful ablation site of the PVCs originating from the LV PPM. The first beat is a sinus beat and the second a PVC. Note that at the successful ablation site, no Purkinje potentials were observed during sinus rhythm, and a sp ...
... Cardiac tracings (left) and fluoroscopic images (right) exhibiting the successful ablation site of the PVCs originating from the LV PPM. The first beat is a sinus beat and the second a PVC. Note that at the successful ablation site, no Purkinje potentials were observed during sinus rhythm, and a sp ...
The Weight of the Heart and Its Chambers in with and
... Values in Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease A complete analysis of the sequence and degrees of hypertrophy in the different cardiac chambers has not been possible for two major reasons: (a) the onset of hypertension is rarely known, hence, the effect of duration of hypertension upon degree of left ...
... Values in Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease A complete analysis of the sequence and degrees of hypertrophy in the different cardiac chambers has not been possible for two major reasons: (a) the onset of hypertension is rarely known, hence, the effect of duration of hypertension upon degree of left ...
Past and future aspects of clinical electrophysiology
... favoured these advances. On the one hand, patients live longer and thus are more likely to experience arrhythmias. On the other hand, circulatory problems of the cardiac vessels have increased enormously, and this has been identified as the primary cause of cardiac rhythm disorders. Coronary heart d ...
... favoured these advances. On the one hand, patients live longer and thus are more likely to experience arrhythmias. On the other hand, circulatory problems of the cardiac vessels have increased enormously, and this has been identified as the primary cause of cardiac rhythm disorders. Coronary heart d ...
Atrial Fibrillation
... ventricular arrhythmias, bradycardia, and depression of left ventricular function. It was further theorized that maintenance of sinus rhythm would reduce rates of thromboembolism and the need for anticoagulation; however, trial results demonstrated no significant reduction in thromboembolic risk. Pe ...
... ventricular arrhythmias, bradycardia, and depression of left ventricular function. It was further theorized that maintenance of sinus rhythm would reduce rates of thromboembolism and the need for anticoagulation; however, trial results demonstrated no significant reduction in thromboembolic risk. Pe ...
Chapter10_Detailed_Answers
... or give an occasional extra strong beat. Palpitations may be infrequent, frequent, or continuous. Other signs and symptoms of dysrhythmias include low blood pressure, lightheadedness and shortness of breath. Symptoms are signs of disease or injury. They are noticed by the patient. b: If the patient ...
... or give an occasional extra strong beat. Palpitations may be infrequent, frequent, or continuous. Other signs and symptoms of dysrhythmias include low blood pressure, lightheadedness and shortness of breath. Symptoms are signs of disease or injury. They are noticed by the patient. b: If the patient ...
Chapter on Heart Disease
... Systemic blood flow and oxygen delivery to peripheral tissues and organs is under strict neuroendocrine control. Compensatory mechanisms act rapidly to correct any decreases in blood flow or pressure. These mechanisms provide short-term benefit to metabolically active cells but longterm injury to th ...
... Systemic blood flow and oxygen delivery to peripheral tissues and organs is under strict neuroendocrine control. Compensatory mechanisms act rapidly to correct any decreases in blood flow or pressure. These mechanisms provide short-term benefit to metabolically active cells but longterm injury to th ...
Caring for the Heart Failure Patient: Contemporary Nursing
... Congestive heart failure (CHF) is the heart’s inability to pump enough blood to meet the body’s oxygen and nutrient demands. Heart failure can be systolic or diastolic, left or right sided, and acute or chronic1. CHF is a clinical syndrome, i.e. a constellation of symptoms and signs and can result f ...
... Congestive heart failure (CHF) is the heart’s inability to pump enough blood to meet the body’s oxygen and nutrient demands. Heart failure can be systolic or diastolic, left or right sided, and acute or chronic1. CHF is a clinical syndrome, i.e. a constellation of symptoms and signs and can result f ...
Right Ventricular Functions in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Below
... with diabetes. We performed detailed echocardiographic evaluation of right ventricular systolic and diastolic functions in patients of type-2 diabetes mellitus. Twenty five patients with type-2 diabetes were evaluated after strict exclusion of conditions that could independently affect ventricular f ...
... with diabetes. We performed detailed echocardiographic evaluation of right ventricular systolic and diastolic functions in patients of type-2 diabetes mellitus. Twenty five patients with type-2 diabetes were evaluated after strict exclusion of conditions that could independently affect ventricular f ...
The Heart-‐ A parody of The Fox, by Ylvis
... How does the heart go? Beat beat beat beat beat beat beat beat beat x3 How does the heart go? Pump pump pump pump pump pump pump x3 How does the heart go? Lub lub lub ...
... How does the heart go? Beat beat beat beat beat beat beat beat beat x3 How does the heart go? Pump pump pump pump pump pump pump x3 How does the heart go? Lub lub lub ...
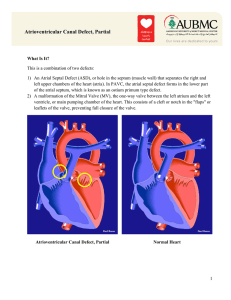
Atrioventricular Canal Defect, Partial
... pumped to the lungs via the right ventricle, reducing the efficiency of the circulatory system. This may lead to heart failure with congestion of the lungs. Eventually, the atrial septal defect will cause the enlargement (dilatation) of the right atrium and right ventricle, which may lead to irregul ...
... pumped to the lungs via the right ventricle, reducing the efficiency of the circulatory system. This may lead to heart failure with congestion of the lungs. Eventually, the atrial septal defect will cause the enlargement (dilatation) of the right atrium and right ventricle, which may lead to irregul ...
The Heart: Conduction System
... the ventricles contract, blood is forced out through the semilunar valves into the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. ► After the ventricles complete their contraction phase, they relax and the SA node initiates another impulse to start another cardiac cycle. ...
... the ventricles contract, blood is forced out through the semilunar valves into the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. ► After the ventricles complete their contraction phase, they relax and the SA node initiates another impulse to start another cardiac cycle. ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.