Microarray Analysis of Normal and Abnormal Chick Ventricular
... Norwood palliation ending in complete Fontan (Sedmera et al. 2005), the major problem of those surviving into adolescence is gradual intractable failure of the single right ventricle. Many hypotheses about the possible origin of this failure have been proposed, including ischemic injury during repea ...
... Norwood palliation ending in complete Fontan (Sedmera et al. 2005), the major problem of those surviving into adolescence is gradual intractable failure of the single right ventricle. Many hypotheses about the possible origin of this failure have been proposed, including ischemic injury during repea ...
Systolic and Diastolic Heart Failure (HFrEF and HFpEF) 2016
... build up in the lungs, the right ventricle finds it harder to pump blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. Right-sided heart failure can occur on its own, for example, when caused by lung disease (COPD) or heart valve disease. ...
... build up in the lungs, the right ventricle finds it harder to pump blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. Right-sided heart failure can occur on its own, for example, when caused by lung disease (COPD) or heart valve disease. ...
hypothyroidism - Hormone Health Network
... Rare but serious problems can include • Heart failure (called congestive heart failure): when the heart can’t pump enough blood for your body to work properly • Heart attack: when a blood clot blocks the flow of blood in your heart • Stroke: when the blood vessels to the brain are blocked and you ...
... Rare but serious problems can include • Heart failure (called congestive heart failure): when the heart can’t pump enough blood for your body to work properly • Heart attack: when a blood clot blocks the flow of blood in your heart • Stroke: when the blood vessels to the brain are blocked and you ...
Keeping Your Heart Healthy After Treatment for Childhood Cancer
... The blood vessels of the heart may become scarred or blocked (coronary artery disease), preventing delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the heart and other tissues. ...
... The blood vessels of the heart may become scarred or blocked (coronary artery disease), preventing delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the heart and other tissues. ...
echocardiographic differentiation of pre
... index > 1.2, a dilated inferior vena cava without inspiratory collapse, and the right ventricle forming the heart apex7. Our study confirmed that E/E’ is lower in PAH patients than in pulmonary venous hypertension patients (p = 0.001). Furthermore, we proposed a cut-off value of E/E’ = 11.6 which ha ...
... index > 1.2, a dilated inferior vena cava without inspiratory collapse, and the right ventricle forming the heart apex7. Our study confirmed that E/E’ is lower in PAH patients than in pulmonary venous hypertension patients (p = 0.001). Furthermore, we proposed a cut-off value of E/E’ = 11.6 which ha ...
Renal Insufficiency and Heart Failure Prognostic and Therapeutic
... -blockers in community-dwelling patients with heart failure are uncertain. Methods and Results—We analyzed data from a prospective cohort of 754 patients with heart failure who had ejection fraction, serum creatinine, and weight measured at baseline. Median age was 69 years, and 43% had an ejection ...
... -blockers in community-dwelling patients with heart failure are uncertain. Methods and Results—We analyzed data from a prospective cohort of 754 patients with heart failure who had ejection fraction, serum creatinine, and weight measured at baseline. Median age was 69 years, and 43% had an ejection ...
Single Arterial Trunk - Heart
... bulbo-truncal ridges failed to develop and divide the primitive truncus into aorta and pulmonary artery. Siddoway and Chernish (1952) rejected 21 of the 25 published cases which were claimed to be examples of a single ventricle with a persistent truncus on the grounds that the single arterial trunk ...
... bulbo-truncal ridges failed to develop and divide the primitive truncus into aorta and pulmonary artery. Siddoway and Chernish (1952) rejected 21 of the 25 published cases which were claimed to be examples of a single ventricle with a persistent truncus on the grounds that the single arterial trunk ...
- Wiley Online Library
... vascular bed) causing myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, acute ventricular dysfunction, and sudden death. This may be exacerbated by increased ventricular enddiastolic pressure. It may be preceded by low diastolic blood pressure which is an indicator of high pulmonary to systemic blood flow ratio (Qp ...
... vascular bed) causing myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, acute ventricular dysfunction, and sudden death. This may be exacerbated by increased ventricular enddiastolic pressure. It may be preceded by low diastolic blood pressure which is an indicator of high pulmonary to systemic blood flow ratio (Qp ...
ductus arteriosus dependent congenital heart disease
... Lesions characterized by the entire or part of the systemic blood flow depends solely on the patency of the ductus arteriosus. – Coarctation of Aorta (severe) – Interrupted Aortic Arch – Hypoplastic Left Heart ...
... Lesions characterized by the entire or part of the systemic blood flow depends solely on the patency of the ductus arteriosus. – Coarctation of Aorta (severe) – Interrupted Aortic Arch – Hypoplastic Left Heart ...
0132873559_CH_08 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... pumping about 2,000 galsupply the heart wall. lons (7,571 liters) of A collection of specialized cells that generate or carry impulses that stimulate the heart to conblood. tract include the: ...
... pumping about 2,000 galsupply the heart wall. lons (7,571 liters) of A collection of specialized cells that generate or carry impulses that stimulate the heart to conblood. tract include the: ...
Mitral valve stenosis - Great Ormond Street Hospital
... as diabetes or medicines taken during pregnancy can also increase the risk. Congenital heart defects are more common in children with other congenital conditions. ...
... as diabetes or medicines taken during pregnancy can also increase the risk. Congenital heart defects are more common in children with other congenital conditions. ...
IHDmodule FY2011Q2
... Left Ventricular Systolic Function (LVSF) assessment: diagnostic measure of left ventricular contractile performance/wall motion. Ejection fraction (EF) is an index of LVSF and reflects the proportion of blood ejected during each ventricular contraction compared with the total ventricular filling vo ...
... Left Ventricular Systolic Function (LVSF) assessment: diagnostic measure of left ventricular contractile performance/wall motion. Ejection fraction (EF) is an index of LVSF and reflects the proportion of blood ejected during each ventricular contraction compared with the total ventricular filling vo ...
PFO Patient Brochure
... or two. This congential heart defect is fairly common and occurs in about 25% of the population. ...
... or two. This congential heart defect is fairly common and occurs in about 25% of the population. ...
IHDmodule FY2011Q3
... Left Ventricular Systolic Function (LVSF) assessment: diagnostic measure of left ventricular contractile performance/wall motion. Ejection fraction (EF) is an index of LVSF and reflects the proportion of blood ejected during each ventricular contraction compared with the total ventricular filling vo ...
... Left Ventricular Systolic Function (LVSF) assessment: diagnostic measure of left ventricular contractile performance/wall motion. Ejection fraction (EF) is an index of LVSF and reflects the proportion of blood ejected during each ventricular contraction compared with the total ventricular filling vo ...
Cardiac remodelling: general aspects and
... eart failure (HF) is a worldwide health problem that affects approximately 26 million individuals (1). It is known that heart disease progresses to HF, and there is a link between cardiac remodelling and the development of HF. Cardiac remodelling is defined as a group of molecular, cellular and inte ...
... eart failure (HF) is a worldwide health problem that affects approximately 26 million individuals (1). It is known that heart disease progresses to HF, and there is a link between cardiac remodelling and the development of HF. Cardiac remodelling is defined as a group of molecular, cellular and inte ...
Mechanical circulatory support in the new era: an overview
... expanding with experienced centers reporting favorable outcomes [5]. Other minimally invasive percutaneous ventricular assist devices (pVADs) have also been used in acute settings. Similarly, the implantable, durable, rotary blood pump‐driven VADs have revolutionized the care of patients with chroni ...
... expanding with experienced centers reporting favorable outcomes [5]. Other minimally invasive percutaneous ventricular assist devices (pVADs) have also been used in acute settings. Similarly, the implantable, durable, rotary blood pump‐driven VADs have revolutionized the care of patients with chroni ...
Realdo Colombo - Wiley Online Library
... through minute pores in the intervening septum. From this blood and from some of the air received from the lungs, the left ventricle generated vital spirits and arterial blood, which it distributed to the entire body through the arteries to preserve life.1(a) Colombo disproved the Galenic teaching t ...
... through minute pores in the intervening septum. From this blood and from some of the air received from the lungs, the left ventricle generated vital spirits and arterial blood, which it distributed to the entire body through the arteries to preserve life.1(a) Colombo disproved the Galenic teaching t ...
O A
... [24], work performed may be good indicator of resistance training efficacy. Moritany and Vries [14] depicted that neuronal and muscular adaptations involved in training-induced enhancement of the rat muscular strength. Resistance training is a known stimulus for cardiac hypertrophy due to pressure o ...
... [24], work performed may be good indicator of resistance training efficacy. Moritany and Vries [14] depicted that neuronal and muscular adaptations involved in training-induced enhancement of the rat muscular strength. Resistance training is a known stimulus for cardiac hypertrophy due to pressure o ...
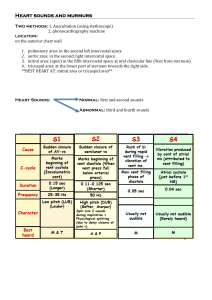
Heart sounds and murmurs
... 1. pulmonary area: in the second left intercostal space 2. aortic area: in the second right intercostal space 3. mitral area: (apex) in the fifth intercostal space at mid clavicular line (9cm from sternum) 4. tricuspid area: at the lower part of sternum towards the right side. **BEST HEART AT: mitra ...
... 1. pulmonary area: in the second left intercostal space 2. aortic area: in the second right intercostal space 3. mitral area: (apex) in the fifth intercostal space at mid clavicular line (9cm from sternum) 4. tricuspid area: at the lower part of sternum towards the right side. **BEST HEART AT: mitra ...
Mutations affecting the formation and function of the cardiovascular
... mutations affect the rhythm of the heart causing, for example, a slow rate, a fibrillating pattern or an apparent block to conduction. In several other mutants, regurgitation of blood flow from ventricle to atrium is the most prominent abnormality, due either to the absence of valves or to poor coor ...
... mutations affect the rhythm of the heart causing, for example, a slow rate, a fibrillating pattern or an apparent block to conduction. In several other mutants, regurgitation of blood flow from ventricle to atrium is the most prominent abnormality, due either to the absence of valves or to poor coor ...
Hawthorn Berry - Dr. Christopher`s Herbal Legacy
... the added benefit of lowering blood pressure, lower heart rates while exercising, improved stamina and endurance while exercising, pumped more blood at lower pressure, had less fatigue, and less shortness of breath. When compared with NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ...
... the added benefit of lowering blood pressure, lower heart rates while exercising, improved stamina and endurance while exercising, pumped more blood at lower pressure, had less fatigue, and less shortness of breath. When compared with NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ...
Aortic Stenosis Explained - New - CardioRespiratory Pet Referrals
... **Note: Puppies under 16 weeks of age sometimes demonstrate what is called a ‘physiological’ or ‘innocent’ murmur. These are not very loud and disappear as the puppy gets older; any murmur that persists or is felt to be loud should be pursued. When the heart is not properly pumping blood to the body ...
... **Note: Puppies under 16 weeks of age sometimes demonstrate what is called a ‘physiological’ or ‘innocent’ murmur. These are not very loud and disappear as the puppy gets older; any murmur that persists or is felt to be loud should be pursued. When the heart is not properly pumping blood to the body ...
Sparse classifiers for Automated Heart Wall Motion Abnormality
... LV can be imaged in a number of ways. The most common method is the echocardiogram – an ultrasound video of different 2-D cross-sections of the LV. Unfortunately, echocardiograms are notoriously difficult to interpret, even for the best of physicians. Inter-observer studies have shown that even worl ...
... LV can be imaged in a number of ways. The most common method is the echocardiogram – an ultrasound video of different 2-D cross-sections of the LV. Unfortunately, echocardiograms are notoriously difficult to interpret, even for the best of physicians. Inter-observer studies have shown that even worl ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.