The History of Thermodynamics
... • Aristoteles (around 350 BC): Earth, air, fire, and water. The fifth element (the quintessence), was the aether. • Albert A. Michelson & Edward Morley (1887): Attempted to measure the aether wind, but achieved the contrary. • Lord Kelvin (1896): ... “I know no more of electric and magnetic force, o ...
... • Aristoteles (around 350 BC): Earth, air, fire, and water. The fifth element (the quintessence), was the aether. • Albert A. Michelson & Edward Morley (1887): Attempted to measure the aether wind, but achieved the contrary. • Lord Kelvin (1896): ... “I know no more of electric and magnetic force, o ...
Catalog (pdfTYPE、373.435KByte)
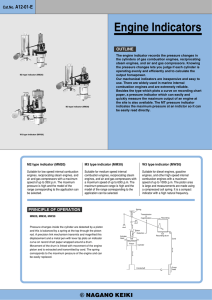
... the cylinders of gas combustion engines, reciprocating steam engines, and air and gas compressors. Knowing the pressure changes lets you judge if each cylinder is operating evenly and efficiently and to calculate the output horsepower. Our mechanical indicators are inexpensive and easy to use. There ...
... the cylinders of gas combustion engines, reciprocating steam engines, and air and gas compressors. Knowing the pressure changes lets you judge if each cylinder is operating evenly and efficiently and to calculate the output horsepower. Our mechanical indicators are inexpensive and easy to use. There ...
Section 23 22 13 - STEAM AND CONDENSATE
... 2. Trap bodies: Bronze, cast iron, or semi-steel, constructed to permit ease of removal and servicing working parts without disturbing connecting piping. For systems without relief valve traps shall be 5. Mechanism: Brass, stainless steel or corrosion resistant alloy. rated for the pressure upstream ...
... 2. Trap bodies: Bronze, cast iron, or semi-steel, constructed to permit ease of removal and servicing working parts without disturbing connecting piping. For systems without relief valve traps shall be 5. Mechanism: Brass, stainless steel or corrosion resistant alloy. rated for the pressure upstream ...
Frequently misspelt words
... The type of gasoline designed to power a diesel engine. A device for slowing or stopping motion, as of a vehicle, especially by contact friction a device in which a toothed rack or wheel is engaged by a pawl to permit motion in one direction only ...
... The type of gasoline designed to power a diesel engine. A device for slowing or stopping motion, as of a vehicle, especially by contact friction a device in which a toothed rack or wheel is engaged by a pawl to permit motion in one direction only ...
History of the steam engine

The history of the steam engine stretches back as far as the 1st century AD; the first recorded rudimentary steam engine being the aeolipile described by Hero of Alexandria. Over a millennium after Hero's (or ""Heron's"") experiments, a number of steam-powered devices were experimented with or proposed, but it was not until 1712 that a commercially successful steam engine was finally developed, Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine. During the industrial revolution, steam engines became the dominant source of power and remained so into the early decades of the 20th century, when advances in the design of the electric motor and the internal combustion engine resulted in the rapid replacement of the steam engine by these technologies. However, the steam turbine, an alternative form of steam engine, has become the most common method by which electrical power generators are driven. Investigations are being made into the practicalities of reviving the reciprocating steam engine as the basis for a new wave of 'advanced steam technology' .