AVSC 1010 - optical cloud studies
... PROPULSION SYSTEM PG. 453: includes the propellant used, the containers for the propellant, all plumbing that may be required to get the propellant from the containers to the engine, and the rocket engine itself. GUIDANCE SYSTEM PG. 454: a self-contained electronic unit that employs a computer and a ...
... PROPULSION SYSTEM PG. 453: includes the propellant used, the containers for the propellant, all plumbing that may be required to get the propellant from the containers to the engine, and the rocket engine itself. GUIDANCE SYSTEM PG. 454: a self-contained electronic unit that employs a computer and a ...
Planetary Sciences
... exponential dropoff with depth, with “scale depth” equal to LT conduction takes time, so heating/cooling not immediate surface is insulator at night because conductivity depends on … temperature seasonal effects can also be significant observations are made at radio wavelengths ...
... exponential dropoff with depth, with “scale depth” equal to LT conduction takes time, so heating/cooling not immediate surface is insulator at night because conductivity depends on … temperature seasonal effects can also be significant observations are made at radio wavelengths ...
Atmospheric circulation
... • Warm air rises. But air cools as it rises, causing clouds to form, and releasing heat that pushes air upward even faster.! ...
... • Warm air rises. But air cools as it rises, causing clouds to form, and releasing heat that pushes air upward even faster.! ...
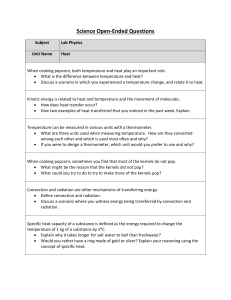
Physics-Heat OEQs
... Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the energy required to change the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1⁰C. Explain why it takes longer for salt water to boil than freshwater? Would you rather have a ring made of gold or silver? Explain your reasoning using the concept of sp ...
... Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the energy required to change the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1⁰C. Explain why it takes longer for salt water to boil than freshwater? Would you rather have a ring made of gold or silver? Explain your reasoning using the concept of sp ...
CHAPTER 10 NOTES FOR EIGHTH GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... D. SUBSTANCES THAT CONDUCT HEAT MORE EFFECTIVELY THAN OTHERS ARE CALLED HEAT CONDUCTORS. 1. COPPER 2. SILVER E. SUBSTANCES THAT DO NOT CONDUCT HEAT EASILY ARE CALLED INSULATORS. 1. GLASS 2. WOOD 2. CONVECTION A. HEAT IS TRANSFERRED IN LIQUIDS AND GASES AS MOLECULES MOVE IN CURRENTS B. THE WARMER PAR ...
... D. SUBSTANCES THAT CONDUCT HEAT MORE EFFECTIVELY THAN OTHERS ARE CALLED HEAT CONDUCTORS. 1. COPPER 2. SILVER E. SUBSTANCES THAT DO NOT CONDUCT HEAT EASILY ARE CALLED INSULATORS. 1. GLASS 2. WOOD 2. CONVECTION A. HEAT IS TRANSFERRED IN LIQUIDS AND GASES AS MOLECULES MOVE IN CURRENTS B. THE WARMER PAR ...
Energy: Conservation and Transfer
... experiences the same pressure as the atmospheric pressure. • Freezing Point – The temperature at which liquid matter turns to solid. ...
... experiences the same pressure as the atmospheric pressure. • Freezing Point – The temperature at which liquid matter turns to solid. ...
Heat Transfer conduction
... Heat energy is transferred from a high heat “source” to a low heat “sink”. Heat energy will “flow” from high temperature areas to low temperature ones through one of three methods; radiation, convection or conduction. Radiation is a mode of energy transfer that does not require a medium, or substanc ...
... Heat energy is transferred from a high heat “source” to a low heat “sink”. Heat energy will “flow” from high temperature areas to low temperature ones through one of three methods; radiation, convection or conduction. Radiation is a mode of energy transfer that does not require a medium, or substanc ...
7th Grade
... surroundings. This is an endothermic reaction. The temperature of the solution falls to about 35 F for 10 to 15 minutes. ...
... surroundings. This is an endothermic reaction. The temperature of the solution falls to about 35 F for 10 to 15 minutes. ...
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Latent Heat In addition
... to the ground.....over the lowest few cm, really a thin layer of air warmed by conduction ...
... to the ground.....over the lowest few cm, really a thin layer of air warmed by conduction ...
Name____________________________
... Convection: Transfer of heat within a liquid or gas. Conduction: Transfer of heat through matter by direct contact. Thermal Radiation: The energy radiated by solids, liquids, and gases in the form of electromagnetic waves as a result of their temperature. Deformation: Alteration of shape, as by pres ...
... Convection: Transfer of heat within a liquid or gas. Conduction: Transfer of heat through matter by direct contact. Thermal Radiation: The energy radiated by solids, liquids, and gases in the form of electromagnetic waves as a result of their temperature. Deformation: Alteration of shape, as by pres ...
Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
... a pool is cooler at the deep end? • Examples: air movement in a home, pot of heating water. • Pick one of these examples and draw the circular pattern in your notes. ...
... a pool is cooler at the deep end? • Examples: air movement in a home, pot of heating water. • Pick one of these examples and draw the circular pattern in your notes. ...
Direct use of Solar Energy for Heating and Cooling - UTSOA
... house for an exhibition in Zilker Park in 1975. This was also their first experiment with ideas about modular and mobile systems. After the exhibition they moved the solar greenhouse to the University’s Balcones Research Center (now the J.J. Pickle Center) where they attached the greenhouse to an ea ...
... house for an exhibition in Zilker Park in 1975. This was also their first experiment with ideas about modular and mobile systems. After the exhibition they moved the solar greenhouse to the University’s Balcones Research Center (now the J.J. Pickle Center) where they attached the greenhouse to an ea ...
Earthquakes
... 4a-Students know the sun is the major source of energy for phenomena on Earth's surface; it powers winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle. 4d-Students know convection currents distribute heat in the atmosphere and oceans. ...
... 4a-Students know the sun is the major source of energy for phenomena on Earth's surface; it powers winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle. 4d-Students know convection currents distribute heat in the atmosphere and oceans. ...
Heat Standard 4a/4d p. 400-409 1. The earth receives energy from
... 4a-Students know the sun is the major source of energy for phenomena on Earth's surface; it powers winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle. 4d-Students know convection currents distribute heat in the atmosphere and oceans. ...
... 4a-Students know the sun is the major source of energy for phenomena on Earth's surface; it powers winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle. 4d-Students know convection currents distribute heat in the atmosphere and oceans. ...
Vocabulary
... • British Thermal Unit- quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit ...
... • British Thermal Unit- quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit ...
Passive Solar Energy
... shade a building by natural vegetation and using special glazing in windows. External shading devices can reduce solar gains by up to 90%, while still admitting a large amount of indirect light. • External heat gain can also be minimized by good insulation, reduced window size and by the use of refl ...
... shade a building by natural vegetation and using special glazing in windows. External shading devices can reduce solar gains by up to 90%, while still admitting a large amount of indirect light. • External heat gain can also be minimized by good insulation, reduced window size and by the use of refl ...
Mechanical Equivalent of Heat
... surroundings). This change from mechanical energy to thermal energy is equivalent to the thermal energy gained from heat. The relationship between temperature and thermal energy is given by the calorimeter equation: [2] ΔEth = mcΔT ΔEth = change in thermal energy m = mass of the substance in kg c = ...
... surroundings). This change from mechanical energy to thermal energy is equivalent to the thermal energy gained from heat. The relationship between temperature and thermal energy is given by the calorimeter equation: [2] ΔEth = mcΔT ΔEth = change in thermal energy m = mass of the substance in kg c = ...
Note: Moving air
... Answer: The shiny surface of foil reflects infrared radiation, which would reduce heating from outside radiation. The surface also does not emit IR very well, so it would lose less energy by radiation than a non-shiny surface. ...
... Answer: The shiny surface of foil reflects infrared radiation, which would reduce heating from outside radiation. The surface also does not emit IR very well, so it would lose less energy by radiation than a non-shiny surface. ...
Specific Heat Capacity - Tasker Milward
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
Heat
... bumps into a slower moving molecule (cooler), the faster moving, hotter molecule transfers heat (thermal) energy to the other particle. Example: Feet burned by walking on hot sand. 4. Explain convection: Liquids and gases move easily. As the particle move , their energy goes along with them. Example ...
... bumps into a slower moving molecule (cooler), the faster moving, hotter molecule transfers heat (thermal) energy to the other particle. Example: Feet burned by walking on hot sand. 4. Explain convection: Liquids and gases move easily. As the particle move , their energy goes along with them. Example ...
2 Pieces - cloudfront.net
... Insulators serve to (increase, decrease or not change) the transfer of heat energy. ...
... Insulators serve to (increase, decrease or not change) the transfer of heat energy. ...
California State University, Monterey Bay Tanimura and Antle Family
... into various “green” initiatives. Tests of commercial buildings show that they tend to be more leaky than the average house, based on air leakage per square foot of surface area. That means that commercial buildings are less energy efficient than the average house. To measure the actual airtightness ...
... into various “green” initiatives. Tests of commercial buildings show that they tend to be more leaky than the average house, based on air leakage per square foot of surface area. That means that commercial buildings are less energy efficient than the average house. To measure the actual airtightness ...