Specific Heat
... 1 calorie = energy required to heat 1 gram of water by 1°C 1 Calorie (food labels) = 1 kilocalorie 1 calorie = 4.184 joules ...
... 1 calorie = energy required to heat 1 gram of water by 1°C 1 Calorie (food labels) = 1 kilocalorie 1 calorie = 4.184 joules ...
Ideal Gas Law / Heat Transfer
... The sun warms the Earth, but they aren’t touching What mechanism is responsible for this??? ...
... The sun warms the Earth, but they aren’t touching What mechanism is responsible for this??? ...
Weather Maps (Isopleths)
... Slower and closer together ….. Faster and farther apart Fig. 2.1, p. 37 ...
... Slower and closer together ….. Faster and farther apart Fig. 2.1, p. 37 ...
389H_NO_02_review_I
... (refers to force, not to mass) • specific gravity = ratio of weight of volume of liquid to same volume of water at std. conditions (usually 60 °F or 20 °C and 1 atm) ...
... (refers to force, not to mass) • specific gravity = ratio of weight of volume of liquid to same volume of water at std. conditions (usually 60 °F or 20 °C and 1 atm) ...
Chemistry 30
... How much heat would have to be absorbed by 2000 grams of water to change its temperature from 20C to 50C? Use the value 4.2 J/(gC) for the specific heat of water. Hint: You will need to use the formula: Q = mcT. Solve for Q ...
... How much heat would have to be absorbed by 2000 grams of water to change its temperature from 20C to 50C? Use the value 4.2 J/(gC) for the specific heat of water. Hint: You will need to use the formula: Q = mcT. Solve for Q ...
Chemistry 30
... How much heat would have to be absorbed by 2000 grams of water to change its temperature from 20°C to 50°C? Use the value 4.2 J/(g°C) for the specific heat of water. Hint: You will need to use the formula: Q = mc∆T. Solve for Q ...
... How much heat would have to be absorbed by 2000 grams of water to change its temperature from 20°C to 50°C? Use the value 4.2 J/(g°C) for the specific heat of water. Hint: You will need to use the formula: Q = mc∆T. Solve for Q ...
RTF
... How much heat would have to be absorbed by 2000 grams of water to change its temperature from 20C to 50C? Use the value 4.2 J/(gC) for the specific heat of water. Hint: You will need to use the formula: Q = mcT. Solve for Q ...
... How much heat would have to be absorbed by 2000 grams of water to change its temperature from 20C to 50C? Use the value 4.2 J/(gC) for the specific heat of water. Hint: You will need to use the formula: Q = mcT. Solve for Q ...
phy 1044 determination of specific heat spring 03
... OBJECTIVE: The amount of heat energy that can be transferred to or from a material is dependent on the mass of material, the temperature gradient, and a material property known as its specific heat capacity. The principles of calorimetry will be employed to determine an experimental value for a mate ...
... OBJECTIVE: The amount of heat energy that can be transferred to or from a material is dependent on the mass of material, the temperature gradient, and a material property known as its specific heat capacity. The principles of calorimetry will be employed to determine an experimental value for a mate ...
Specific Heat Equation Practice Worksheet
... c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. You have probably noticed that a metal spoon heats up quickly when placed in a cup of soap while a plastic spoon heats more slowly. The difference between the final temperatures of the two spoons depends on whe ...
... c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. You have probably noticed that a metal spoon heats up quickly when placed in a cup of soap while a plastic spoon heats more slowly. The difference between the final temperatures of the two spoons depends on whe ...
THERMODYNAMICS - FSU High Energy Physics
... heat, depends on atomic/molecular structure; metals typically 400 times better than other solids; most solids little better than liquids; liquids about 10 times better than gases; good heat conductor usually good electric conductor ...
... heat, depends on atomic/molecular structure; metals typically 400 times better than other solids; most solids little better than liquids; liquids about 10 times better than gases; good heat conductor usually good electric conductor ...
Energy
... Potential: due to position or composition can be converted to work Kinetic: due to motion of the object KE = 1/2 mv2 (m = mass, v = velocity) ...
... Potential: due to position or composition can be converted to work Kinetic: due to motion of the object KE = 1/2 mv2 (m = mass, v = velocity) ...
greek traditional bioclimatic architecture
... Use of local building materials in traditional architecture, was due to limited transportation potential, in older times. Nevertheless, ecologically was a perfect choice, and contributed substantially to the morphological wealth of Greek traditional architecture. When building materials with special ...
... Use of local building materials in traditional architecture, was due to limited transportation potential, in older times. Nevertheless, ecologically was a perfect choice, and contributed substantially to the morphological wealth of Greek traditional architecture. When building materials with special ...
Passive House and High- Performance New
... With a background in natural building and energy efficiency (including time as a Snug Planet installer), Craig Modisher founded Ironwood Builders to guide clients through the homebuilding process from concept to completion. His passion for ultra-efficient homes has led his company to specialize in P ...
... With a background in natural building and energy efficiency (including time as a Snug Planet installer), Craig Modisher founded Ironwood Builders to guide clients through the homebuilding process from concept to completion. His passion for ultra-efficient homes has led his company to specialize in P ...
The Geosphere
... Heat transfer through the motion of a hot material When a material heats, it expands The expanded material is less dense The material then rises, carrying heat ...
... Heat transfer through the motion of a hot material When a material heats, it expands The expanded material is less dense The material then rises, carrying heat ...
Lab 1: Temperature and Heat
... V is the voltage and R is the resistance. The thermal energy Q absorbed by the water is given by Q = mc∆T. Use these equations to predict how much the temperature of the water should change after 1 min, 2 min, 3 min, 4 min, and 5 min. Compare your predictions with your results using a percent differ ...
... V is the voltage and R is the resistance. The thermal energy Q absorbed by the water is given by Q = mc∆T. Use these equations to predict how much the temperature of the water should change after 1 min, 2 min, 3 min, 4 min, and 5 min. Compare your predictions with your results using a percent differ ...
middle east technical university department of physics
... In industries the largest share of process heat (two thirds of all industrial process heat) is met by steam. Significantly different approaches is used for producing steam using solar energy then that for air or water process heating. Following three possible ways to supply steam with solar collecto ...
... In industries the largest share of process heat (two thirds of all industrial process heat) is met by steam. Significantly different approaches is used for producing steam using solar energy then that for air or water process heating. Following three possible ways to supply steam with solar collecto ...
heat
... 1.Why, or why not, does one drop of boiling water at 100 oC burn your hand? 2.Would you burn your hand if you poured the entire beaker of 100 oC of boiling water on your hand? Why or why not? 3.What is being transferred from the water to your hand? 4.How does energy transfer from the water to hand o ...
... 1.Why, or why not, does one drop of boiling water at 100 oC burn your hand? 2.Would you burn your hand if you poured the entire beaker of 100 oC of boiling water on your hand? Why or why not? 3.What is being transferred from the water to your hand? 4.How does energy transfer from the water to hand o ...
Chapter 11 1. While checking the temperature of an IC. chip the
... 10. A 10 ohm resistor connected to a 12V battery is used as a heater in a 10kg pot of water. If the heater runs for 250 seconds, what is the change in temperature of the water in Celcius? ...
... 10. A 10 ohm resistor connected to a 12V battery is used as a heater in a 10kg pot of water. If the heater runs for 250 seconds, what is the change in temperature of the water in Celcius? ...
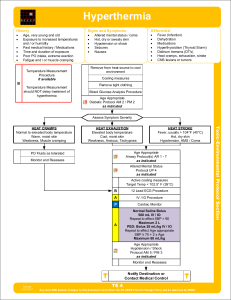
Hyperthermia
... Consists of dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, temperature 104°F (40°C), and an altered mental status. Sweating generally disappears as body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional heat stroke (a ...
... Consists of dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, temperature 104°F (40°C), and an altered mental status. Sweating generally disappears as body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional heat stroke (a ...
Lecture 6
... to Exist as a Liquid at Normal Temperatures And across a wide range in temperatures ...
... to Exist as a Liquid at Normal Temperatures And across a wide range in temperatures ...
Chapter 5 PPT 2 - Kawameeh Middle School
... Liquid – Expands more than solid but less than gas ...
... Liquid – Expands more than solid but less than gas ...