Thermochemistry Problems
... m, mass of the substance cp, specific heat of the substance t, change in temperature Heat: energy that flows from a system at higher temperature to a system at lower temperature: the sum total of the KE of the individual particles in a system; represented by Q. Temperature: degree of hotness or col ...
... m, mass of the substance cp, specific heat of the substance t, change in temperature Heat: energy that flows from a system at higher temperature to a system at lower temperature: the sum total of the KE of the individual particles in a system; represented by Q. Temperature: degree of hotness or col ...
Cooling Rate Calculation of Non-Equilibrium
... in the gas stream. The smaller droplets can gain larger acceleration, thus which can reach quickly the atomizing gas velocities and solidify swiftly. While the larger droplets gain smaller acceleration, so they can not keep up with the high-speed gas, but they disengage the fast gas beam area. Based ...
... in the gas stream. The smaller droplets can gain larger acceleration, thus which can reach quickly the atomizing gas velocities and solidify swiftly. While the larger droplets gain smaller acceleration, so they can not keep up with the high-speed gas, but they disengage the fast gas beam area. Based ...
Heat - Indian Institute of Technology Madras
... Chapter 3 Temperature and Heat In Chapter 1, temperature was described as an intensive property of a system. In common parlance, we understand temperature as a property which is related to the degree of hotness (or coldness) of a substance for physical touch. It is to be noted however, that human pe ...
... Chapter 3 Temperature and Heat In Chapter 1, temperature was described as an intensive property of a system. In common parlance, we understand temperature as a property which is related to the degree of hotness (or coldness) of a substance for physical touch. It is to be noted however, that human pe ...
HEAT TRANSFER_012110043920_1
... 14) Saturated F-12 vapour at 12.3/bar condenses on the outside of a bank of horizontal tubes 1 cm OD arranged in 5X5 square array. Calculate the rate of condensation per meter length of the array if the tube surface is maintained at 40oC. F-12 has following properties:Liquid density = 1218kg/m3 ,Lat ...
... 14) Saturated F-12 vapour at 12.3/bar condenses on the outside of a bank of horizontal tubes 1 cm OD arranged in 5X5 square array. Calculate the rate of condensation per meter length of the array if the tube surface is maintained at 40oC. F-12 has following properties:Liquid density = 1218kg/m3 ,Lat ...
Indiana University - Purdue University Fort Wayne Department of Engineering ENGR 411
... commissioned the design of a solar cooling demonstration unit. The unit is to be based upon and active type solar cooling system. The unit is also to make use of an absorption cycle and a desiccant. For the detailed mechanical design, an Engineering Equation Solver program was created to model the a ...
... commissioned the design of a solar cooling demonstration unit. The unit is to be based upon and active type solar cooling system. The unit is also to make use of an absorption cycle and a desiccant. For the detailed mechanical design, an Engineering Equation Solver program was created to model the a ...
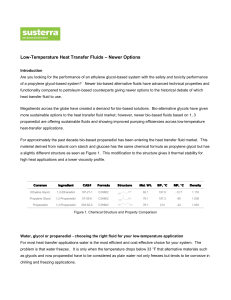
Low-Temperature Heat Transfer Fluids Newer Options
... Heat transfer fluids are widely used in food processing, commercial refrigeration, geothermal, and other lowtemperature heat-transfer applications that typically operate in a temperature range from 0°F to 42°F (-18°C to 6°C). Most heat transfer fluids have lower heat-transfer efficiencies than wate ...
... Heat transfer fluids are widely used in food processing, commercial refrigeration, geothermal, and other lowtemperature heat-transfer applications that typically operate in a temperature range from 0°F to 42°F (-18°C to 6°C). Most heat transfer fluids have lower heat-transfer efficiencies than wate ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry
... Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry refers to the study of the heat flow that accompanies chemical reactions. Heat is a particular form of energy that is transferred from a body at a high temperature to one at a lower temperature when they are brought into contact with each other. ...
... Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry refers to the study of the heat flow that accompanies chemical reactions. Heat is a particular form of energy that is transferred from a body at a high temperature to one at a lower temperature when they are brought into contact with each other. ...
Review of 1st and 2nd Law + Entropy
... Refrigerators and heat pumps are devices that absorb heat from low-temperature media and reject it to higher-temperature ones. The performance of a refrigerator or a heat pump is expressed in terms of the coefficient of performance, which is defined as ...
... Refrigerators and heat pumps are devices that absorb heat from low-temperature media and reject it to higher-temperature ones. The performance of a refrigerator or a heat pump is expressed in terms of the coefficient of performance, which is defined as ...
Heat review sheet
... Another heat source that produces radiation is fire. As you can see, radiates out in all direction. When a heat wave hits an object, the heat is absorbed (absorption). The object retains the heat produced by the heat wave. This is why you don’t want to wear dark colors in the summer. A dark color ab ...
... Another heat source that produces radiation is fire. As you can see, radiates out in all direction. When a heat wave hits an object, the heat is absorbed (absorption). The object retains the heat produced by the heat wave. This is why you don’t want to wear dark colors in the summer. A dark color ab ...
Exercises to the Textbook “Physical Chemistry from
... b) The same house is heated under otherwise identical conditions by common electric heating, i. e., the amount of entropy of 30 Ct per second necessary for compensation of entropy loss is not transferred from outside but is generated in the house. The temperature in the house should be again 25 °C. ...
... b) The same house is heated under otherwise identical conditions by common electric heating, i. e., the amount of entropy of 30 Ct per second necessary for compensation of entropy loss is not transferred from outside but is generated in the house. The temperature in the house should be again 25 °C. ...
Period 15: Electro magnetism
... amount of matter being heated. Temperature change also depends on the type of material being heated. It takes more energy to raise the temperature of water than to raise the temperature of an equal amount of metal, for example. The amount of energy that must be added to an object to raise its temper ...
... amount of matter being heated. Temperature change also depends on the type of material being heated. It takes more energy to raise the temperature of water than to raise the temperature of an equal amount of metal, for example. The amount of energy that must be added to an object to raise its temper ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... H2O (with a specific heat of 4.184 J/g·oC) is heated from 22oC to 98oC. q = msΔT Is heat being put into the system or given off by the system? If a piece of hot metal is placed in cold water, what gains heat and what loses heat? Which one will have a positive q value and which will have a negative q ...
... H2O (with a specific heat of 4.184 J/g·oC) is heated from 22oC to 98oC. q = msΔT Is heat being put into the system or given off by the system? If a piece of hot metal is placed in cold water, what gains heat and what loses heat? Which one will have a positive q value and which will have a negative q ...
Thermochemistry 2 Matching Match each item with the correct
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
THR-BRO-Thermoelectric Assembly 1110
... thermal components or building blocks that mate fans and TEMs to heat exchangers. Laird Technologies has conducted two decades worth of design and validation testing on various combinations of thermal components to optimize cooling power and efficiency at various heat loads. This results in engineer ...
... thermal components or building blocks that mate fans and TEMs to heat exchangers. Laird Technologies has conducted two decades worth of design and validation testing on various combinations of thermal components to optimize cooling power and efficiency at various heat loads. This results in engineer ...
Fabric and ventilation heat loss
... • Heat flows from hot areas to cold areas. (Second law of thermodynamics) • Most people like to live and work in room temperatures of approximately 20 0C. • In many European countries, outside air temperatures in winter are well below 20 0C. • Heat from warm areas flows out through the fabric of the ...
... • Heat flows from hot areas to cold areas. (Second law of thermodynamics) • Most people like to live and work in room temperatures of approximately 20 0C. • In many European countries, outside air temperatures in winter are well below 20 0C. • Heat from warm areas flows out through the fabric of the ...
Guidelines for Work in Hot Environments
... Convection - the exchange of body heat with the surrounding air. If the moving air is cooler than the body temperature, it will cool the body; if warmer, it will increase the heat load. Air speed is an important factor in heat loss or gain. Evaporation - evaporation of perspiration from the skin is ...
... Convection - the exchange of body heat with the surrounding air. If the moving air is cooler than the body temperature, it will cool the body; if warmer, it will increase the heat load. Air speed is an important factor in heat loss or gain. Evaporation - evaporation of perspiration from the skin is ...
Electric Arc Furnace as Thermoenergetical Unit
... is converted into useful heat. If this portion of energy decreases substantially while the power of the source increases, then such an increase in heat generation becomes inexpedient. In such cases, it is necessary in the first place to improve the heat transfer conditions rather than to increase th ...
... is converted into useful heat. If this portion of energy decreases substantially while the power of the source increases, then such an increase in heat generation becomes inexpedient. In such cases, it is necessary in the first place to improve the heat transfer conditions rather than to increase th ...
Copy of Ch6-Energy in Chemical Reactions
... constant pressure, qp is called enthalpy (H). E = qp + w; w = -PVE = qp -PV + w; qp = E + PV; H = E + PV Enthalpy change = sum of the internal energy and volume expansion work. Internal energy (E) For systems that involve heat change (qv) at constant volume (V =0) is called internal e ...
... constant pressure, qp is called enthalpy (H). E = qp + w; w = -PVE = qp -PV + w; qp = E + PV; H = E + PV Enthalpy change = sum of the internal energy and volume expansion work. Internal energy (E) For systems that involve heat change (qv) at constant volume (V =0) is called internal e ...
Cure Epoxies with Heat Heating Devices
... costs associated with providing heat is not consistent with industrywide objectives of lowering overall manufacturing costs. “Heat-curable epoxies are still widely available, but most companies are looking to decrease their overall costs to manufacture, especially time requirements,” claims Small. “ ...
... costs associated with providing heat is not consistent with industrywide objectives of lowering overall manufacturing costs. “Heat-curable epoxies are still widely available, but most companies are looking to decrease their overall costs to manufacture, especially time requirements,” claims Small. “ ...
Principles of Heat Transfer - WSU Energy Program
... reflectivity” and its “far-infrared emissivity” because both these properties affect radiation heat transfer of a sun-exposed surface. Total solar reflectivity is the surface’s reflectivity just to those wavelengths that compose solar radiation; i.e., it is the fraction of solar radiation2 that is r ...
... reflectivity” and its “far-infrared emissivity” because both these properties affect radiation heat transfer of a sun-exposed surface. Total solar reflectivity is the surface’s reflectivity just to those wavelengths that compose solar radiation; i.e., it is the fraction of solar radiation2 that is r ...
Chapter 14 – Temperature and Heat
... a thermometric property and the volume is used as thermometric quantity. Due to the fixed crossed sectional area, thermometer can have the length of the capillary of mercury as thermometric quantity. The following chart shows the type of thermometer with its thermometric quantity. ...
... a thermometric property and the volume is used as thermometric quantity. Due to the fixed crossed sectional area, thermometer can have the length of the capillary of mercury as thermometric quantity. The following chart shows the type of thermometer with its thermometric quantity. ...
Thermal monitoring and indoor temperature predictions in a passive
... the meteorological station, except for outdoor ambient temperature, which was monitored adjacent to building. Results indicated that the calculation of the building’s energy demand for air-conditioning based on temperature data collected at the meteorological station would yield half of the cooling ...
... the meteorological station, except for outdoor ambient temperature, which was monitored adjacent to building. Results indicated that the calculation of the building’s energy demand for air-conditioning based on temperature data collected at the meteorological station would yield half of the cooling ...
Station spec meanings-TD
... c. The tolerance that exists in the heater. Heaters aren't made with 10-10 precision in their mix - if they were they'd cost more than your house - and each one is just the least little bit off-centre from perfect. d. The size and shape of the tip. The laws of thermodynamics and heat transfer work. ...
... c. The tolerance that exists in the heater. Heaters aren't made with 10-10 precision in their mix - if they were they'd cost more than your house - and each one is just the least little bit off-centre from perfect. d. The size and shape of the tip. The laws of thermodynamics and heat transfer work. ...
AP Thermo I Notes
... Using ∆H°f to find ∆Hrxn C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ∆Hcomb = ? We can “add” these three equations to find ∆Hcomb. ...
... Using ∆H°f to find ∆Hrxn C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ∆Hcomb = ? We can “add” these three equations to find ∆Hcomb. ...