Chapter 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture Goals of Period 5
... motion of small dust particles suspended in air. The molecules or atoms making up the air are constantly in random motion. As air molecules strike dust particles in the air, the dust particles also move about in a random fashion. This random motion of the dust particles is known as Brownian motion. ...
... motion of small dust particles suspended in air. The molecules or atoms making up the air are constantly in random motion. As air molecules strike dust particles in the air, the dust particles also move about in a random fashion. This random motion of the dust particles is known as Brownian motion. ...
Effect of Temperature on Heat Transfer Coefficient of Titanium
... enhancement than SiO2. Also, thermal conductivity was affected by particle size and the stability of the nanofluid [13-16]. A study on forced convection using Al2O3 nanofluid for laminar flow in a plain tube by Sharma and Syam Sundar [17] found that the twisted tape inserts contributed to the enhanc ...
... enhancement than SiO2. Also, thermal conductivity was affected by particle size and the stability of the nanofluid [13-16]. A study on forced convection using Al2O3 nanofluid for laminar flow in a plain tube by Sharma and Syam Sundar [17] found that the twisted tape inserts contributed to the enhanc ...
A Mathematical Analysis of Two Dimensional Steady State Heat
... In developing heaters typically and induction heater in specific temperature limits can be a key issue disturbing the efficiency of the overall policy. Since typical loading of induction heater is commonly costly. The estimation of temperature rise by tools of mathematical modelling becomes a lot of ...
... In developing heaters typically and induction heater in specific temperature limits can be a key issue disturbing the efficiency of the overall policy. Since typical loading of induction heater is commonly costly. The estimation of temperature rise by tools of mathematical modelling becomes a lot of ...
Course Pack3 Phase Diagrams
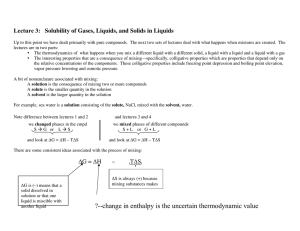
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
Lecture Ch#5 Thermochemistry
... A. When the gas expands isothermally, it does work without a decrease in its energy, so heat must flow into the system. B. During the expansion, the gas pressure decreases, thereby releasing heat to the surroundings. C. The fact that the process is isothermal means that heat does not flow. Isotherma ...
... A. When the gas expands isothermally, it does work without a decrease in its energy, so heat must flow into the system. B. During the expansion, the gas pressure decreases, thereby releasing heat to the surroundings. C. The fact that the process is isothermal means that heat does not flow. Isotherma ...
q - gearju.com
... State functions are properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. energy, pressure, volume, temperature ...
... State functions are properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. energy, pressure, volume, temperature ...
Integrating Low-temperature Heating Systems into Energy
... system or an exhaust air heat pump. All these potential measures lead to a reduction in the heating season and the space heating load, providing an opportunity to use low-temperature heating systems. Low-temperature heating systems usually work with a maximum supply water temperature of 45 °C [2]. S ...
... system or an exhaust air heat pump. All these potential measures lead to a reduction in the heating season and the space heating load, providing an opportunity to use low-temperature heating systems. Low-temperature heating systems usually work with a maximum supply water temperature of 45 °C [2]. S ...
Part IV - TTU Physics
... the energy of particle can only have discrete energy values. It cannot increase infinitely from one value to another. It has to go up in steps. ...
... the energy of particle can only have discrete energy values. It cannot increase infinitely from one value to another. It has to go up in steps. ...
Average Air Temperature Inside a Room With a Semitransparent
... formed by an isothermal vertical wall, two adiabatic horizontal walls and a semitransparent wall with and without a control solar radiation film. The governing equations for turbulent flow in 2D were solved using a finite volume formulation and k- turbulent model. Results for an isothermal wall at ...
... formed by an isothermal vertical wall, two adiabatic horizontal walls and a semitransparent wall with and without a control solar radiation film. The governing equations for turbulent flow in 2D were solved using a finite volume formulation and k- turbulent model. Results for an isothermal wall at ...
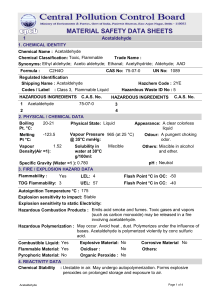
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEETS
... Fire Extinguishing Media : Dry chemical powder, alcohol foam, CO2. Special Procedure : Keep the containers cool by spraying water if exposed to heat or fire. Unusual Hazards : Flashback along vapour trail may occur. EXPOSURE: First Aid Measures: Inhalation: Remove from exposure to fresh air immediat ...
... Fire Extinguishing Media : Dry chemical powder, alcohol foam, CO2. Special Procedure : Keep the containers cool by spraying water if exposed to heat or fire. Unusual Hazards : Flashback along vapour trail may occur. EXPOSURE: First Aid Measures: Inhalation: Remove from exposure to fresh air immediat ...
Heat
... • Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form of electromagnetic waves (or photons) as a result of the changes in the electronic configurations of the atoms or molecules. • Unlike conduction and convection, the transfer of heat by radiation does not require the presence of an intervening med ...
... • Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form of electromagnetic waves (or photons) as a result of the changes in the electronic configurations of the atoms or molecules. • Unlike conduction and convection, the transfer of heat by radiation does not require the presence of an intervening med ...
A roller coaster ride is a thrilling experience which involves a wealth
... 4. A reaction must be spontaneous if the results in products that have A. lower potential energy and less randomness B. more potential energy and more randomness C. lower potential energy and more randomness D. more potential energy and less randomness 5. The change of the reactants into products wi ...
... 4. A reaction must be spontaneous if the results in products that have A. lower potential energy and less randomness B. more potential energy and more randomness C. lower potential energy and more randomness D. more potential energy and less randomness 5. The change of the reactants into products wi ...
Mapping Heat Origin in Plasmonic Structures
... the surroundings), TðrÞ is the temperature distribution, and hðrÞ represents the heat source density (HSD) that has dimensions of a power per unit volume. For submicrometric metal structures heated by external illumination, the HSD hðrÞ can be strongly nonuniform, depending on the morphology of the ...
... the surroundings), TðrÞ is the temperature distribution, and hðrÞ represents the heat source density (HSD) that has dimensions of a power per unit volume. For submicrometric metal structures heated by external illumination, the HSD hðrÞ can be strongly nonuniform, depending on the morphology of the ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... 1. What are the two major ways in which the internal energy of an object can be categorized? How do these ways differ from one another? 2. If a system loses heat, where does it go? 3. Describe the following processes as exothermic or endothermic: a. an ice cube melts on a warm surface b. water freez ...
... 1. What are the two major ways in which the internal energy of an object can be categorized? How do these ways differ from one another? 2. If a system loses heat, where does it go? 3. Describe the following processes as exothermic or endothermic: a. an ice cube melts on a warm surface b. water freez ...
Heat - FER
... The heat transfer problems encountered in practice can be considered in two groups: (1) rating and (2) sizing problems. The rating problems deal with the determination of the heat transfer rate for an existing system at a specified temperature difference. The sizing problems deal with the determinat ...
... The heat transfer problems encountered in practice can be considered in two groups: (1) rating and (2) sizing problems. The rating problems deal with the determination of the heat transfer rate for an existing system at a specified temperature difference. The sizing problems deal with the determinat ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... of clay is increased when it is moved from the ground to the top of the wall. b) As the ball falls, its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. c) When it hits the ground, its kinetic energy falls to zero (since it is no longer moving); some of the energy does work on the ball, the rest is ...
... of clay is increased when it is moved from the ground to the top of the wall. b) As the ball falls, its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. c) When it hits the ground, its kinetic energy falls to zero (since it is no longer moving); some of the energy does work on the ball, the rest is ...
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
... The heat transfer problems encountered in practice can be considered in two groups: (1) rating and (2) sizing problems. The rating problems deal with the determination of the heat transfer rate for an existing system at a specified temperature difference. The sizing problems deal with the determinat ...
... The heat transfer problems encountered in practice can be considered in two groups: (1) rating and (2) sizing problems. The rating problems deal with the determination of the heat transfer rate for an existing system at a specified temperature difference. The sizing problems deal with the determinat ...
Heat Transfer
... The heat transfer problems encountered in practice can be considered in two groups: (1) rating and (2) sizing problems. The rating problems deal with the determination of the heat transfer rate for an existing system at a specified temperature difference. The sizing problems deal with the determinat ...
... The heat transfer problems encountered in practice can be considered in two groups: (1) rating and (2) sizing problems. The rating problems deal with the determination of the heat transfer rate for an existing system at a specified temperature difference. The sizing problems deal with the determinat ...
Two moles of gas at 1 bar and 298 K are compressed at constant T
... DEFINITION of Standard Heat of Formation of Compounds: This is the heat required to form the compound [in its most stable form] from its constituent elements in their standard states. Thus we need to know the most stable state of the compound and elements in order to be able to write the formation ...
... DEFINITION of Standard Heat of Formation of Compounds: This is the heat required to form the compound [in its most stable form] from its constituent elements in their standard states. Thus we need to know the most stable state of the compound and elements in order to be able to write the formation ...
basic concept of thermodynamics
... pV = mRT • Where, P = pressure in N/m2 or pa, V = Volume in m3, m = Mass of gas in kg, T = absolute temperature in K & R = Gas constant in J/kg.K = 0.287 kJ/kg.K ...
... pV = mRT • Where, P = pressure in N/m2 or pa, V = Volume in m3, m = Mass of gas in kg, T = absolute temperature in K & R = Gas constant in J/kg.K = 0.287 kJ/kg.K ...
Thermal Transmittance Values for Residential Buildings
... (PUR) products for building end-use applications - Part 2 : Specification for laminated boards with auto adhesively bonded facings for use as thermal insulation for internal wall linings and ceilings " SASO-GSO- BS- 4841-3:2010 "Rigid polyisocyanurate (PIR) and polyurethane (PUR) products for buildi ...
... (PUR) products for building end-use applications - Part 2 : Specification for laminated boards with auto adhesively bonded facings for use as thermal insulation for internal wall linings and ceilings " SASO-GSO- BS- 4841-3:2010 "Rigid polyisocyanurate (PIR) and polyurethane (PUR) products for buildi ...
Window Condensation - RLC Engineering, LLC
... Summer condensation occurs when the outside window surface is cooler than the dew point temperature of the outside air. In the southeast US, summer dew point temperatures range from about 65F to 75F. When temperatures inside the building are within this range, summer condensation problems can occur. ...
... Summer condensation occurs when the outside window surface is cooler than the dew point temperature of the outside air. In the southeast US, summer dew point temperatures range from about 65F to 75F. When temperatures inside the building are within this range, summer condensation problems can occur. ...
Lecture 8 notes, ppt file
... (born, 1821-1895, first estimation of Avogadro number, Boltzmann’s colleague) ...
... (born, 1821-1895, first estimation of Avogadro number, Boltzmann’s colleague) ...
Name
... To calculate the kJ/mol we will simply determine the kJ from the q rxn and then determine the moles of H2SO4 present – and then literally divide the kJ by the moles! ...
... To calculate the kJ/mol we will simply determine the kJ from the q rxn and then determine the moles of H2SO4 present – and then literally divide the kJ by the moles! ...
Hybrid Solar Thermal Integration at Existing Fossil
... HYBRID CONCEPTS OF INTEGRATED SOLAR THERMAL (ICSS) ...
... HYBRID CONCEPTS OF INTEGRATED SOLAR THERMAL (ICSS) ...