List 6-10 types of energy and give an example of each. State
... 7. What materials make good thermal energy conductors? What materials make poor thermal energy conductors? [Thermal Conductivity of Unknown Metals] Dense materials, such as metals, make good conductors because molecules are closer together and can therefore the rate of energy transfer is higher; col ...
... 7. What materials make good thermal energy conductors? What materials make poor thermal energy conductors? [Thermal Conductivity of Unknown Metals] Dense materials, such as metals, make good conductors because molecules are closer together and can therefore the rate of energy transfer is higher; col ...
Spiral Store A PCM Thermal - Knowledge Transfer Ireland
... of over 10,000 kWe. However, this makes it an ideal test bed for new technologies prior to commercialisation in the European and US markets. ...
... of over 10,000 kWe. However, this makes it an ideal test bed for new technologies prior to commercialisation in the European and US markets. ...
Controlling Condensation in Steep Slope Metal Roofing Systems
... building insulation. The practice is applicable for both wall and roofing applications. For most roofing applications, the proper location would be above the building’s drywall ceiling. The building owner is advised to contact a design professional to determine the proper design for and placement of ...
... building insulation. The practice is applicable for both wall and roofing applications. For most roofing applications, the proper location would be above the building’s drywall ceiling. The building owner is advised to contact a design professional to determine the proper design for and placement of ...
Electronics Cooling MEP 635
... 1. To establish fundamental understanding of heat transfer in electronic equipment. 2. To select a suitable cooling processes for electronic components and systems. 3. To increase the capabilities of post-graduate students in design and analysis of cooling of electronic packages. 4. To analysis the ...
... 1. To establish fundamental understanding of heat transfer in electronic equipment. 2. To select a suitable cooling processes for electronic components and systems. 3. To increase the capabilities of post-graduate students in design and analysis of cooling of electronic packages. 4. To analysis the ...
Heat Transfer Equipment Wort kettle – External calandria
... Layers of dirt, particles, biological growth, etc. effect resistance to heat transfer ...
... Layers of dirt, particles, biological growth, etc. effect resistance to heat transfer ...
Dry heat - Grainchain
... Foods which are baked, grilled or roasted undergo colour, odour and flavour changes. The process is called dextrinisation. ...
... Foods which are baked, grilled or roasted undergo colour, odour and flavour changes. The process is called dextrinisation. ...
Name: Date: ______ Thermochemistry Round Robin
... 14. Benzene, C6H6, is an organic liquid that freezes at 5.5˚C to beautiful, feather-like crystals. How much heat is evolved when 15.5 g of benzene freezes at 5.5˚C? (The heat of fusion of benzene is 9.95 kJ/mol). If the 15.5 g sample is re-melted, again at 5.5˚C, what quantity of heat is required to ...
... 14. Benzene, C6H6, is an organic liquid that freezes at 5.5˚C to beautiful, feather-like crystals. How much heat is evolved when 15.5 g of benzene freezes at 5.5˚C? (The heat of fusion of benzene is 9.95 kJ/mol). If the 15.5 g sample is re-melted, again at 5.5˚C, what quantity of heat is required to ...
Specific Heat Lab Experiment Sixteen p
... Purpose: To determine the identity of an unknown metal by determining its specific heat capacity, “c” Materials: unknown metal sample, calorimeter, styrofoam cup, water, beaker, hot plate, string, thermometer, balance Background: If substances of different temperatures are in contact with each other ...
... Purpose: To determine the identity of an unknown metal by determining its specific heat capacity, “c” Materials: unknown metal sample, calorimeter, styrofoam cup, water, beaker, hot plate, string, thermometer, balance Background: If substances of different temperatures are in contact with each other ...
Conduction
... Btu/(h·ft ·°F) as well as by radiation with the open sky with an equivalent sky temperature of T sky = 510 R. Also, the temperature of the upper surface of the plate is measured to be 75°F. Assuming steady onedimensional heat transfer, (a) express the differential equation and the boundary condition ...
... Btu/(h·ft ·°F) as well as by radiation with the open sky with an equivalent sky temperature of T sky = 510 R. Also, the temperature of the upper surface of the plate is measured to be 75°F. Assuming steady onedimensional heat transfer, (a) express the differential equation and the boundary condition ...
Lessons 3 and 4 Thermodynamics
... A refrigerator does transfer heat from cold to hot, but work must be done (electricity supplied and some converted into heat) to do this A boat could use the temperature difference between the sea and atmosphere to run, but eventually the two reservoirs would reach the same temperature ...
... A refrigerator does transfer heat from cold to hot, but work must be done (electricity supplied and some converted into heat) to do this A boat could use the temperature difference between the sea and atmosphere to run, but eventually the two reservoirs would reach the same temperature ...
Bacon¹s inductive method, example of heat.
... nothing more than those laws and determinations of absolute actuality which govern and constitute any simple nature, as heat, light, weight, in every kind of matter and subject that is susceptible of them (Bacon IV [1901], 145–6); They are not identical with natural law, but with definitions of simp ...
... nothing more than those laws and determinations of absolute actuality which govern and constitute any simple nature, as heat, light, weight, in every kind of matter and subject that is susceptible of them (Bacon IV [1901], 145–6); They are not identical with natural law, but with definitions of simp ...
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN TURBULENT CONVECTION IN A BUNDLE
... As experimental velocity and temperature profiles are not available in the literature, a preliminary validation of the method employed is performed by the comparison of the global quantities like f and Nu against results in Ref. [4] and [2]. The time averaged velocity and temperature fields are repo ...
... As experimental velocity and temperature profiles are not available in the literature, a preliminary validation of the method employed is performed by the comparison of the global quantities like f and Nu against results in Ref. [4] and [2]. The time averaged velocity and temperature fields are repo ...
Note Guide 7-4
... •Potential energy = energy of position/stored energy. But in chemistry we have chemical potential energy = energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance --how much energy stored is determined by kinds of atoms and how they are arranged. •Heat(q) = energy that transfers from one object to anothe ...
... •Potential energy = energy of position/stored energy. But in chemistry we have chemical potential energy = energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance --how much energy stored is determined by kinds of atoms and how they are arranged. •Heat(q) = energy that transfers from one object to anothe ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... compare heat capacities, because there are two different variables, SO they compare 1g of substances to come up with the specific heat capacity. ...
... compare heat capacities, because there are two different variables, SO they compare 1g of substances to come up with the specific heat capacity. ...
Exercises – Chapter 8
... E.18 The hotter the water, the more thermal energy can be harnessed and the greater the temperature difference between the hot water and the colder surrounding, the more efficient the hurricane is at converting that thermal energy into mechanical work. 19. On a clear sunny day, the ground is heated ...
... E.18 The hotter the water, the more thermal energy can be harnessed and the greater the temperature difference between the hot water and the colder surrounding, the more efficient the hurricane is at converting that thermal energy into mechanical work. 19. On a clear sunny day, the ground is heated ...
Page 1 of 2 Gerbing`s Heated Clothing // How it Works 02/11/2009
... further tune how the heat is delivered. More, when using the ribbon matrix, we could refine the heat delivery to an even greater degree by altering the number of wires in the ribbon (from 2 up to 6). It is this “tunability” to each garment application that is one of the major advantages of Microwire ...
... further tune how the heat is delivered. More, when using the ribbon matrix, we could refine the heat delivery to an even greater degree by altering the number of wires in the ribbon (from 2 up to 6). It is this “tunability” to each garment application that is one of the major advantages of Microwire ...
Protection against cold in prehospital care: thermal insulation
... heat loss from the airways. Sweating and evaporative heat loss from the skin often is minimal in cold environments, but could be considerable in case of wet clothing or skin due to immersion or previous physical activity. In addition, if the injured or ill person is lying on the ground or is in dire ...
... heat loss from the airways. Sweating and evaporative heat loss from the skin often is minimal in cold environments, but could be considerable in case of wet clothing or skin due to immersion or previous physical activity. In addition, if the injured or ill person is lying on the ground or is in dire ...
2016 Q7 - Loreto Balbriggan
... As part of his presentation, Joule proposed that the temperature of the water at the bottom of the Niagara Falls would be 0.12 °C greater than that at the top, due to gravitational potential energy being converted into heat energy. Calculate the height of the Niagara Falls. In reality the increase i ...
... As part of his presentation, Joule proposed that the temperature of the water at the bottom of the Niagara Falls would be 0.12 °C greater than that at the top, due to gravitational potential energy being converted into heat energy. Calculate the height of the Niagara Falls. In reality the increase i ...
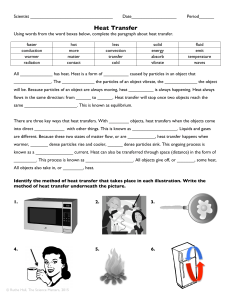
Heat Transfer - Granville County Public Schools
... All _____________ has heat. Heat is a form of __________ caused by particles in an object that _______________. The _____________ the particles of an object vibrate, the _____________ the object will be. Because particles of an object are always moving, heat __________ is always happening. Heat alwa ...
... All _____________ has heat. Heat is a form of __________ caused by particles in an object that _______________. The _____________ the particles of an object vibrate, the _____________ the object will be. Because particles of an object are always moving, heat __________ is always happening. Heat alwa ...
Thermodynamics-d2
... surroundings due to organized motion in the surroundings. (rubbing a block of wood vigorously, stir a glass of water, allow a gas to expand against an external pressure.) ...
... surroundings due to organized motion in the surroundings. (rubbing a block of wood vigorously, stir a glass of water, allow a gas to expand against an external pressure.) ...
Thermochemistry PPT
... Definitions • Energy – capacity for doing work or supplying heat. • Thermochemistry – study of energy changes that occur during phase changes and chem. rxns. • Chem. Potential Energy – energy stored in chemical bonds. ...
... Definitions • Energy – capacity for doing work or supplying heat. • Thermochemistry – study of energy changes that occur during phase changes and chem. rxns. • Chem. Potential Energy – energy stored in chemical bonds. ...
Joule`s Law and Heat Transfer Name:
... 7. Open DataStudio, select "Open Activity", select "Library", select "Physics Labs folder", and select "P16-Temperature and Heat". Click on the digits display and click start. 8. Plug in the power, and stir the water gently with the temperature sensor. 9. When the temperature reaches 20oC, the PC wi ...
... 7. Open DataStudio, select "Open Activity", select "Library", select "Physics Labs folder", and select "P16-Temperature and Heat". Click on the digits display and click start. 8. Plug in the power, and stir the water gently with the temperature sensor. 9. When the temperature reaches 20oC, the PC wi ...
Ideal Gas Law / Heat Transfer
... Heat Capacity But what if the two objects were different sizes? Lake Michigan vs. cup of water Which one do you need to add more heat to in order to raise the temperature? ...
... Heat Capacity But what if the two objects were different sizes? Lake Michigan vs. cup of water Which one do you need to add more heat to in order to raise the temperature? ...
Building insulation materials

Building insulation materials are the building materials which form the thermal envelope of a building or otherwise reduce heat transfer.Insulation may be categorized by its composition (natural or synthetic materials), form (batts, blankets, loose-fill, spray foam, and panels), structural contribution (insulating concrete forms, structured panels, and straw bales), functional mode (conductive, radiative, convective), resistance to heat transfer, environmental impacts, and more. Sometimes a thermally reflective surface called a radiant barrier is added to a material to reduce the transfer of heat through radiation as well as conduction. The choice of which material or combination of materials is used depends on a wide variety of factors. Some insulation materials have health risks, some so significant the materials are no longer allowed to be used but remain in use in some older buildings such as asbestos fibers and urea