Study-Questions3
... 12. Explain how plate tectonic processes can split apart a continent and form a new ocean. Explain how an ocean can close up and have a mountain range form in its place. 13. List the specific types of geologic structures (types of faults, types of folds) that can occur at each type of plate boundary ...
... 12. Explain how plate tectonic processes can split apart a continent and form a new ocean. Explain how an ocean can close up and have a mountain range form in its place. 13. List the specific types of geologic structures (types of faults, types of folds) that can occur at each type of plate boundary ...
Natural Hazards – Earthquakes, Volcanoes and
... An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the ground due to the movement of tectonic plates. The convection currents in the mantle causes the plates to move away or towards each other, or slide past each other. Frictions occur along plate boundaries and build up pressure in the rocks. ...
... An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the ground due to the movement of tectonic plates. The convection currents in the mantle causes the plates to move away or towards each other, or slide past each other. Frictions occur along plate boundaries and build up pressure in the rocks. ...
Earthquake - SchoolNova
... displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate strain energy over time. Stress results from tectonic plate movement, magmatic or volcanic activity. When stress exceeds strength of rocks, rock breaks and slips. Rock slippage/rupture occurs a ...
... displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate strain energy over time. Stress results from tectonic plate movement, magmatic or volcanic activity. When stress exceeds strength of rocks, rock breaks and slips. Rock slippage/rupture occurs a ...
Earthquakes - PreventionWeb
... geologists, others are hidden many kilometres below the surface. These faults are places where earthquakes can occur. The driving forces for earthquake activity in the UK are unclear; however they include regional compression caused by motion of the Earth’s tectonic plates, and uplift resulting from ...
... geologists, others are hidden many kilometres below the surface. These faults are places where earthquakes can occur. The driving forces for earthquake activity in the UK are unclear; however they include regional compression caused by motion of the Earth’s tectonic plates, and uplift resulting from ...
Lecture 7.3 - Heat production.key
... sphere are thought to be crucial to the initiation of subduction and tectonic impact of a thick and buoyant continent surrounded by a stag1,2 the operation of plate tectonics , which characterizes the present- nant lithospheric lid, we produced a series of two-dimensional thermo200 was hotter mechan ...
... sphere are thought to be crucial to the initiation of subduction and tectonic impact of a thick and buoyant continent surrounded by a stag1,2 the operation of plate tectonics , which characterizes the present- nant lithospheric lid, we produced a series of two-dimensional thermo200 was hotter mechan ...
Slide 1
... 3) During continental collision tectonics deformation is not anymore localized along the plate margin (accretionary wedge), but affects a large area in the upper plate and propagate cratonward in the lower plate (fold and thrust belt) 4) Deformation in the upper plate is absorbed via : ...
... 3) During continental collision tectonics deformation is not anymore localized along the plate margin (accretionary wedge), but affects a large area in the upper plate and propagate cratonward in the lower plate (fold and thrust belt) 4) Deformation in the upper plate is absorbed via : ...
Introduction to Earth Science
... A) Physical geology is the study of fossils and sequences of rock strata; historical geology is the study of how rocks and minerals were used in the past. B) Historical geology involves the study of rock strata, fossils, and geologic events, utilizing the geologic time scale as a reference; physical ...
... A) Physical geology is the study of fossils and sequences of rock strata; historical geology is the study of how rocks and minerals were used in the past. B) Historical geology involves the study of rock strata, fossils, and geologic events, utilizing the geologic time scale as a reference; physical ...
MolnarAugust29
... What does convective removal of mantle lithosphere predict? 1. Convective instability implies large lateral heterogeneity in the upper mantle. 2. Increased elevation and replacement of heavy material imply both: an increased propensity for normal faulting within the plateau. and an increased force ...
... What does convective removal of mantle lithosphere predict? 1. Convective instability implies large lateral heterogeneity in the upper mantle. 2. Increased elevation and replacement of heavy material imply both: an increased propensity for normal faulting within the plateau. and an increased force ...
Scientific Drilling
... energy among global reservoirs drive long-term changes in Earth’s structure and composition, cause volcanism and tectonism, and create hospitable environments for the development and evolution of life. Plate tectonic processes have been eclipsed at times in Earth’s history by episodes of massive mag ...
... energy among global reservoirs drive long-term changes in Earth’s structure and composition, cause volcanism and tectonism, and create hospitable environments for the development and evolution of life. Plate tectonic processes have been eclipsed at times in Earth’s history by episodes of massive mag ...
Plate tectonics
... boundary. Plate boundaries are commonly associated with geological events such as earthquakes and the creation of topographic features such as mountains, volcanoes, mid-ocean ridges, and oceanic trenches. The majority of the world’s active volcanoes occur along plate boundaries, with the Pacific Plat ...
... boundary. Plate boundaries are commonly associated with geological events such as earthquakes and the creation of topographic features such as mountains, volcanoes, mid-ocean ridges, and oceanic trenches. The majority of the world’s active volcanoes occur along plate boundaries, with the Pacific Plat ...
I. Lesson 1: Modeling the Earth--Motion Mock-Ups
... Please note that the “What you have learned” column of the table will be filled out at the end of the lesson. We phrase this as “What you think you know” so that we can accept all knowledge, but come back and check our thinking after research. Some possible answers for the “What you think you know” ...
... Please note that the “What you have learned” column of the table will be filled out at the end of the lesson. We phrase this as “What you think you know” so that we can accept all knowledge, but come back and check our thinking after research. Some possible answers for the “What you think you know” ...
Plate Tectonics - Yorkville CUSD 115
... You learned that the main objection to Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis was that he could not explain how or why Earth’s continents move. Scientists now understand that continents move because the asthenosphere moves underneath the rigid lithosphere. ...
... You learned that the main objection to Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis was that he could not explain how or why Earth’s continents move. Scientists now understand that continents move because the asthenosphere moves underneath the rigid lithosphere. ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... either side of the break along which rocks move might move as a result of elastic rebound. The surface of such a break along which rocks move is called a fault. Several types of faults exist. The type that forms depends on how forces were applied to the rocks. When rocks are pulled apart under tensi ...
... either side of the break along which rocks move might move as a result of elastic rebound. The surface of such a break along which rocks move is called a fault. Several types of faults exist. The type that forms depends on how forces were applied to the rocks. When rocks are pulled apart under tensi ...
ppt link
... Plate tectonics Convergent Movement Convergent plate boundaries have the following characteristics: 1. plate motion is toward plate boundary, 2. oceanic lithosphere sinks back into Earth and is recycled, 3. the volcanic arc is region of highly explosive volcanoes, like Mt. St. Helens and Mt. Rainer ...
... Plate tectonics Convergent Movement Convergent plate boundaries have the following characteristics: 1. plate motion is toward plate boundary, 2. oceanic lithosphere sinks back into Earth and is recycled, 3. the volcanic arc is region of highly explosive volcanoes, like Mt. St. Helens and Mt. Rainer ...
Earth`s Crust Name
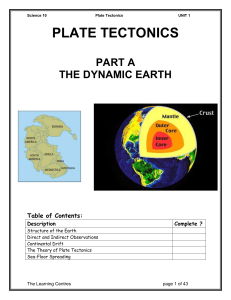
... Earth has three layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core. The crust is made of solid rocks and minerals. Beneath the crust is the mantle, which is also mostly solid rocks and minerals, but punctuated by malleable areas of semi-solid magma. At the center of the Earth is a hot, dense, mostly iron a ...
... Earth has three layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core. The crust is made of solid rocks and minerals. Beneath the crust is the mantle, which is also mostly solid rocks and minerals, but punctuated by malleable areas of semi-solid magma. At the center of the Earth is a hot, dense, mostly iron a ...
The tenn karst defines a terrain with distinctive landfonns and
... 24 drillholes, and the configurationof the marble rockheadis shown in Figure 18. It is dominatedby a north-southtrending ridge with a steepeasternface. The marble shelvesboth to the eastand west to depths greaterthan -70 mPD, with the top of the ridge closeto -20 mPD proving a relief of some 50 m. A ...
... 24 drillholes, and the configurationof the marble rockheadis shown in Figure 18. It is dominatedby a north-southtrending ridge with a steepeasternface. The marble shelvesboth to the eastand west to depths greaterthan -70 mPD, with the top of the ridge closeto -20 mPD proving a relief of some 50 m. A ...
Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Jeopardy Review
... Magma is molten rock under the Earth’s surface, what is it called when it is above the Earth’s surface? ...
... Magma is molten rock under the Earth’s surface, what is it called when it is above the Earth’s surface? ...
Unit 1 – Plate Tectonics – april 2012GLC
... Until about 100 years ago, all that was known about the structure of the Earth was that it is spherical and has a diameter of about 12 700 km at the equator. Scientists now know a lot more about the structure of our Earth. They have made their discoveries through both direct and indirect observation ...
... Until about 100 years ago, all that was known about the structure of the Earth was that it is spherical and has a diameter of about 12 700 km at the equator. Scientists now know a lot more about the structure of our Earth. They have made their discoveries through both direct and indirect observation ...
U4-T2.2-Convection and a Moving Seafloor
... could be the mechanism responsible for plate tectonics. Harry Hess was influenced by Holmes’ ideas, and suggested that deep within the asthenosphere, heated material expands, becomes less dense, rises, and pushes its way up through ridges. It then moves along the base of oceanic plates, pulling th ...
... could be the mechanism responsible for plate tectonics. Harry Hess was influenced by Holmes’ ideas, and suggested that deep within the asthenosphere, heated material expands, becomes less dense, rises, and pushes its way up through ridges. It then moves along the base of oceanic plates, pulling th ...
a collisional model for the Grenville-aged orogenic belt - Cin
... PSD and VSD. A large (6 by 2.3 km) tabular which contains the highest pressure rocks, difbody of serpentinized harzburgite, interpreted fers from the eastern uplift in many respects; as CCD arc basement or backarc-spreading– we summarize new unpublished structural related oceanic crust, was tectonic ...
... PSD and VSD. A large (6 by 2.3 km) tabular which contains the highest pressure rocks, difbody of serpentinized harzburgite, interpreted fers from the eastern uplift in many respects; as CCD arc basement or backarc-spreading– we summarize new unpublished structural related oceanic crust, was tectonic ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) Physical geology is the study of fossils and sequences of rock strata; historical geology is the study of how rocks and minerals were used in the past. B) Historical geology involves the study of rock strata, fossils, and geologic events, utilizing the geologic time scale as a reference; physical ...
... A) Physical geology is the study of fossils and sequences of rock strata; historical geology is the study of how rocks and minerals were used in the past. B) Historical geology involves the study of rock strata, fossils, and geologic events, utilizing the geologic time scale as a reference; physical ...
Using earthquakes to uncover the Earth`s inner secrets
... 1 meter-long strike-slip fault made by two blocks representing the hanging-wall and foot-wall of the fault. The surface is realistically rendered with buildings, factories, bridges and trees. When one of the two blocks is pushed, it slips, causing the rupture along a vertical plane. The stronger the ...
... 1 meter-long strike-slip fault made by two blocks representing the hanging-wall and foot-wall of the fault. The surface is realistically rendered with buildings, factories, bridges and trees. When one of the two blocks is pushed, it slips, causing the rupture along a vertical plane. The stronger the ...
FREE Sample Here
... plates move away from each other; convergent boundaries, where two plates collide; and transform boundaries, where two plates slide past each other. ...
... plates move away from each other; convergent boundaries, where two plates collide; and transform boundaries, where two plates slide past each other. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.