Low-energy charged particle measurement by MAP-PACE onboard SELENE
... from the lunar surface are mainly composed of neutrals, which are ionized by solar photons and electrons. Both ionized particles and sputtered/desorped ions are accelerated and transported by the solar wind in cycloidal motion. These ions will be observed by the in-situ low-energy ion measurement by ...
... from the lunar surface are mainly composed of neutrals, which are ionized by solar photons and electrons. Both ionized particles and sputtered/desorped ions are accelerated and transported by the solar wind in cycloidal motion. These ions will be observed by the in-situ low-energy ion measurement by ...
Introducing the fission–fusion reaction process: using a
... reflected in the theoretical calculations shown in Fig. 2, where contributions from different temperatures and neutron densities are superimposed to the observed data. We note the pronounced third peak in the abundance distribution around A = 180–200, corresponding to the group of elements around go ...
... reflected in the theoretical calculations shown in Fig. 2, where contributions from different temperatures and neutron densities are superimposed to the observed data. We note the pronounced third peak in the abundance distribution around A = 180–200, corresponding to the group of elements around go ...
Proposal: Concept of a test stand for laser accelerated
... (60 MeV protons, 5 MeV/u palladium) and they showed complete space charge- and current neutralization due to accompanying electrons. In the experiments particle numbers of more than 1013 ions per pulse and beam currents in the MA regime were observed. Another outstanding beam parameter is its excell ...
... (60 MeV protons, 5 MeV/u palladium) and they showed complete space charge- and current neutralization due to accompanying electrons. In the experiments particle numbers of more than 1013 ions per pulse and beam currents in the MA regime were observed. Another outstanding beam parameter is its excell ...
Annular Comb Gate
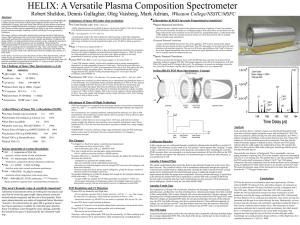
... •Long TOF & UV rejection are both possible with a helical path. -This may be the best of both worlds. ...
... •Long TOF & UV rejection are both possible with a helical path. -This may be the best of both worlds. ...
Pulsars
... by no more than two particles of opposite spin • Electrons in a White Dwarf occupy a small volume and have very well defined positions – hence from uncertainty principle, they have large momentum/energy and generate a high pressure or electron ...
... by no more than two particles of opposite spin • Electrons in a White Dwarf occupy a small volume and have very well defined positions – hence from uncertainty principle, they have large momentum/energy and generate a high pressure or electron ...
Diapositiva 1
... every 60 pc); ne/nH≈0,002 (in bubbles) to 0,02 (in continuum). A recent work of Inoue (2005) is based on UV absorption. Two stable phases are found (cold and warm) for neutral gas with T<10000 K. Cold clumps are assumed to be gravitationally stable (with Jeans radius of 10,4 pc) and in thermal equil ...
... every 60 pc); ne/nH≈0,002 (in bubbles) to 0,02 (in continuum). A recent work of Inoue (2005) is based on UV absorption. Two stable phases are found (cold and warm) for neutral gas with T<10000 K. Cold clumps are assumed to be gravitationally stable (with Jeans radius of 10,4 pc) and in thermal equil ...
Electron-ion recombination of the open-4f
... zero electron-ion collision energy. It exceeds the expectation for nonresonant radiative recombination (RR) by more than two orders of magnitude. This follows the pattern seen previously for the neighboring charge states of tungsten. The results of our present theoretical calculations, which were ca ...
... zero electron-ion collision energy. It exceeds the expectation for nonresonant radiative recombination (RR) by more than two orders of magnitude. This follows the pattern seen previously for the neighboring charge states of tungsten. The results of our present theoretical calculations, which were ca ...
Slide 1
... • A high-mass star can continue to fuse elements in its core right up to iron • As heavier elements are fused, the reactions go faster and the stage is over more quickly. (i.e.) A 20-solar-mass star will burn carbon for about 10,000 years, but its iron core lasts less than a day. ...
... • A high-mass star can continue to fuse elements in its core right up to iron • As heavier elements are fused, the reactions go faster and the stage is over more quickly. (i.e.) A 20-solar-mass star will burn carbon for about 10,000 years, but its iron core lasts less than a day. ...
Helium Production in Big Bang Weighing a Galaxy12 Nov 11/12/2010
... • When T is between 10BK and 3BK, the density drops so that – number of collisions falls & neutrons and protons are no longer in equilibrium. – Protons no longer change into neutrons. Neutrons decay into protons. ...
... • When T is between 10BK and 3BK, the density drops so that – number of collisions falls & neutrons and protons are no longer in equilibrium. – Protons no longer change into neutrons. Neutrons decay into protons. ...
Collisionless interaction of an energetic laser produced plasma C. Constantin
... Past laser experiments at the LAPD (VanZeeland et al. 2001; Gekelman et al. 2003) with low laser energies (∼1 J) and intensities (∼5 × 1010 W/cm2 ) discovered that shear Alfvén waves are radiated from the laser-plasma. These experiments also studied the evolution of the laser plasma expansion in mag ...
... Past laser experiments at the LAPD (VanZeeland et al. 2001; Gekelman et al. 2003) with low laser energies (∼1 J) and intensities (∼5 × 1010 W/cm2 ) discovered that shear Alfvén waves are radiated from the laser-plasma. These experiments also studied the evolution of the laser plasma expansion in mag ...
hessdalen a perfect “natural battery”
... “lights” – a phenomenon that has been observed by hundreds of people, including valley dwellers, tourists, curious passer-by people. These lights have never been associated to a clear identification; since the ‘80s they have been literally defined as UFOs. Following the several extemporary observati ...
... “lights” – a phenomenon that has been observed by hundreds of people, including valley dwellers, tourists, curious passer-by people. These lights have never been associated to a clear identification; since the ‘80s they have been literally defined as UFOs. Following the several extemporary observati ...
Summary
... forces come into play. This is the case in the generalized Jeans instability. The number of free electrons is less than the number of ions, because some of the electrons are captured by the grains, and are therefore immobilized by the high dust masses. The charge of the dust grain depends on the loc ...
... forces come into play. This is the case in the generalized Jeans instability. The number of free electrons is less than the number of ions, because some of the electrons are captured by the grains, and are therefore immobilized by the high dust masses. The charge of the dust grain depends on the loc ...
Two-stream instability in collisionless shocks and foreshock
... magnetosonic speed CMS = (VA2 + CS2 ) and the speed of light c. The satellite observations of Solar system shocks, e.g. by the Cluster mission [18–20] and numerous others, have shed considerable light on the shock dynamics. The Solar wind has a typical magnetic field of ≈5 nT and a plasma number den ...
... magnetosonic speed CMS = (VA2 + CS2 ) and the speed of light c. The satellite observations of Solar system shocks, e.g. by the Cluster mission [18–20] and numerous others, have shed considerable light on the shock dynamics. The Solar wind has a typical magnetic field of ≈5 nT and a plasma number den ...
Document
... factors influencing the β-decay lifetime of an unstable nucleus both β- and β+ decay are hampered in the presence of electron or positron degeneracy β- and β+ decays may occur from excited isomeric states maintained in equilibrium with ground state by radiative transitions electron-capture rat ...
... factors influencing the β-decay lifetime of an unstable nucleus both β- and β+ decay are hampered in the presence of electron or positron degeneracy β- and β+ decays may occur from excited isomeric states maintained in equilibrium with ground state by radiative transitions electron-capture rat ...
The Structure of White Dwarf and Neutron Stars∗ Abstract
... Stars in their prime, while they are on the “main sequence,” support themselves against gravitational collapse by the pressure of hot gas, the energy being released in nuclear fusion reactions at the star’s core. For most of its life, the fusion reactions are dominated by protons (hydrogen nuclei) f ...
... Stars in their prime, while they are on the “main sequence,” support themselves against gravitational collapse by the pressure of hot gas, the energy being released in nuclear fusion reactions at the star’s core. For most of its life, the fusion reactions are dominated by protons (hydrogen nuclei) f ...
Measurement of the 52Fe mass via the precise proton
... The experiment was performed at the RIBLL (Radioactive Ions Beam Line in Lanzhou) facility [14] of HIRFL (Heavy Ion Research Facility in Lanzhou). Projectile fragmentation (PF) method was used to produce a series of radioactive heavy ions. A 58Ni 25+ primary beam with an intensity of 30 enA and an e ...
... The experiment was performed at the RIBLL (Radioactive Ions Beam Line in Lanzhou) facility [14] of HIRFL (Heavy Ion Research Facility in Lanzhou). Projectile fragmentation (PF) method was used to produce a series of radioactive heavy ions. A 58Ni 25+ primary beam with an intensity of 30 enA and an e ...
Stellar Evolution
... Planetary nebula get their name because some looked like round, green planets in early telescopes. We now know that they are entirely different than the planets and are about one or more light years across (much larger than our solar system!). Many planetary nebulae will look like rings (for example ...
... Planetary nebula get their name because some looked like round, green planets in early telescopes. We now know that they are entirely different than the planets and are about one or more light years across (much larger than our solar system!). Many planetary nebulae will look like rings (for example ...
Lecture 24. Degenerate Fermi Gas (Ch. 7)
... Why can we treat this dense gas as ideal? Indeed, the Coulomb interactions between electrons at this density must be extremely strong, and in a a solid, the electrons move in the strong electric fields of the positive ions. The first objection is addressed by the Landau’s Fermi liquid theory. The an ...
... Why can we treat this dense gas as ideal? Indeed, the Coulomb interactions between electrons at this density must be extremely strong, and in a a solid, the electrons move in the strong electric fields of the positive ions. The first objection is addressed by the Landau’s Fermi liquid theory. The an ...
HEA_Pulsars_2002
... 1. Between densities of 4.3 x 10 14 kg m -3 and 2 x10 17 kg m -3, the lowest energy state is reached when nuclei are embedded in an electron and neutron fluid. 2. Above 2x1017 kg m -3, there is a continuous neutron fluid with electrons and protons as ...
... 1. Between densities of 4.3 x 10 14 kg m -3 and 2 x10 17 kg m -3, the lowest energy state is reached when nuclei are embedded in an electron and neutron fluid. 2. Above 2x1017 kg m -3, there is a continuous neutron fluid with electrons and protons as ...
Relativistic electron-positron plasmas
... remnants, Gamma Ray Bursts and jets from Active Galactic Nuclei, among other examples. Because of the low density of astrophysical plasmas, the mean free path due to Coulomb collisions is typically very large, so most shock waves in astrophysics are “collisionless,” or mediated by plasma instabiliti ...
... remnants, Gamma Ray Bursts and jets from Active Galactic Nuclei, among other examples. Because of the low density of astrophysical plasmas, the mean free path due to Coulomb collisions is typically very large, so most shock waves in astrophysics are “collisionless,” or mediated by plasma instabiliti ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 8 Notes: Nuclear
... Z C, where A is the atomic weight, Z is the atomic number, and C is the symbol for that element. This is slightly redundant, since a chemical symbol C uniquely identifies the atomic number Z. However, writing out the numbers explicitly makes it easier to keep track of the charges, and to assure ours ...
... Z C, where A is the atomic weight, Z is the atomic number, and C is the symbol for that element. This is slightly redundant, since a chemical symbol C uniquely identifies the atomic number Z. However, writing out the numbers explicitly makes it easier to keep track of the charges, and to assure ours ...
The influence of negatively charged, heavier
... compact form. A complete numerical study would thus extend our analytical results while at the same time exploring a larger parameter space. Second Phase: We also propose to extend our investigations on the stability of obliquely propagating lower hybrid waves in a plasma environment containing posi ...
... compact form. A complete numerical study would thus extend our analytical results while at the same time exploring a larger parameter space. Second Phase: We also propose to extend our investigations on the stability of obliquely propagating lower hybrid waves in a plasma environment containing posi ...
Written Transcript of this video lesson
... You know, that for fluorescent lamp to light up an important component of lamp, called "starter" should be available. The starter is simply a small lamp similar to the camera flash, it consists of two wires. When the lamp is turned on, electrical discharge happens, giving a glow appears. This glow h ...
... You know, that for fluorescent lamp to light up an important component of lamp, called "starter" should be available. The starter is simply a small lamp similar to the camera flash, it consists of two wires. When the lamp is turned on, electrical discharge happens, giving a glow appears. This glow h ...
Fusor
A fusor is a device that uses an electric field to heat ions to conditions suitable for nuclear fusion. The machine has a voltage between two metal cages inside a vacuum. Positive ions fall down this voltage drop, building up speed. If they collide in the center, they can fuse. This is a type of Inertial electrostatic confinement device.A Farnsworth–Hirsch fusor is the most common type of fusor. This design came from work by Philo T. Farnsworth (in 1964) and Robert L. Hirsch in 1967. A variant of fusor had been proposed previously by William Elmore, James L. Tuck, and Ken Watson at the Los Alamos National Laboratory though they never built the machine.Fusors have been built by various institutions. These include academic institutions such as the University of Wisconsin–Madison, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and government entities, such as the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran and the Turkish Atomic Energy Authority. Fusors have also been developed commercially, as sources for neutrons by DaimlerChrysler Aerospace and as a method for generating medical isotopes. Fusors have also become very popular for hobbyists and amateurs. A growing number of amateurs have performed nuclear fusion using simple fusor machines.