Charged-Particle Probing of X-Ray-Driven Inertial-Fusion Implosions PSFC/JA-10-29
... quantitative characterization of critical aspects of indirect-drive inertial fusion. Three types of spontaneous electric fields differing in strength by two orders of magnitude, the largest being nearly one-tenth of the Bohr field, were discovered with time-gated proton radiographic imaging and spec ...
... quantitative characterization of critical aspects of indirect-drive inertial fusion. Three types of spontaneous electric fields differing in strength by two orders of magnitude, the largest being nearly one-tenth of the Bohr field, were discovered with time-gated proton radiographic imaging and spec ...
magnetospheres of the outer planets
... of sputtering and decomposition of methane ice is given in Fig. 3. Magnetospheric ions will impact 10 or its atmosphere at high speeds even if they do not have high random velocities (that is, they do not need high temperatures) because of plasma corotation. Jupiter's magnetic field rotates with the ...
... of sputtering and decomposition of methane ice is given in Fig. 3. Magnetospheric ions will impact 10 or its atmosphere at high speeds even if they do not have high random velocities (that is, they do not need high temperatures) because of plasma corotation. Jupiter's magnetic field rotates with the ...
Nuclear Reactions
... counted twice. vAB is the relative velocity of A with respect to B, σAB is the cross section, which is a function of vAB . We must view the reaction in the center of mass frame, and the kinetic energy E is the energy of A + B measured in that frame, the relative velocity vAB is measured in that fram ...
... counted twice. vAB is the relative velocity of A with respect to B, σAB is the cross section, which is a function of vAB . We must view the reaction in the center of mass frame, and the kinetic energy E is the energy of A + B measured in that frame, the relative velocity vAB is measured in that fram ...
H3O Overtone Spectroscopy
... the chemically relevant energy levels. Unlike the fundamental bands, the overtone transitions are strictly forbidden in the harmonic limit of the potential, and therefore their non-zero oscillator strengths are derived from the anharmonic effects. Moreover due to the higher energy of the excitation ...
... the chemically relevant energy levels. Unlike the fundamental bands, the overtone transitions are strictly forbidden in the harmonic limit of the potential, and therefore their non-zero oscillator strengths are derived from the anharmonic effects. Moreover due to the higher energy of the excitation ...
Stellar Evolu1on Stars spend most of their lives on the main
... Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. Evidence -‐> 90% of stars observable from Earth are main-‐sequence stars. Stellar evolu,on during the main-‐sequence life-‐,me, and during the ...
... Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. Evidence -‐> 90% of stars observable from Earth are main-‐sequence stars. Stellar evolu,on during the main-‐sequence life-‐,me, and during the ...
Stellar Evolution
... combined with large distance implies huge energy output of GRBs, if they are emitting isotropically: E ~ 1054 erg L ~ 1051 erg/s ...
... combined with large distance implies huge energy output of GRBs, if they are emitting isotropically: E ~ 1054 erg L ~ 1051 erg/s ...
GRBItalySABER
... Dim bursts are dim because they are absorbed (do not see them) via Compton scattering! Scattered light should arrive after the prompt (unabsorbed) emission. Dense material is needed ! Dim bursts come earlier ...
... Dim bursts are dim because they are absorbed (do not see them) via Compton scattering! Scattered light should arrive after the prompt (unabsorbed) emission. Dense material is needed ! Dim bursts come earlier ...
ppt - Serbian Virtual Observatory - astronomical observatory belgrade
... •The MSE method is also very useful whenever line broadening data for a large number of lines are required, and the high precision of every particular result is not so important like e.g. for opacity calculations or plasma modeling. Moreover, in the case of more complex atoms or multiply charged ion ...
... •The MSE method is also very useful whenever line broadening data for a large number of lines are required, and the high precision of every particular result is not so important like e.g. for opacity calculations or plasma modeling. Moreover, in the case of more complex atoms or multiply charged ion ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: Life and Death of a Low Mass Star
... • In order to avoid being in the same state some of the electrons need to move faster • Is there a limit to how much you can shrink a white dwarf? ...
... • In order to avoid being in the same state some of the electrons need to move faster • Is there a limit to how much you can shrink a white dwarf? ...
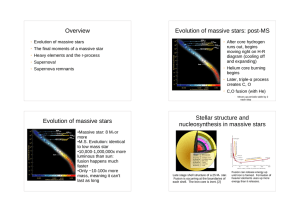
Overview Evolution of massive stars Evolution of massive stars
... Core rapidly collapses until neutron degeneracy pressure suddenly kicks in Material from outside core is falling inward; it hasn't 'gotten the message' that the core is supported. Material bounces off of core. ...
... Core rapidly collapses until neutron degeneracy pressure suddenly kicks in Material from outside core is falling inward; it hasn't 'gotten the message' that the core is supported. Material bounces off of core. ...
Pickup ions near Mars associated with escaping oxygen atoms
... vary with radial distance r differently depending whether the responsible particles are on ballistic, satellite, or escape trajectories [Chamberlin, 1978]. Neglecting satellite orbits, the escape component should dominate at radial distances of many planetary radii. In this case the neutral density ...
... vary with radial distance r differently depending whether the responsible particles are on ballistic, satellite, or escape trajectories [Chamberlin, 1978]. Neglecting satellite orbits, the escape component should dominate at radial distances of many planetary radii. In this case the neutral density ...
Low energy Electron Collision with Polar Molecules HCl and HBr in
... collision in plasma medium. Those results are shown in Fig. (3) and (4). The present results are compared with the results of Mohanan et.al., using FBA method at energy 0.1 and 0.5 eV., with screening parameter λ=0.03 a0-1 and λ=0.05 a0-1 respectively. It can be seen from the Fig. (1) to (4) that in ...
... collision in plasma medium. Those results are shown in Fig. (3) and (4). The present results are compared with the results of Mohanan et.al., using FBA method at energy 0.1 and 0.5 eV., with screening parameter λ=0.03 a0-1 and λ=0.05 a0-1 respectively. It can be seen from the Fig. (1) to (4) that in ...
Simulations of Collisionless Perpendicular Shocks in Partially
... length scale becomes about 107 c/ωpp for young SNRs with vsh ≈ 102 vA . Furthermore, in the shock rest frame, the velocity jump at the subshock with the length scale of 10 c/ωpp (x = 12700 c/ωpp ) is 3.47 and smaller than the total compression ratio, rtot = 3.77. This is because the pickup ions prod ...
... length scale becomes about 107 c/ωpp for young SNRs with vsh ≈ 102 vA . Furthermore, in the shock rest frame, the velocity jump at the subshock with the length scale of 10 c/ωpp (x = 12700 c/ωpp ) is 3.47 and smaller than the total compression ratio, rtot = 3.77. This is because the pickup ions prod ...
Inertial fusion advance towards ignition
... high-intense laser (PW-1015w) system can provide intensities 1018-21w/cm2 for each beam. Interaction of the petawatt (PW) laser with matter may accelerate charged particles (electrons, protons and heavy ions) to kinetic energy over GeV. The acceleration of high-energy charged particle beam generated ...
... high-intense laser (PW-1015w) system can provide intensities 1018-21w/cm2 for each beam. Interaction of the petawatt (PW) laser with matter may accelerate charged particles (electrons, protons and heavy ions) to kinetic energy over GeV. The acceleration of high-energy charged particle beam generated ...
E. Waxman, Weizmann Institute Lecture notes for the 2008 SLAC Summer institute:
... of characteristic amplitude B and correlation length λ. Assuming that the total deflection is small, over a propagation distance d there are (d/λ) independent deflections of δθ~λ/RL, where the Larmor radius is RL=Ep/eB. The total deflection is θ~(d/λ)1/2(λ/RL)=(λd)1/2eB/Ep, and the time delay is ΔtC ...
... of characteristic amplitude B and correlation length λ. Assuming that the total deflection is small, over a propagation distance d there are (d/λ) independent deflections of δθ~λ/RL, where the Larmor radius is RL=Ep/eB. The total deflection is θ~(d/λ)1/2(λ/RL)=(λd)1/2eB/Ep, and the time delay is ΔtC ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... nuclear fusion. 7.3.9. Apply the graph in 7.3.6. to account for the energy release in the processes of fission and fusion. 7.3.10. State that nuclear fusion is the main source of the Sun’s energy. 7.3.11. Solve problems involving fission and fusion ...
... nuclear fusion. 7.3.9. Apply the graph in 7.3.6. to account for the energy release in the processes of fission and fusion. 7.3.10. State that nuclear fusion is the main source of the Sun’s energy. 7.3.11. Solve problems involving fission and fusion ...
The energetics of relativistic magnetic reconnection: ion
... turns around, and is transferred by the motional electric field E = −u∧B present in the inflow. Drury (2012) derives the powerlaw spectrum for non-relativistic particles: dn(v)/dv ∝ v−p with v the velocity, p = (r + 2)/(r + 1), where r = nout /nin is the compression ratio that is not restricted to l ...
... turns around, and is transferred by the motional electric field E = −u∧B present in the inflow. Drury (2012) derives the powerlaw spectrum for non-relativistic particles: dn(v)/dv ∝ v−p with v the velocity, p = (r + 2)/(r + 1), where r = nout /nin is the compression ratio that is not restricted to l ...
Radio and X-ray signatures of merging neutron stars
... where sin c cos Vt cos u sin a 2 sin u cos a and V V sin a; 0; cos a ), i.e. c is the polar angle in the frame aligned with V and rotating with the neutron star. This charge density is stationary in the frame of the neutron star while in the laboratory frame it yields an additional surface curre ...
... where sin c cos Vt cos u sin a 2 sin u cos a and V V sin a; 0; cos a ), i.e. c is the polar angle in the frame aligned with V and rotating with the neutron star. This charge density is stationary in the frame of the neutron star while in the laboratory frame it yields an additional surface curre ...
Binding Energy Powerpoint
... nuclear fusion. 7.3.9. Apply the graph in 7.3.6. to account for the energy release in the processes of fission and fusion. 7.3.10. State that nuclear fusion is the main source of the Sun’s energy. 7.3.11. Solve problems involving fission and fusion ...
... nuclear fusion. 7.3.9. Apply the graph in 7.3.6. to account for the energy release in the processes of fission and fusion. 7.3.10. State that nuclear fusion is the main source of the Sun’s energy. 7.3.11. Solve problems involving fission and fusion ...
++ (?) Non-thermal heating
... SWDP & EM forces push bulk light/heavy ion plasma anti-sunward at the momentum transfer boundary region. ...
... SWDP & EM forces push bulk light/heavy ion plasma anti-sunward at the momentum transfer boundary region. ...
Generation of highly energetic electrons at
... are of special interest since a substantial part of the energy released during a flare is deposited into the energetic electrons. RHESSI observations, e.g. of the solar event on October 28, 2003, show that 1036 electrons with energies > 20 keV are typically produced per second during large flares. T ...
... are of special interest since a substantial part of the energy released during a flare is deposited into the energetic electrons. RHESSI observations, e.g. of the solar event on October 28, 2003, show that 1036 electrons with energies > 20 keV are typically produced per second during large flares. T ...
Is an RFQ a good candidate for a next
... In any accelerator design there will be tradeoffs and choices must be made. • How much physics remains to be studied by low-voltage(<1 MV), low-current DC accelerators by the time this facility will be built? Will higher current accelerators be needed? • Although DE/E=10-4 is most desirable, would ...
... In any accelerator design there will be tradeoffs and choices must be made. • How much physics remains to be studied by low-voltage(<1 MV), low-current DC accelerators by the time this facility will be built? Will higher current accelerators be needed? • Although DE/E=10-4 is most desirable, would ...
impulsive electron acceleration by gravitational waves
... We investigate the nonlinear interaction of a strong gravitational wave with the plasma during the collapse of a massive magnetized star and subsequent formation of a black hole or during the merging of neutron star binaries (the central engine). We found that under certain conditions this coupling ...
... We investigate the nonlinear interaction of a strong gravitational wave with the plasma during the collapse of a massive magnetized star and subsequent formation of a black hole or during the merging of neutron star binaries (the central engine). We found that under certain conditions this coupling ...
Isolated Attosecond Pulses from Laser
... broad range of researchers in moderate-size laser labs. From the radiation physics perspective, an advantage of lasers is their ability to generate unprecedentedly short pulses of extreme ultraviolet (XUV) and x-ray radiation [2–5]. High-order harmonic generation in gas jets [6–8] when driven by wav ...
... broad range of researchers in moderate-size laser labs. From the radiation physics perspective, an advantage of lasers is their ability to generate unprecedentedly short pulses of extreme ultraviolet (XUV) and x-ray radiation [2–5]. High-order harmonic generation in gas jets [6–8] when driven by wav ...
Fusor
A fusor is a device that uses an electric field to heat ions to conditions suitable for nuclear fusion. The machine has a voltage between two metal cages inside a vacuum. Positive ions fall down this voltage drop, building up speed. If they collide in the center, they can fuse. This is a type of Inertial electrostatic confinement device.A Farnsworth–Hirsch fusor is the most common type of fusor. This design came from work by Philo T. Farnsworth (in 1964) and Robert L. Hirsch in 1967. A variant of fusor had been proposed previously by William Elmore, James L. Tuck, and Ken Watson at the Los Alamos National Laboratory though they never built the machine.Fusors have been built by various institutions. These include academic institutions such as the University of Wisconsin–Madison, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and government entities, such as the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran and the Turkish Atomic Energy Authority. Fusors have also been developed commercially, as sources for neutrons by DaimlerChrysler Aerospace and as a method for generating medical isotopes. Fusors have also become very popular for hobbyists and amateurs. A growing number of amateurs have performed nuclear fusion using simple fusor machines.