Chapter 15
... • NORMAL - one side of a fault slips down relative to another • REVERSE (& Thrust) - one side of a fault is driven up and over the other • STRIKE-SLIP – occur where plates meet evenly and slip past each other horizontally. (The angle at which a fault cuts through the earth is referred to as the stri ...
... • NORMAL - one side of a fault slips down relative to another • REVERSE (& Thrust) - one side of a fault is driven up and over the other • STRIKE-SLIP – occur where plates meet evenly and slip past each other horizontally. (The angle at which a fault cuts through the earth is referred to as the stri ...
The Nature of Tectonic Plates
... today like he did in 1492, his sailors would more likely mutiny because the trip would be longer today by about 10 meters. Running down the center of the Atlantic Ocean is a long, volcanic, undersea mountain range known as the Mid Atlantic Ridge. This ridge is a divergent plate boundary; that is, th ...
... today like he did in 1492, his sailors would more likely mutiny because the trip would be longer today by about 10 meters. Running down the center of the Atlantic Ocean is a long, volcanic, undersea mountain range known as the Mid Atlantic Ridge. This ridge is a divergent plate boundary; that is, th ...
6-Plate Tectonics
... ridge provides an additional force (called "ridge push") to propel and maintain plate movement. • Most scientists now favor the notion that forces associated with subduction are more important than seafloor spreading. ...
... ridge provides an additional force (called "ridge push") to propel and maintain plate movement. • Most scientists now favor the notion that forces associated with subduction are more important than seafloor spreading. ...
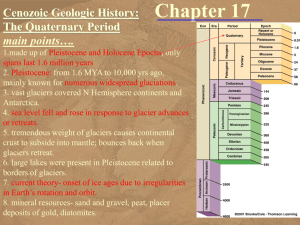
Chapter 17 - Cenozoic - Quaternary
... – been able to correlate – these detailed climatic changes – with corresponding changes recorded ...
... – been able to correlate – these detailed climatic changes – with corresponding changes recorded ...
SwissRe - Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences
... For Large Earthquakes, Seismic Waves Circle the Earth for Months to Years, Making it Ring Like a Gong. ...
... For Large Earthquakes, Seismic Waves Circle the Earth for Months to Years, Making it Ring Like a Gong. ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... b. When one plate dives under another plate, earthquakes can result and can form. ...
... b. When one plate dives under another plate, earthquakes can result and can form. ...
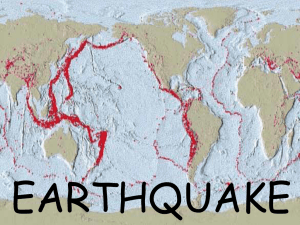
Faults are the boundaries of the tectonic plates
... researched the internet to find the necessary background for our discussions. Since my students don’t have a textbook for reference they are really reliant on studying key terms. The students tend to struggle with using key terms in their explanations and need extra practice to help with the unders ...
... researched the internet to find the necessary background for our discussions. Since my students don’t have a textbook for reference they are really reliant on studying key terms. The students tend to struggle with using key terms in their explanations and need extra practice to help with the unders ...
chpt 7Plate Tectonics
... transform boundaries are result where two plates slide past each other They move in opposite direction and usually earthquakes are associated with transform boundaries San Andreas fault is an example ...
... transform boundaries are result where two plates slide past each other They move in opposite direction and usually earthquakes are associated with transform boundaries San Andreas fault is an example ...
A Q A G E O G R A P H Y
... where subduction of oceanic crust draws two continental masses together, a collision margin may develop. As continents have similar density and thus buoyancy, they will not be subducted. Instead they collide with each other. Volcanic associated with earlier subduction and sediments scraped off the v ...
... where subduction of oceanic crust draws two continental masses together, a collision margin may develop. As continents have similar density and thus buoyancy, they will not be subducted. Instead they collide with each other. Volcanic associated with earlier subduction and sediments scraped off the v ...
Tsunamis - LsSharks
... earthquake below Earth’s surface. A tsunami can also be caused if an underwater volcano erupts. These are called submarine volcanos. As the lava is pushed up, water is displaced. This causes big waves. Tsunamis can also happen due to an underwater landslide. People living on the coast experience tsu ...
... earthquake below Earth’s surface. A tsunami can also be caused if an underwater volcano erupts. These are called submarine volcanos. As the lava is pushed up, water is displaced. This causes big waves. Tsunamis can also happen due to an underwater landslide. People living on the coast experience tsu ...
File - Science with Mrs. Persico
... Hydrothermal vents are deep, dark locations on the sea floor which release high temperature fluids and chemicals into the ocean water above. They are usually found in areas of volcanic activity. Even though we might consider this to be a harsh environment, hydrothermal vents are abundant with life. ...
... Hydrothermal vents are deep, dark locations on the sea floor which release high temperature fluids and chemicals into the ocean water above. They are usually found in areas of volcanic activity. Even though we might consider this to be a harsh environment, hydrothermal vents are abundant with life. ...
01 - Mayfield City Schools
... 28. What does the speed of a seismic wave depend on? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. Which are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected? _________________________________________________ ...
... 28. What does the speed of a seismic wave depend on? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. Which are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected? _________________________________________________ ...
Document
... 28. What does the speed of a seismic wave depend on? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. Which are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected? _________________________________________________ ...
... 28. What does the speed of a seismic wave depend on? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. Which are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected? _________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 8 Section 1 Guided Reading
... 28. What does the speed of a seismic wave depend on? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. Which are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected? _________________________________________________ ...
... 28. What does the speed of a seismic wave depend on? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. Which are always the first waves of an earthquake to be detected? _________________________________________________ ...
Evolution of continents, cratons and supercontinents: building the
... between crustal evolution and life evolution are emerging as an important theme in understanding the history of the Earth. The formation of cratons through building cold, rigid and thick rafts beneath ancient continents, and their subsequent erosion are also topics of wide interest. The episodic ama ...
... between crustal evolution and life evolution are emerging as an important theme in understanding the history of the Earth. The formation of cratons through building cold, rigid and thick rafts beneath ancient continents, and their subsequent erosion are also topics of wide interest. The episodic ama ...
Plate Tech WebQuest
... 1. List one types of supporting evidence that Alfred Wegener noted as theories to there being one giant supercontinent. ...
... 1. List one types of supporting evidence that Alfred Wegener noted as theories to there being one giant supercontinent. ...
Plate Tectonics Question Bank
... (1) trenches created by the subduction of the Pacific Plate (2) rift valleys created by seafloor spreading of the Pacific Plate (3) secondary plates created by volcanic activity within the Pacific Plate (4) mid-ocean ridges created by faulting below the Pacific Plate The Himalayan Mountains are loca ...
... (1) trenches created by the subduction of the Pacific Plate (2) rift valleys created by seafloor spreading of the Pacific Plate (3) secondary plates created by volcanic activity within the Pacific Plate (4) mid-ocean ridges created by faulting below the Pacific Plate The Himalayan Mountains are loca ...
The Earth
... (the rock cycle). b. Students know how to identify common rock-forming minerals (including quartz, calcite, feldspar, mica, and hornblende) and ore minerals by using a table of diagnostic of properties. 5.0 Waves, wind, water, and ice shape and reshape Earth’s land surface. As a basis for understand ...
... (the rock cycle). b. Students know how to identify common rock-forming minerals (including quartz, calcite, feldspar, mica, and hornblende) and ore minerals by using a table of diagnostic of properties. 5.0 Waves, wind, water, and ice shape and reshape Earth’s land surface. As a basis for understand ...
graham cracker plate tectonics _17
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of 7 major plates and numerous smaller plates. These plates move on the top of the hot plastic upper mantle known as the asthenosphere. This theory also says that most of these plates are in motion, creating a variety of in ...
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of 7 major plates and numerous smaller plates. These plates move on the top of the hot plastic upper mantle known as the asthenosphere. This theory also says that most of these plates are in motion, creating a variety of in ...
Plate Tectonics - Londonderry School District
... Evidence for Plate Tectonics First evidence used for Continental Drift Theory • Continents fit together • Fossil distribution • Common rock formations: same age ...
... Evidence for Plate Tectonics First evidence used for Continental Drift Theory • Continents fit together • Fossil distribution • Common rock formations: same age ...
Isostasy and Rock Density
... (represented by pine blocks) and oceanic crust (represented by oak blocks) and how it affects the way they float on the denser astenosphere (represented by water). The process of reaching an equilibrium level as a function of relative densities is called isostasy. Isostasy literally translates from ...
... (represented by pine blocks) and oceanic crust (represented by oak blocks) and how it affects the way they float on the denser astenosphere (represented by water). The process of reaching an equilibrium level as a function of relative densities is called isostasy. Isostasy literally translates from ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.