Topic 12 Earth`s Dynamic Crust and Interior
... Topic 12 Earth’s Dynamic Crust and Interior Lithosphere: Crust: Small Scale Crustal Changes Law of Original Horizontality: What are three ways that rock layers are changed? ...
... Topic 12 Earth’s Dynamic Crust and Interior Lithosphere: Crust: Small Scale Crustal Changes Law of Original Horizontality: What are three ways that rock layers are changed? ...
Earth Science Course: Aims 1.) Stud
... along with description, altitude, and weather associated ...
... along with description, altitude, and weather associated ...
Continental Drift
... The Appalachian Mountains in North America and the Caledonian Mountains in Scotland are of the same age, made of the same rock type, and have the same appearance. Wegener took this to mean they were in fact the same mountain range, but that they had become separated by the Atlantic Ocean in the las ...
... The Appalachian Mountains in North America and the Caledonian Mountains in Scotland are of the same age, made of the same rock type, and have the same appearance. Wegener took this to mean they were in fact the same mountain range, but that they had become separated by the Atlantic Ocean in the las ...
Physical Geology Lab
... 2. How does heat inside the Earth power our planet‟s dynamic processes (plate movement, earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, and formation of the atmosphere, weather and climate)? How is this heat essential for life on Earth? 3. Why are we not able to make direct observations of the Earth‟s co ...
... 2. How does heat inside the Earth power our planet‟s dynamic processes (plate movement, earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, and formation of the atmosphere, weather and climate)? How is this heat essential for life on Earth? 3. Why are we not able to make direct observations of the Earth‟s co ...
plate tectonics
... AS DEPTH INCREASES (closer to center of earth) As depth INCREASES, Temperature INCREASES As depth INCREASES, Pressure INCREASES As depth INCREASES, Density INCREASES TEMPERATURE INCREASES PRESSURE INCREASES DENSITY INCREASES ...
... AS DEPTH INCREASES (closer to center of earth) As depth INCREASES, Temperature INCREASES As depth INCREASES, Pressure INCREASES As depth INCREASES, Density INCREASES TEMPERATURE INCREASES PRESSURE INCREASES DENSITY INCREASES ...
Chapter 19
... global ocean the body of salt water that covers nearly three-fourths of Earth’s surface • The global ocean contains more than 97% of all of the water on Earth. • The global ocean is divided into five major oceans. These major oceans are the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Oceans. sea ...
... global ocean the body of salt water that covers nearly three-fourths of Earth’s surface • The global ocean contains more than 97% of all of the water on Earth. • The global ocean is divided into five major oceans. These major oceans are the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Oceans. sea ...
Earth`s Changing Face
... forming and being shaped. Sometimes these transformations are quite small, and at other times they are extraordinary. While many of the changes to Earth’s landforms are brought about by natural forces, others are caused by people. Earth’s changing landforms have an effect on Earth’s environment and ...
... forming and being shaped. Sometimes these transformations are quite small, and at other times they are extraordinary. While many of the changes to Earth’s landforms are brought about by natural forces, others are caused by people. Earth’s changing landforms have an effect on Earth’s environment and ...
Chapter 6 - Cloudfront.net
... • What is the difference between oceanic crust and continental crust? – Oceanic crust is denser (heavier) than continental crust – Ocean water is on top of the oceanic crust – Oceanic crust is made of basalt – Continental crust is made of granite ...
... • What is the difference between oceanic crust and continental crust? – Oceanic crust is denser (heavier) than continental crust – Ocean water is on top of the oceanic crust – Oceanic crust is made of basalt – Continental crust is made of granite ...
Flash Cards - tclauset.org
... Q3-2: Draw a simplified diagram of Earth’s interior: a.) Indicate where on the diagram you would find aluminum & silicon & iron. b.) Using the following density values (Al-2.7, Si2.3, Fe-7.9, H2O-1.0) to explain why water floats on the earth’s surface. c.) How does the density of the mantle compare ...
... Q3-2: Draw a simplified diagram of Earth’s interior: a.) Indicate where on the diagram you would find aluminum & silicon & iron. b.) Using the following density values (Al-2.7, Si2.3, Fe-7.9, H2O-1.0) to explain why water floats on the earth’s surface. c.) How does the density of the mantle compare ...
Plate Tectonics
... Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus • land-dwelling dinosaurs Fossils of these organisms are found on many different continents separated by great oceans!! How could that be possible? ...
... Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus • land-dwelling dinosaurs Fossils of these organisms are found on many different continents separated by great oceans!! How could that be possible? ...
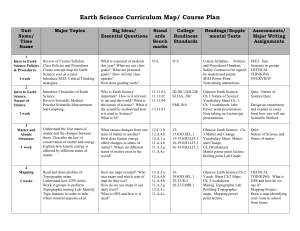
Earth Science Curriculum Map 11-12
... theories of the fate of the Universe. Analyze different types of galaxies and solar systems and how scientists study them in order to better understand the universe. Understand how Cosmic ...
... theories of the fate of the Universe. Analyze different types of galaxies and solar systems and how scientists study them in order to better understand the universe. Understand how Cosmic ...
Chemistry C1a file
... The group number is the same as the number of electrons in the outermost shell. Eg all elements in group 1 have 1 electron in their outer shell. Elements in the same group have similar what? Chemical properties. They all behave in a similar way. What are the elements in group 0 known as? The n ...
... The group number is the same as the number of electrons in the outermost shell. Eg all elements in group 1 have 1 electron in their outer shell. Elements in the same group have similar what? Chemical properties. They all behave in a similar way. What are the elements in group 0 known as? The n ...
CHAPTER 14
... 14-1 What are the earth’s major geological processes and hazards? A. The earth is made up of a core, mantle, and crust and is constantly changing as a result of processes taking place on and below its surface. Geology is the study of dynamic processes occurring on the earth’s surface and in its inte ...
... 14-1 What are the earth’s major geological processes and hazards? A. The earth is made up of a core, mantle, and crust and is constantly changing as a result of processes taking place on and below its surface. Geology is the study of dynamic processes occurring on the earth’s surface and in its inte ...
Geology of Planet Earth
... 1. What is the most likely geologic hazard in your part of the country? Is there more than one, if so what are they? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries and where does each most commonly occur on the Earth? Circle and example location of each on the map. ...
... 1. What is the most likely geologic hazard in your part of the country? Is there more than one, if so what are they? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries and where does each most commonly occur on the Earth? Circle and example location of each on the map. ...
Warm-Up # 56 Seafloor spreading - East Hanover Township School
... B. Evidence that tectonic plates are being created at divergent boundaries is that younger _______ rocks are found at the mid-ocean ridges and older ______________rocks are found further away. ...
... B. Evidence that tectonic plates are being created at divergent boundaries is that younger _______ rocks are found at the mid-ocean ridges and older ______________rocks are found further away. ...
Questions
... Plate tectonics theory suggests that Earth’s surface is not a static arrangement of continents and ocean, but a dynamic mosaic of jostling segments called lithospheric plates. The plates have collided, moved apart, and slipped past one another since Earth’s crust first solidified. The confirmation o ...
... Plate tectonics theory suggests that Earth’s surface is not a static arrangement of continents and ocean, but a dynamic mosaic of jostling segments called lithospheric plates. The plates have collided, moved apart, and slipped past one another since Earth’s crust first solidified. The confirmation o ...
Lecture 1a Plate Tectonics
... (supercontinent) cycle • J. Tuzo Wilson (“Did the Atlantic close and then re-open?”, Nature, 1966, pp. 676681) suggested that plate tectonics allow supercontinents to rift apart and reform over and over on a roughly half billion year cycle • Evidence for this: evidence of pre-Pangea supercontinents, ...
... (supercontinent) cycle • J. Tuzo Wilson (“Did the Atlantic close and then re-open?”, Nature, 1966, pp. 676681) suggested that plate tectonics allow supercontinents to rift apart and reform over and over on a roughly half billion year cycle • Evidence for this: evidence of pre-Pangea supercontinents, ...
I. Marine Biology Then and Now
... oceans are a vast resource that benefits mankind. They will also comprehend how marine organisms can cause problems for humans directly or indirectly. The course also includes how marine environments determine the very nature of our planet. Students will acquire the knowledge that gives them the und ...
... oceans are a vast resource that benefits mankind. They will also comprehend how marine organisms can cause problems for humans directly or indirectly. The course also includes how marine environments determine the very nature of our planet. Students will acquire the knowledge that gives them the und ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide TEST ON LESSON 1 Use your textbook
... Continental drift is the theory that the continents drifted apart over millions of years to their present location. Plate tectonics describes the Earth’s crust as broken into pieces (plates), and that each plate is made of material from a layer below the crust called the mantle. The plates slide on ...
... Continental drift is the theory that the continents drifted apart over millions of years to their present location. Plate tectonics describes the Earth’s crust as broken into pieces (plates), and that each plate is made of material from a layer below the crust called the mantle. The plates slide on ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.