1 - Portal UniMAP
... 9. The armature of a 120V dc motor has a resistance of 1.5 Ω and takes 4A when operating at full load. Calculate: a) The counter EMF produced by the armature. b) The power developed by the armature. c) Calculate the speed of the motor if the armature winding of the four poles dc motor has 360 conduc ...
... 9. The armature of a 120V dc motor has a resistance of 1.5 Ω and takes 4A when operating at full load. Calculate: a) The counter EMF produced by the armature. b) The power developed by the armature. c) Calculate the speed of the motor if the armature winding of the four poles dc motor has 360 conduc ...
Understanding the Basics of Electrical Systems
... System (power supply) grounding is the intentional connection of one terminal of a power supply to the earth for the purpose of stabilizing the phase-to-earth voltage during normal operation [250.4(A)(1)]. (A) AC Circuits of Less than 50V. Alternating-current circuits supplied from a transformer tha ...
... System (power supply) grounding is the intentional connection of one terminal of a power supply to the earth for the purpose of stabilizing the phase-to-earth voltage during normal operation [250.4(A)(1)]. (A) AC Circuits of Less than 50V. Alternating-current circuits supplied from a transformer tha ...
Chapter 1
... are used by the computer to determine the best shift points. 8. Conventional automatic transmissions waste a good amount of the torque produced by the engine through the heat generated by the moving fluid. Also, because gear changes were dependent upon the movement of fluid, up and down shifts were ...
... are used by the computer to determine the best shift points. 8. Conventional automatic transmissions waste a good amount of the torque produced by the engine through the heat generated by the moving fluid. Also, because gear changes were dependent upon the movement of fluid, up and down shifts were ...
Document
... • Add a 0.5 volt offset so that the square wave goes from 0 volts to 1 volt 24 May 2017 ...
... • Add a 0.5 volt offset so that the square wave goes from 0 volts to 1 volt 24 May 2017 ...
The Sensitivity of the Input Impedance Parameters of Track Circuits
... siding in Orlova. The results are used to design a predictor of occupancy of a track section. In particular, we were interested in the frequencies of 75 and 275 Hz for this purpose. Many parameter values of track substructures have already been solved in different works in literature. At first, we h ...
... siding in Orlova. The results are used to design a predictor of occupancy of a track section. In particular, we were interested in the frequencies of 75 and 275 Hz for this purpose. Many parameter values of track substructures have already been solved in different works in literature. At first, we h ...
document
... Motor circuits include motor control devices such as motor starters and contactors, together with overcurrent protection components such as overload relays, circuit breakers, and fuses are often assembled into motor control panels and motor control centers as well as individual enclosures. Motor con ...
... Motor circuits include motor control devices such as motor starters and contactors, together with overcurrent protection components such as overload relays, circuit breakers, and fuses are often assembled into motor control panels and motor control centers as well as individual enclosures. Motor con ...
NEMA Evaluating Water damaged Electrical Equipment
... Motor circuits include motor control devices such as motor starters and contactors, together with overcurrent protection components such as overload relays, circuit breakers, and fuses are often assembled into motor control panels and motor control centers as well as individual enclosures. Motor con ...
... Motor circuits include motor control devices such as motor starters and contactors, together with overcurrent protection components such as overload relays, circuit breakers, and fuses are often assembled into motor control panels and motor control centers as well as individual enclosures. Motor con ...
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS reading
... They do not let electrons flow very easily from one atom to another. Insulators are materials whose atoms have tightly bound electrons. These electrons are not free to roam around and be shared by neighboring atoms. Some common insulator materials are glass, plastic, rubber, air, and wood. ...
... They do not let electrons flow very easily from one atom to another. Insulators are materials whose atoms have tightly bound electrons. These electrons are not free to roam around and be shared by neighboring atoms. Some common insulator materials are glass, plastic, rubber, air, and wood. ...
Photovoltaic Protection (Solar Systems)
... in parallel with another electrical power source such as being connected to an electrical utility system. An interactive system may also supply electric power to the production or distribution network. Hybrid systems include other power sources, such as wind and hydroelectric generation, in addition ...
... in parallel with another electrical power source such as being connected to an electrical utility system. An interactive system may also supply electric power to the production or distribution network. Hybrid systems include other power sources, such as wind and hydroelectric generation, in addition ...
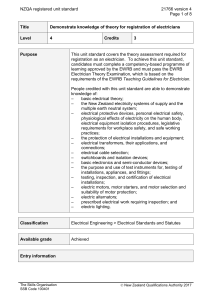
21766 Demonstrate knowledge of theory for registration of
... Certificate in Electrical Engineering Theory and Practice (Trade) (Level 4) [Ref: 2388]; or demonstrate equivalent knowledge and skills. Before being assessed against this unit standard all candidates must have achieved unit standard 29484, Demonstrate knowledge of theory and practice for electrical ...
... Certificate in Electrical Engineering Theory and Practice (Trade) (Level 4) [Ref: 2388]; or demonstrate equivalent knowledge and skills. Before being assessed against this unit standard all candidates must have achieved unit standard 29484, Demonstrate knowledge of theory and practice for electrical ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... Coulomb’s Law and Charge Polarization The Force Between The Two Charged Particles Varies Directly As The Product Of Their Charges And Inversely As The Square Of The Separation Distance Coulomb (C) – is the unit of charge A charge of 1 C is the charge on 6.25 billion billion electrons (6,250,000 ...
... Coulomb’s Law and Charge Polarization The Force Between The Two Charged Particles Varies Directly As The Product Of Their Charges And Inversely As The Square Of The Separation Distance Coulomb (C) – is the unit of charge A charge of 1 C is the charge on 6.25 billion billion electrons (6,250,000 ...
A Unity Gain Fully-Differential 10bit and 40MSps Sample-And
... speed signals. Specifically, when high speed signals are being sampled, the input signal changes rapidly, resulting in small amounts of aperture uncertainty causing the held voltage to be significantly different from the ideal held voltage[2]. There are also other factors such as dynamic range, line ...
... speed signals. Specifically, when high speed signals are being sampled, the input signal changes rapidly, resulting in small amounts of aperture uncertainty causing the held voltage to be significantly different from the ideal held voltage[2]. There are also other factors such as dynamic range, line ...
RAL Template
... the Capacitance would be identical and energy would be transferred with an alternating current between them and at a resonant frequency. Inductance reactance XL = Capacitive reactance XC ωL = 1/ωC ω = 2π f Resonant Frequency f = 1/(2π√LC ) ...
... the Capacitance would be identical and energy would be transferred with an alternating current between them and at a resonant frequency. Inductance reactance XL = Capacitive reactance XC ωL = 1/ωC ω = 2π f Resonant Frequency f = 1/(2π√LC ) ...
ueeneee003b
... RPL recognises any prior knowledge and experience and measures it against the qualification in which you are or wish to be enrolled. The process: complete the Self Assessment checklist included in the RPL Assessment Tool with as much information as you can. Please fill in the “grey” shaded areas. ...
... RPL recognises any prior knowledge and experience and measures it against the qualification in which you are or wish to be enrolled. The process: complete the Self Assessment checklist included in the RPL Assessment Tool with as much information as you can. Please fill in the “grey” shaded areas. ...
2156 Leader`s Guide
... • Shock is what happens to us when electric current passes through our bodies. Shocks can produce quite a range of effects, from mild tingling to severe burns, nerve damage, cardiac arrest and death. • The two types of electrical current are alternating current (called AC) and direct current (calle ...
... • Shock is what happens to us when electric current passes through our bodies. Shocks can produce quite a range of effects, from mild tingling to severe burns, nerve damage, cardiac arrest and death. • The two types of electrical current are alternating current (called AC) and direct current (calle ...
Chapter 1 - Elements of Electrical Circuits: The Nuts and Bolts of
... The battery will push electric charges around the wire loop, resulting in a flow of positive charges from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery. This flow of electric charge is called an electrical current. (This is called the conventional current flow, but in reality in meta ...
... The battery will push electric charges around the wire loop, resulting in a flow of positive charges from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery. This flow of electric charge is called an electrical current. (This is called the conventional current flow, but in reality in meta ...
Electrical Systems Existing Conditions and Building Load Summary
... The electrical system of the Bahen Centre for Information Technology should be designed so that it is a reliable system. A reliable power system is vital to a building that is mainly for computer use where important electronic data are handled. Any type of power system failure may cause the loss of ...
... The electrical system of the Bahen Centre for Information Technology should be designed so that it is a reliable system. A reliable power system is vital to a building that is mainly for computer use where important electronic data are handled. Any type of power system failure may cause the loss of ...
and p(t) - Binus Repository
... Fig. 11.1 (and 11.2) Instantaneous power example. Fig. 11.3 The average value P of a periodic function p(t) is … Fig. 11.5 Curves of v(t), i(t), and p(t) are plotted as functions of … Fig. 11.8 A simple loop circuit used to illustrate … Fig. 11.14 A circuit in which we seek the average power deliver ...
... Fig. 11.1 (and 11.2) Instantaneous power example. Fig. 11.3 The average value P of a periodic function p(t) is … Fig. 11.5 Curves of v(t), i(t), and p(t) are plotted as functions of … Fig. 11.8 A simple loop circuit used to illustrate … Fig. 11.14 A circuit in which we seek the average power deliver ...
PDF Version(81KB)
... Three-phase converter circuit and brake circuit. Short-circuit protection (by shunt resistance). Functions Control power supply under-voltage (UV) protection: FO output on N-side protection. Analog temperature voltage output (VOT). Environmental Awareness The DIPIPM+ series are compliant with the Re ...
... Three-phase converter circuit and brake circuit. Short-circuit protection (by shunt resistance). Functions Control power supply under-voltage (UV) protection: FO output on N-side protection. Analog temperature voltage output (VOT). Environmental Awareness The DIPIPM+ series are compliant with the Re ...
Electrical engineering

Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. This field first became an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electric power distribution and use. Subsequently, broadcasting and recording media made electronics part of daily life. The invention of the transistor, and later the integrated circuit, brought down the cost of electronics to the point they can be used in almost any household object.Electrical engineering has now subdivided into a wide range of subfields including electronics, digital computers, power engineering, telecommunications, control systems, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, and microelectronics. The subject of electronic engineering is often treated as its own subfield but it intersects with all the other subfields, including the power electronics of power engineering.Electrical engineers typically hold a degree in electrical engineering or electronic engineering. Practicing engineers may have professional certification and be members of a professional body. Such bodies include the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Institution of Engineering and Technology (professional society) (IET).Electrical engineers work in a very wide range of industries and the skills required are likewise variable. These range from basic circuit theory to the management skills required of a project manager. The tools and equipment that an individual engineer may need are similarly variable, ranging from a simple voltmeter to a top end analyzer to sophisticated design and manufacturing software.