t2 images part 1
... into a disk with the majority of the material in the center Once the interior of the Sun was hot enough, it became a T Tauri star, and as it contracted further the ...
... into a disk with the majority of the material in the center Once the interior of the Sun was hot enough, it became a T Tauri star, and as it contracted further the ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... γ has no mass ( ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... γ has no mass ( ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
Explorations of the Universe
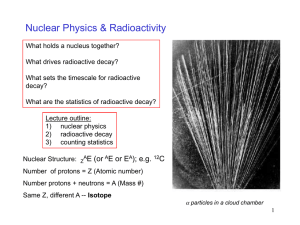
... – Protons repel (electromagnetism) but strong nuclear force is stronger, holds it together – Too many protons: unstable (radioactive) ...
... – Protons repel (electromagnetism) but strong nuclear force is stronger, holds it together – Too many protons: unstable (radioactive) ...
Star Arsenic, Star Selenium The Big Bang produced lots of hydrogen
... stars can synthesize heavier elements, those with more protons in their nuclei, up to iron by nuclear fusion—the process in which atomic nuclei fuse and release lots of energy. Most of the elements heavier than iron are made by a process called neutron-capture nucleosynthesis. "Although neutrons hav ...
... stars can synthesize heavier elements, those with more protons in their nuclei, up to iron by nuclear fusion—the process in which atomic nuclei fuse and release lots of energy. Most of the elements heavier than iron are made by a process called neutron-capture nucleosynthesis. "Although neutrons hav ...
ASTRONOMY 120
... If a star is massive enough, it will be able to fuse nuclei into iron, thus building up a core of iron. But due to the high amount of repulsion iron atoms experience, it requires more energy to fuse iron with something else than the reaction releases. This actually decreases the amount of energy av ...
... If a star is massive enough, it will be able to fuse nuclei into iron, thus building up a core of iron. But due to the high amount of repulsion iron atoms experience, it requires more energy to fuse iron with something else than the reaction releases. This actually decreases the amount of energy av ...
Earth Science 25.2B : Stellar Evolution
... Earth Science 25.2B: Stellar Evolution As a star contracts into a white dwarf, it’s surface becomes very hot, sometimes exceeding 25,000 K. Even so, without a source of energy, it can become cooler and dimmer. The sun began as a nebula, will spend much of it’s life as a main-sequence star, wi ...
... Earth Science 25.2B: Stellar Evolution As a star contracts into a white dwarf, it’s surface becomes very hot, sometimes exceeding 25,000 K. Even so, without a source of energy, it can become cooler and dimmer. The sun began as a nebula, will spend much of it’s life as a main-sequence star, wi ...
"Cosmic furnaces"()
... state’: the deuteron (the nucleus of the isotope of hydrogen 2H). While this would have happened during the Big Bang when there were free neutrons around, all those that did not pair up with protons will have undergone beta decay long ago. Free neutrons cannot survive longer than a few minutes befor ...
... state’: the deuteron (the nucleus of the isotope of hydrogen 2H). While this would have happened during the Big Bang when there were free neutrons around, all those that did not pair up with protons will have undergone beta decay long ago. Free neutrons cannot survive longer than a few minutes befor ...
Document
... EB = strong nuclear force binding -surface tension binding + spin pairing +shell binding-Coulomb repulsion 1) strong nuclear force -- the more nucleons the better 2) surface tension -- the less surface/volume the better (U better than He) 3) spin pairing -- neutrons and protons have + and - spins, p ...
... EB = strong nuclear force binding -surface tension binding + spin pairing +shell binding-Coulomb repulsion 1) strong nuclear force -- the more nucleons the better 2) surface tension -- the less surface/volume the better (U better than He) 3) spin pairing -- neutrons and protons have + and - spins, p ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... because the force of gravity pulls the matter inward. Some white dwarfs will just cool and die, they are then called black dwarfs ...
... because the force of gravity pulls the matter inward. Some white dwarfs will just cool and die, they are then called black dwarfs ...
MBuzaTalk2
... Normal stars are fighting with Hydrodynamic pressure, and radiation pressure. But in by-products we see both electron and neutron degeneracy’s, along with neutrino pressures. Where density is the dominating factor. Mainly, White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black holes. ...
... Normal stars are fighting with Hydrodynamic pressure, and radiation pressure. But in by-products we see both electron and neutron degeneracy’s, along with neutrino pressures. Where density is the dominating factor. Mainly, White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black holes. ...
Lecture 28 Formation of chemical elements
... that produces our sun’s energy and it is occurring in the vast majority of stars we can see. How much energy is released in hydrogen nuclear burning? We use E = Δmc2 to calculate nuclear mass of He 42He: rest mass of n: rest mass of p: C (speed of light): ...
... that produces our sun’s energy and it is occurring in the vast majority of stars we can see. How much energy is released in hydrogen nuclear burning? We use E = Δmc2 to calculate nuclear mass of He 42He: rest mass of n: rest mass of p: C (speed of light): ...
Basic properties of atomic nuclei
... When the total number of nucleons A is even, j is an integer; when it is odd, j is a half-integer. All nuclides for which both Z and N are even have 1 = 0, which suggests that pairing of particles with opposite spin components may be an important consideration in nuclear structure. nuclear magneton ...
... When the total number of nucleons A is even, j is an integer; when it is odd, j is a half-integer. All nuclides for which both Z and N are even have 1 = 0, which suggests that pairing of particles with opposite spin components may be an important consideration in nuclear structure. nuclear magneton ...
Stellar evolution - Chandra X
... various evolutionary stages, and what Chandra has learned about them. X-ray data reveal extreme or violent conditions where gas has been heated to very high temperatures or particles have been accelerated to extremely high energies. These conditions can exist near collapsed objects such as white dwa ...
... various evolutionary stages, and what Chandra has learned about them. X-ray data reveal extreme or violent conditions where gas has been heated to very high temperatures or particles have been accelerated to extremely high energies. These conditions can exist near collapsed objects such as white dwa ...
mass per nucleon
... shell Hydrogen burning (red giant) core Helium burning (Helium Flash) shell Helium burning (double-shell burning red giant) planetary nebula white dwarf ...
... shell Hydrogen burning (red giant) core Helium burning (Helium Flash) shell Helium burning (double-shell burning red giant) planetary nebula white dwarf ...
Chapter 7 Neutron Stars - Ira-Inaf
... to support the star. Thus a more dramatic collapse must ensue in which higher densities are achieved: much more gravitational work is done on the collapsing matter, heating it. This energy powers the subsequent shock wave, neutrino emission, and mantle ejection of a supernova, which we have already ...
... to support the star. Thus a more dramatic collapse must ensue in which higher densities are achieved: much more gravitational work is done on the collapsing matter, heating it. This energy powers the subsequent shock wave, neutrino emission, and mantle ejection of a supernova, which we have already ...
Probing the Edge of the Solar System: Formation of
... •Protostar: the clump formed from dense and cold nebula under gravitational contraction •The protostar contracts, because the pressure inside is too low to support all the mass. ...
... •Protostar: the clump formed from dense and cold nebula under gravitational contraction •The protostar contracts, because the pressure inside is too low to support all the mass. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.