THE NUCLEUS
... Opportunities are usually disguised as hard work, so most people don't recognize them. - Ann Landers ...
... Opportunities are usually disguised as hard work, so most people don't recognize them. - Ann Landers ...
31 October: Supernovae and Neutron Stars
... Formation of a neutron star from stellar core • As core collapses, matter becomes compressed • Electrons and protons forced together e+p > n + nu (neutronization) • Core of the becomes a neutron fluid • Neutronization produces a burst of neutrinos • Neutron fluid in core becomes degenerate and rigi ...
... Formation of a neutron star from stellar core • As core collapses, matter becomes compressed • Electrons and protons forced together e+p > n + nu (neutronization) • Core of the becomes a neutron fluid • Neutronization produces a burst of neutrinos • Neutron fluid in core becomes degenerate and rigi ...
Electric Fields Worksheet 2
... 1. In a uniform electric field, the potential difference between two points 12.0 cm apart is 1.50 x 102 V. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field. [1.25 x 103 N/C] 2. The magnitude of the electric field strength between two parallel plates is 4.0 x 103 N/C. The plates are connected to a batte ...
... 1. In a uniform electric field, the potential difference between two points 12.0 cm apart is 1.50 x 102 V. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field. [1.25 x 103 N/C] 2. The magnitude of the electric field strength between two parallel plates is 4.0 x 103 N/C. The plates are connected to a batte ...
Nuclear chem PPT NUC LECTURE
... Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons (Z1= Z2), but a different number of neutrons (N). (A1 A2) ...
... Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons (Z1= Z2), but a different number of neutrons (N). (A1 A2) ...
Death of Low Mass Stars 8 Solar Masses or less
... • The resistance of electrons from being squeezed together (electromagnetic repulsion) keeps gravity from compressing it further. Called Electron Degeneracy • The black dwarf will continue to exist at temps close to absolute zero forever…. ...
... • The resistance of electrons from being squeezed together (electromagnetic repulsion) keeps gravity from compressing it further. Called Electron Degeneracy • The black dwarf will continue to exist at temps close to absolute zero forever…. ...
When radiation ruled
... Key idea: When the universe was smaller (when the distance between us and some object was smaller), the temperature was hotter. There is no obvious limit to the temperature. Events in the universe’s life, when the universe was smaller & hotter. Production of the first nuclei other than H (3min) ( Re ...
... Key idea: When the universe was smaller (when the distance between us and some object was smaller), the temperature was hotter. There is no obvious limit to the temperature. Events in the universe’s life, when the universe was smaller & hotter. Production of the first nuclei other than H (3min) ( Re ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 2
... He white dwarf. Do the same for the radius of the neutron star. Evaluate both assuming that the Chandrasekhar limit for a pure He white dwarf is 1.46 M⊙ and its radius is 0.01 R⊙ . ...
... He white dwarf. Do the same for the radius of the neutron star. Evaluate both assuming that the Chandrasekhar limit for a pure He white dwarf is 1.46 M⊙ and its radius is 0.01 R⊙ . ...
A Conceptual Introduction to Chemistry, First Edition
... and zirconium-97. How many neutrons are emitted? Write a balanced nuclear equation to describe this fission process. Neutrons change the mass number by 1 but do not affect the atomic number. Adding the mass numbers on either side: 235 = 137 + 97 + A A=1 So, only one nuclide is used. ...
... and zirconium-97. How many neutrons are emitted? Write a balanced nuclear equation to describe this fission process. Neutrons change the mass number by 1 but do not affect the atomic number. Adding the mass numbers on either side: 235 = 137 + 97 + A A=1 So, only one nuclide is used. ...
Supernovae – the biggest bangs since the Big Bang
... A massive star with an iron core lives for less than one day. The outer layers squeeze down on the core and it explodes. Astronomers call this a “Type II supernova”. Stars that end as Type II supernovae range in mass from 8 to (maybe) 100 times that of the Sun. Because the amount of material that ...
... A massive star with an iron core lives for less than one day. The outer layers squeeze down on the core and it explodes. Astronomers call this a “Type II supernova”. Stars that end as Type II supernovae range in mass from 8 to (maybe) 100 times that of the Sun. Because the amount of material that ...
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... • Strong force is very strong, short range and the same for all nucleons (as nuclei all have the same density) • Adding more neutrons (compared to protons) contributes to binding and does not add to tendency to split the nucleus / a proton repels every other proton (in the nucleus) so extra neutrons ...
... • Strong force is very strong, short range and the same for all nucleons (as nuclei all have the same density) • Adding more neutrons (compared to protons) contributes to binding and does not add to tendency to split the nucleus / a proton repels every other proton (in the nucleus) so extra neutrons ...
Stars and Deep Time
... • A much large Supernova explosion forces atoms and neutrons together to form elements heavier than Fe56. These include Au, Ag, Pb, and all other natural elements up to 92U238. • Atoms blasted outward in the supernova may eventually become part of a new nebula, which may become a nextgeneration star ...
... • A much large Supernova explosion forces atoms and neutrons together to form elements heavier than Fe56. These include Au, Ag, Pb, and all other natural elements up to 92U238. • Atoms blasted outward in the supernova may eventually become part of a new nebula, which may become a nextgeneration star ...
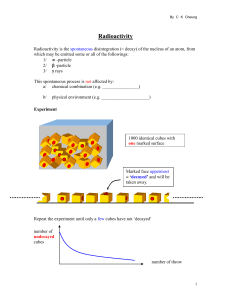
Radioactivity
... minute per gram of carbon. But when the organism dies no intake of C*, but decay process goes on with T1/2 ~ 5700 years. By measuring the activity of some furniture from an ancient village age of the furniture can be estimated within the range of 1000 to 5000 years. ...
... minute per gram of carbon. But when the organism dies no intake of C*, but decay process goes on with T1/2 ~ 5700 years. By measuring the activity of some furniture from an ancient village age of the furniture can be estimated within the range of 1000 to 5000 years. ...
The World Year of Physics is a worldwide celebration of physics
... Roughly once per century in a typical galaxy, a massive star ends its life in a spectacular explosion that shines with the brilliance of all the billions of other stars in the galaxy combined. These explosions are called supernovae, and their fleeting presence in the night sky has been recorded sinc ...
... Roughly once per century in a typical galaxy, a massive star ends its life in a spectacular explosion that shines with the brilliance of all the billions of other stars in the galaxy combined. These explosions are called supernovae, and their fleeting presence in the night sky has been recorded sinc ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... sun will enter the ______________ _____________ phase, which means it loses its outer layers. The star’s mass is lost until it collapses into a _____________ dwarf, which will lose energy and become a ______________ dwarf. ...
... sun will enter the ______________ _____________ phase, which means it loses its outer layers. The star’s mass is lost until it collapses into a _____________ dwarf, which will lose energy and become a ______________ dwarf. ...
A – Z - washburnsciencelies
... Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation with high frequency which are stopped by several cm of lead. When atoms decay by emitting a or b particles to form a new atom, the nuclei of the new atom formed may still have too much energy to be completely stable. This excess energy is emitted as gamma ray ...
... Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation with high frequency which are stopped by several cm of lead. When atoms decay by emitting a or b particles to form a new atom, the nuclei of the new atom formed may still have too much energy to be completely stable. This excess energy is emitted as gamma ray ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.