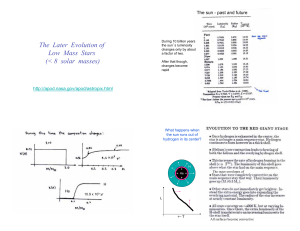
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_Nebula AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin he ...
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_Nebula AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin he ...
Document
... to be sure, but also nitrogen from CNO processing and C and O from helium burning. It is thought that stars in this mass range are responsible for producing most of the nitrogen and maybe 60 – 80% of the carbon in the universe. The rest of carbon and most other elements comes from massive stars. ...
... to be sure, but also nitrogen from CNO processing and C and O from helium burning. It is thought that stars in this mass range are responsible for producing most of the nitrogen and maybe 60 – 80% of the carbon in the universe. The rest of carbon and most other elements comes from massive stars. ...
- Lorentz Center
... If cold (T<3x108 K or so) and ‘low’ accretion rate, ignition is from high densities.. which only occurs for massive white dwarfs.. ...
... If cold (T<3x108 K or so) and ‘low’ accretion rate, ignition is from high densities.. which only occurs for massive white dwarfs.. ...
Encyclopedia of Optical Engineering Stellar Evolution
... outer layers back to the interstellar medium (ISM). Eventually another gaseous nebula forms from this enriched material, and a new generation of stars is created. The key quantity that dictates the evolution of a single star is its mass. The ‘‘weight’’ of a star must be balanced by internal pressure ...
... outer layers back to the interstellar medium (ISM). Eventually another gaseous nebula forms from this enriched material, and a new generation of stars is created. The key quantity that dictates the evolution of a single star is its mass. The ‘‘weight’’ of a star must be balanced by internal pressure ...
If the current flowing in a wire is 1 milliamp (0
... Hey all the energies are the same!! Hey energy must be conserved. That must be why Ms. Walker wrote all the equations involved in electrical energy to be equal to each other and so on the equation sheet it looks like this: UE = qV = W = Fd = ½ mv2 11. A capacitor is charged up to 60.0 V and the sepa ...
... Hey all the energies are the same!! Hey energy must be conserved. That must be why Ms. Walker wrote all the equations involved in electrical energy to be equal to each other and so on the equation sheet it looks like this: UE = qV = W = Fd = ½ mv2 11. A capacitor is charged up to 60.0 V and the sepa ...
CHAPTER 14
... 1. About 90% of the stars in the sky are on the main sequence. This implies that a typical star spends 90% of its luminous lifetime on the main sequence. 2. For most of these stars the next step after leaving the main sequence is to become red giants. 3. A typical star begins to contract once its co ...
... 1. About 90% of the stars in the sky are on the main sequence. This implies that a typical star spends 90% of its luminous lifetime on the main sequence. 2. For most of these stars the next step after leaving the main sequence is to become red giants. 3. A typical star begins to contract once its co ...
The Universe
... the opposite direction, forcing particles towards the core. gravitational force ...
... the opposite direction, forcing particles towards the core. gravitational force ...
– 1 – 1.
... The URCA Process and Electron Capture At high densities, electron capture (inverse β decay, effectively a proton becomes a neutron, e− + p → n + ν) such that e− + (Z, A) → (Z − 1, A) + ν occurs. This inverse β decay is followed by a β decay, (Z − 1, A) → (Z, A) + e− + ν. The combination of these two ...
... The URCA Process and Electron Capture At high densities, electron capture (inverse β decay, effectively a proton becomes a neutron, e− + p → n + ν) such that e− + (Z, A) → (Z − 1, A) + ν occurs. This inverse β decay is followed by a β decay, (Z − 1, A) → (Z, A) + e− + ν. The combination of these two ...
Module G - U1_ L3 - Life Cycle of Stars
... • A star can remain actively fusing hydrogen into helium for billions of years. This stage ends when the star runs out of hydrogen. • Nuclear fusion happens in three steps. • When nearly all the hydrogen in a star’s core has fused into helium, the core contracts under its own gravity and its tempera ...
... • A star can remain actively fusing hydrogen into helium for billions of years. This stage ends when the star runs out of hydrogen. • Nuclear fusion happens in three steps. • When nearly all the hydrogen in a star’s core has fused into helium, the core contracts under its own gravity and its tempera ...
ASTR 1020 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
... What is the smallest mass a newborn star can have? What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity when a protostar radiatively contracts? When does a star become a main-sequence star? What happens to the rotation of a molecular cloud as it collapses to form a star? When is thermal energy tra ...
... What is the smallest mass a newborn star can have? What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity when a protostar radiatively contracts? When does a star become a main-sequence star? What happens to the rotation of a molecular cloud as it collapses to form a star? When is thermal energy tra ...
Mars Project
... this. They start a protostars, then form into a star from nuclear fusion. Here are some pictures. ...
... this. They start a protostars, then form into a star from nuclear fusion. Here are some pictures. ...
Unit 1
... • a. Hydrogen burning is taking place in a spherical shell just outside the core; the core itself is almost pure helium. • b. Helium is being converted into carbon and oxygen in the core. • c. Helium burning is taking place in a spherical shell just outside the core. • d. hydrogen burning is taking ...
... • a. Hydrogen burning is taking place in a spherical shell just outside the core; the core itself is almost pure helium. • b. Helium is being converted into carbon and oxygen in the core. • c. Helium burning is taking place in a spherical shell just outside the core. • d. hydrogen burning is taking ...
Document
... • Density = mass per volume • From Red Giant cores to White Dwarfs to Neutron Stars, density has been increasing. • As density increases, the force of gravity on the surface increases. • The greater the force, the higher the escape velocity: – How fast you need to go in order to escape the surface. ...
... • Density = mass per volume • From Red Giant cores to White Dwarfs to Neutron Stars, density has been increasing. • As density increases, the force of gravity on the surface increases. • The greater the force, the higher the escape velocity: – How fast you need to go in order to escape the surface. ...
File - Prairie Science
... Nova and Supernovas: Some white dwarf stars are part of a binary star system. If a white dwarf is around a red giant, the gravity of the very dense white dwarf may capture loosely held gases from the red giant. As the gases accumulate, the pressure builds up and may lead to an explosion called a n ...
... Nova and Supernovas: Some white dwarf stars are part of a binary star system. If a white dwarf is around a red giant, the gravity of the very dense white dwarf may capture loosely held gases from the red giant. As the gases accumulate, the pressure builds up and may lead to an explosion called a n ...
Chapter 28
... for a second or less and then they decay into something else. Many of them were made by Dr. Seaborg and his team of researchers. ...
... for a second or less and then they decay into something else. Many of them were made by Dr. Seaborg and his team of researchers. ...
Star - Holy Family Regional School
... The mass of a star determines what kind of main sequence star it is. The more massive the star, the hotter it is. The brightest stars are at the top, with the dimmer ones at the bottom. The hottest stars are on the left, and the coolest ones are on the right. ...
... The mass of a star determines what kind of main sequence star it is. The more massive the star, the hotter it is. The brightest stars are at the top, with the dimmer ones at the bottom. The hottest stars are on the left, and the coolest ones are on the right. ...
Radioactivity presentation script
... box left and one box up, as it gains a proton and loses a neutron. We can see that this happens “below” the line of stable nuclei, where there are more neutrons than required. Beta-plus decay (with a proton turning into a neutron) is shown in light blue - this causes the nuclide to jump one box rig ...
... box left and one box up, as it gains a proton and loses a neutron. We can see that this happens “below” the line of stable nuclei, where there are more neutrons than required. Beta-plus decay (with a proton turning into a neutron) is shown in light blue - this causes the nuclide to jump one box rig ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.