2006ph607chaptertwo
... is the energy release per unit mass per unit time, The energy released by the PP chain and CNO cycle are smooth functions of temperature * the rate of fusion is a very sensitive function of temperature * fusion reactions involving successively heavier elements (in ascending order: the PP chain, th ...
... is the energy release per unit mass per unit time, The energy released by the PP chain and CNO cycle are smooth functions of temperature * the rate of fusion is a very sensitive function of temperature * fusion reactions involving successively heavier elements (in ascending order: the PP chain, th ...
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
... decays away and becomes a smaller and smaller fraction of the total carbon in the plant tissue. This fraction can be measured, and tissue age deduced. Objects older than about 60,000 years cannot be dated this way – there is too little carbon14 left. Other isotopes are useful for geologic tim ...
... decays away and becomes a smaller and smaller fraction of the total carbon in the plant tissue. This fraction can be measured, and tissue age deduced. Objects older than about 60,000 years cannot be dated this way – there is too little carbon14 left. Other isotopes are useful for geologic tim ...
AmiraPoster3
... • SMC X-1 is an eclipsing X-ray pulsar located in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). • Optical counterpart is the B0I supergiant Sk 160. • Long quasi stable period of 50-60 days - believed to be result of quasi periodic obscuration of the neutron star by a precessing accretion disk. • Mode of mass tr ...
... • SMC X-1 is an eclipsing X-ray pulsar located in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). • Optical counterpart is the B0I supergiant Sk 160. • Long quasi stable period of 50-60 days - believed to be result of quasi periodic obscuration of the neutron star by a precessing accretion disk. • Mode of mass tr ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... that seen about stars being born Planet composition dependent upon where it formed in solar system ...
... that seen about stars being born Planet composition dependent upon where it formed in solar system ...
Lecture 9
... helium. But, some stars shine by turning heavier elements (like helium) into even heavier elements (possibly oxygen, carbon). Do temperatures need to be higher or lower for the fusion of other elements to occur? Why? • Challenge: Estimate how much higher or lower the temps have to be. ...
... helium. But, some stars shine by turning heavier elements (like helium) into even heavier elements (possibly oxygen, carbon). Do temperatures need to be higher or lower for the fusion of other elements to occur? Why? • Challenge: Estimate how much higher or lower the temps have to be. ...
Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... When the outer layers of the giant are lost to space, the sun will become a white dwarf and move to the lower left quadrant of the diagram. ...
... When the outer layers of the giant are lost to space, the sun will become a white dwarf and move to the lower left quadrant of the diagram. ...
Document
... Only in high mass stars is pressure great enough for carbon to be made by nuclear fusion. Only in high mass stars do we find the C-N-O cycle of nuclear fusion. In low mass stars the pressure due to gravity isn’t as high as the pressure in the core of a high mass star. Only a high mass star ends in a ...
... Only in high mass stars is pressure great enough for carbon to be made by nuclear fusion. Only in high mass stars do we find the C-N-O cycle of nuclear fusion. In low mass stars the pressure due to gravity isn’t as high as the pressure in the core of a high mass star. Only a high mass star ends in a ...
sun elements
... 6% of the Sun, and all the other elements make up just 0.13% (with oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen the three most abundant ``metals''---they make up 0.11%). In astronomy, any atom heavier than helium is called a ``metal'' atom. The Sun also has traces of neon, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phos ...
... 6% of the Sun, and all the other elements make up just 0.13% (with oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen the three most abundant ``metals''---they make up 0.11%). In astronomy, any atom heavier than helium is called a ``metal'' atom. The Sun also has traces of neon, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phos ...
PURDUE UNIVERSITY PHYS221 FINAL EXAM
... The resistance is not changed. The resistance increases by a factor of four. The resistance decreases by a factor of four. ...
... The resistance is not changed. The resistance increases by a factor of four. The resistance decreases by a factor of four. ...
Sources of Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan
... will couple to those modes Or a time-varying mass current quadrupole Higher multipoles too – but no monopole or dipole emission in GR ...
... will couple to those modes Or a time-varying mass current quadrupole Higher multipoles too – but no monopole or dipole emission in GR ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
Stellar Evolution
... A Neutron Star With a thin crust of Iron. It begins to spin super-fast with a period is as little as a second! This generates a strong magnetic field and a beacon of radio energy that acts like a spinning search-light. That appear to us as a Pulsar, a source of a rhythmic radio signal first thought ...
... A Neutron Star With a thin crust of Iron. It begins to spin super-fast with a period is as little as a second! This generates a strong magnetic field and a beacon of radio energy that acts like a spinning search-light. That appear to us as a Pulsar, a source of a rhythmic radio signal first thought ...
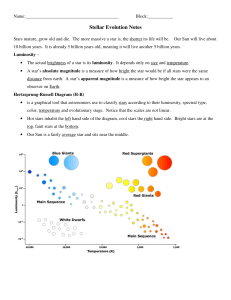
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
What is PREx?
... of a large neutron excess and a large Coulomb barrier. Finding Rn will be a fundamental test of nuclear theory and provide clues about neutron-rich matter. ...
... of a large neutron excess and a large Coulomb barrier. Finding Rn will be a fundamental test of nuclear theory and provide clues about neutron-rich matter. ...
Unit 6--Astronomy
... a. Earth is in the center of the universe b. the universe is contracting c. the universe is expanding d. the universe is smaller than once believed 44.According to the big bang theory, the universe began about ____. a. 4.5 billion years ago c. 49.6 billion years ago b. 13.7 billion years ago d. 130 ...
... a. Earth is in the center of the universe b. the universe is contracting c. the universe is expanding d. the universe is smaller than once believed 44.According to the big bang theory, the universe began about ____. a. 4.5 billion years ago c. 49.6 billion years ago b. 13.7 billion years ago d. 130 ...
Life Cycle of a Star - CullenScience
... ________________ force pulling in. Gravity will cause the core to contract. Helium burns inside the ________, but a rapid hydrogen reaction occurs faster in the ___________of the star. As the temperature in the shell of the star increases, the outer layers of the star expand. 2. What is a Red Giant? ...
... ________________ force pulling in. Gravity will cause the core to contract. Helium burns inside the ________, but a rapid hydrogen reaction occurs faster in the ___________of the star. As the temperature in the shell of the star increases, the outer layers of the star expand. 2. What is a Red Giant? ...
solution - Evergreen Archives
... The intense nuclear repulsion between neutrons, only felt when these neutrons are very closely packed because the nuclear force is very short-ranged. The very high temperature and velocity of the neutrons, which creates a thermal gas pressure to oppose gravity. The centrifugal force of the star’s ve ...
... The intense nuclear repulsion between neutrons, only felt when these neutrons are very closely packed because the nuclear force is very short-ranged. The very high temperature and velocity of the neutrons, which creates a thermal gas pressure to oppose gravity. The centrifugal force of the star’s ve ...
PhD Qualifying Exam (2010) --
... the Jeans mass. For a cloud of uniform temperature T, and average density ρ, find its Jeans mass. (5 points) (b) As a cloud collapses often it fragments, until a lower mass limit of fragments is reached. Find this minimum mass. (5 points) (c) Assuming that a star of mass M has no nuclear energy sour ...
... the Jeans mass. For a cloud of uniform temperature T, and average density ρ, find its Jeans mass. (5 points) (b) As a cloud collapses often it fragments, until a lower mass limit of fragments is reached. Find this minimum mass. (5 points) (c) Assuming that a star of mass M has no nuclear energy sour ...
Origin of the Universe
... Forces holding apart atomic nuclei are overcome Produces free neutrons Heavier atoms formed by neutron capture ...
... Forces holding apart atomic nuclei are overcome Produces free neutrons Heavier atoms formed by neutron capture ...
the 82nd arthur h. compton lecture series
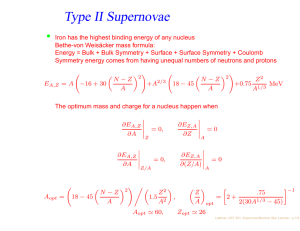
... ➢ Type Ia SNe come from explosions of white dwarfs in binary systems and do not show signs of He, but strong Si absorption. ➢ Type II SNe show H in the spectra. Subtypes are IIP, IIn, IIL. ➢ Type Ib/c SNe have lost their H (Ib) and sometimes also He (Ic) envelopes. ➢ Most supernova light curves are ...
... ➢ Type Ia SNe come from explosions of white dwarfs in binary systems and do not show signs of He, but strong Si absorption. ➢ Type II SNe show H in the spectra. Subtypes are IIP, IIn, IIL. ➢ Type Ib/c SNe have lost their H (Ib) and sometimes also He (Ic) envelopes. ➢ Most supernova light curves are ...
Radioactivity and Nuclear Physics
... Some of the matter on Earth is unstable and undergoing nuclear decay. Alpha decay is the emission of a helium nucleus, causing the product to have an atomic number 2 less than the original and an atomic mass number 4 less than the original. Beta minus decay is the emission of an electron, causing th ...
... Some of the matter on Earth is unstable and undergoing nuclear decay. Alpha decay is the emission of a helium nucleus, causing the product to have an atomic number 2 less than the original and an atomic mass number 4 less than the original. Beta minus decay is the emission of an electron, causing th ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.