name - cloudfront.net
... • Students know how to analyze fossil evidence with regard to biological diversity, episodic speciation, and mass extinction • Students know new mutations are constantly being generated in a gene pool. • Students know variation within a species increases the likelihood that at least some members of ...
... • Students know how to analyze fossil evidence with regard to biological diversity, episodic speciation, and mass extinction • Students know new mutations are constantly being generated in a gene pool. • Students know variation within a species increases the likelihood that at least some members of ...
Chapter 24: The Origin of Species
... Sympatric speciation can occur if gene flow is reduced by such factors are polyploidy, habitat differentiation, and sexual selection. 13. Your response to question 12 should have listed polyploidy, habitat differentiation, and sexual selection. These are not easy concepts to understand, so let’s spe ...
... Sympatric speciation can occur if gene flow is reduced by such factors are polyploidy, habitat differentiation, and sexual selection. 13. Your response to question 12 should have listed polyploidy, habitat differentiation, and sexual selection. These are not easy concepts to understand, so let’s spe ...
Protecting Ecosystems
... • Best to have a buffer from too much human intrusion • easiest if reserves are circular and follow natural boundaries • aim to encompass whole watershed ...
... • Best to have a buffer from too much human intrusion • easiest if reserves are circular and follow natural boundaries • aim to encompass whole watershed ...
Non-random random mutations: a signature of evolution of evolution
... although we are only at the beginning of this pursuit. Surprisingly some of these surprising features of evolution of evolved organisms turn out to be generic properties of Darwinian evolution. They had not before been recognized as such because both population genetics and in silico evolution proto ...
... although we are only at the beginning of this pursuit. Surprisingly some of these surprising features of evolution of evolved organisms turn out to be generic properties of Darwinian evolution. They had not before been recognized as such because both population genetics and in silico evolution proto ...
17.1 Classification
... Classification Classification – the grouping of objects based on similarities Taxonomy – branch of biology that groups and names organisms based on characteristics ...
... Classification Classification – the grouping of objects based on similarities Taxonomy – branch of biology that groups and names organisms based on characteristics ...
Deciphering the genetic footprints of domestication in
... Key words: Domestication, Solanaceae, Evolutionary history, Genomic. The process of domestication started with the shift from hunter/gatherer to agrarian societies. Plants were selected for crop farming based on specific phenotypes. This stringent selection often results in a genetic bottleneck that ...
... Key words: Domestication, Solanaceae, Evolutionary history, Genomic. The process of domestication started with the shift from hunter/gatherer to agrarian societies. Plants were selected for crop farming based on specific phenotypes. This stringent selection often results in a genetic bottleneck that ...
Evolution
... environments (similar ecosystems) but had different organisms (plants and animals) Ex: Argentina and Australia ○ Similar ecosystems (grasslands) ○ Australia had kangaroos but no rabbits ○ Argentina had rabbits but no kangaroos ...
... environments (similar ecosystems) but had different organisms (plants and animals) Ex: Argentina and Australia ○ Similar ecosystems (grasslands) ○ Australia had kangaroos but no rabbits ○ Argentina had rabbits but no kangaroos ...
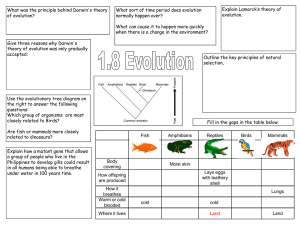
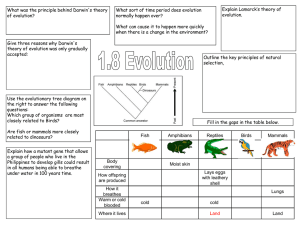
1.8_Evolution
... All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of inheritance not ...
... All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of inheritance not ...
File
... All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of inheritance not ...
... All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of inheritance not ...
Lab 1 - CLAS Users
... Lab sessions are MANDITORY. Attendance will be taken at the beginning of each session. If you plan on missing a lab, you must notify your TA at the beginning of the week and you must have a legitimate reason. The TA will place you into another appropriate session for that week. There will be no lab ...
... Lab sessions are MANDITORY. Attendance will be taken at the beginning of each session. If you plan on missing a lab, you must notify your TA at the beginning of the week and you must have a legitimate reason. The TA will place you into another appropriate session for that week. There will be no lab ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 19 –Microbial
... Unsure student understand that melting means the hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic base stacking interactions between strands are disrupted. The covalent bonds connecting nucleotides within each strand are not affected, thus melting is reversible. GC rich DNA is more stable than AT rich, thus as the GC ...
... Unsure student understand that melting means the hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic base stacking interactions between strands are disrupted. The covalent bonds connecting nucleotides within each strand are not affected, thus melting is reversible. GC rich DNA is more stable than AT rich, thus as the GC ...
Phenotype Genotype and the Environment
... When an organism moves from one area to another, it takes its alleles with it. ...
... When an organism moves from one area to another, it takes its alleles with it. ...
GO 1_1Examing Biological Diveristy
... Definition for organism = an organism is any contiguous living system (such as animal, fungus, micro-organism, or plant). In at least some form, all types of organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homeostasis as a stable whole. ...
... Definition for organism = an organism is any contiguous living system (such as animal, fungus, micro-organism, or plant). In at least some form, all types of organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homeostasis as a stable whole. ...
natural selection
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
Sample File
... A gene is a portion of the DNA molecule that contains a sequence of base pairs that encode a particular protein. Mendel deduced the presence and activity of genes by experimenting with garden peas to determine how traits are passed from one generation to the next. He discovered that inheritance ...
... A gene is a portion of the DNA molecule that contains a sequence of base pairs that encode a particular protein. Mendel deduced the presence and activity of genes by experimenting with garden peas to determine how traits are passed from one generation to the next. He discovered that inheritance ...
NOTE: The provided figures may be useful and beneficial
... 3. Distinguish genetic drift from gene flow in terms of how they occur & their implications for future genetic variation within a population. 4. Suppose 2 plant populations exchange pollen & seeds. In one population, individuals of genotype AA are most common (9,000 AA, 900 Aa, 100 aa), while the op ...
... 3. Distinguish genetic drift from gene flow in terms of how they occur & their implications for future genetic variation within a population. 4. Suppose 2 plant populations exchange pollen & seeds. In one population, individuals of genotype AA are most common (9,000 AA, 900 Aa, 100 aa), while the op ...
Extinction Processes
... over time. Some controversy about the relative magnitude of these “mass extinctions”. ...
... over time. Some controversy about the relative magnitude of these “mass extinctions”. ...
Extinction
... over time. Some controversy about the relative magnitude of these “mass extinctions”. ...
... over time. Some controversy about the relative magnitude of these “mass extinctions”. ...
Content Standards
... Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-LS4-1. Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change of life forms throughout the history of life on Earth under the assumption that natural laws operate today as in the past. ...
... Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-LS4-1. Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change of life forms throughout the history of life on Earth under the assumption that natural laws operate today as in the past. ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.