“What it Means to be 98% Chimpanzee” by Jonathan Marks and
... elucidates. First, there are only 4 bases used by DNA, meaning that at any one point, two sequences have a 25% chance of sharing a base. Second, many DNA segments result from ancient homologies and are shared across species, rendering the number even more similar. Finally, the segments of DNA chosen ...
... elucidates. First, there are only 4 bases used by DNA, meaning that at any one point, two sequences have a 25% chance of sharing a base. Second, many DNA segments result from ancient homologies and are shared across species, rendering the number even more similar. Finally, the segments of DNA chosen ...
Running head: PATHOGEN PREVALENCE AND HUMAN MATE 1
... findings illustrate that pathogen prevalence correlated with average attractiveness. However, the findings were consistent only in environments where pathogen incidence was high. In essence, the results supported the hypothesis suggested by the authors. However, the authors acknowledged the fact tha ...
... findings illustrate that pathogen prevalence correlated with average attractiveness. However, the findings were consistent only in environments where pathogen incidence was high. In essence, the results supported the hypothesis suggested by the authors. However, the authors acknowledged the fact tha ...
Intro to grass flowers
... Neofunctionalization fates for the SEP3 dupliate genes in the grasses. A strong case for SEP3A and SEP3B’s role in the evolution of the lodicules will result in a better understanding of how grass flower develop. This has potential value agriculturally considering that crop yeild is proportional to ...
... Neofunctionalization fates for the SEP3 dupliate genes in the grasses. A strong case for SEP3A and SEP3B’s role in the evolution of the lodicules will result in a better understanding of how grass flower develop. This has potential value agriculturally considering that crop yeild is proportional to ...
Unit 7: Evolution - Blue Valley Schools
... into the history of life on Earth. Describe specific examples of conserved core biological processes and features shared by all domains or within one domain of life, and how these shared, conserved core processes and features support the concept of common ancestry for all organisms. Justify the scie ...
... into the history of life on Earth. Describe specific examples of conserved core biological processes and features shared by all domains or within one domain of life, and how these shared, conserved core processes and features support the concept of common ancestry for all organisms. Justify the scie ...
Chapter 1 - Weber State University
... Walter Cannon (1871-1945) physician/researcher developed term observed animals interact with environment which constantly alters stability of internal parameters (e.g. temperature, pH, ion concentrations) expanded Bernard’s constancy of internal mileu to also include existence of regulatory systems ...
... Walter Cannon (1871-1945) physician/researcher developed term observed animals interact with environment which constantly alters stability of internal parameters (e.g. temperature, pH, ion concentrations) expanded Bernard’s constancy of internal mileu to also include existence of regulatory systems ...
Document
... (1877), admits a greater antiquity of the Earth, but not of the man. This book was based on the work Geology and Revelation of the Dr Molloy and was guaranteed by several Spanish bishops. Almera’s position was in principle of opening, although he pretended the opposite, since the way is necessary to ...
... (1877), admits a greater antiquity of the Earth, but not of the man. This book was based on the work Geology and Revelation of the Dr Molloy and was guaranteed by several Spanish bishops. Almera’s position was in principle of opening, although he pretended the opposite, since the way is necessary to ...
Chapters 14 & 15
... 10. What correct thoughts did Lamarck have about evolution? 1) Types of organisms change over time 2) New types of organisms are modified descendants of older types What incorrect thoughts did Lamarck have? Traits were acquired through an organism’s experience or behavior and could be passed onto of ...
... 10. What correct thoughts did Lamarck have about evolution? 1) Types of organisms change over time 2) New types of organisms are modified descendants of older types What incorrect thoughts did Lamarck have? Traits were acquired through an organism’s experience or behavior and could be passed onto of ...
AP Biology Chapter 46 Take Home Quiz
... D) when a species is expanding into diverse geographic settings. E) when a species has accumulated numerous deleterious mutations. ...
... D) when a species is expanding into diverse geographic settings. E) when a species has accumulated numerous deleterious mutations. ...
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
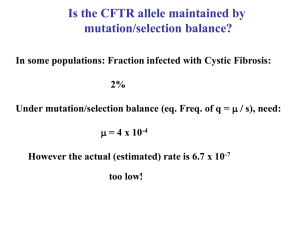
... are determined by different, selective processes. ...
... are determined by different, selective processes. ...
LESSON PLAN
... 2. Starter – students are to describe whether a series of different events would lead to an increase or decrease in genetic diversity. ...
... 2. Starter – students are to describe whether a series of different events would lead to an increase or decrease in genetic diversity. ...
PDF file
... average variance in gene expression across all genes tends to be lower for a wild-type individual subjected to environmental noise than for its knockout derivatives under the same conditions. The amplitude of noise required to induce non-zero variance differs from individual to individual, so for ea ...
... average variance in gene expression across all genes tends to be lower for a wild-type individual subjected to environmental noise than for its knockout derivatives under the same conditions. The amplitude of noise required to induce non-zero variance differs from individual to individual, so for ea ...
Optional: Quick Study Card - Liberty Union High School District
... Define ecosystem services and list 5 examples of ecosystem services. How does biodiversity relate to ecosystem services? Draw a diagram of the greenhouse effect. Create a table of the 6 greenhouse gases. Include the sources for each (both natural and anthropogenic). Which greenhouse gas is the “stro ...
... Define ecosystem services and list 5 examples of ecosystem services. How does biodiversity relate to ecosystem services? Draw a diagram of the greenhouse effect. Create a table of the 6 greenhouse gases. Include the sources for each (both natural and anthropogenic). Which greenhouse gas is the “stro ...
natural selection - faculty.fairfield.edu
... species change over time while also being related to one another. This is usually referred to as “Descent with modification” ...
... species change over time while also being related to one another. This is usually referred to as “Descent with modification” ...
Section 8.7 Mutations
... Two Categories of Mutations: 1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication 2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis . Usually more harmful since many genes are affected. ...
... Two Categories of Mutations: 1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication 2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis . Usually more harmful since many genes are affected. ...
Natural Selection March , 2.009 * 103
... When a significant environmental pressure arises, certain traits will be “selected” for. ...
... When a significant environmental pressure arises, certain traits will be “selected” for. ...
Chapter 22 Part 2 Descent with Modification
... • Direct observation of evolutionary changes. • Fossils • Homology • Convergent Evolution • Biogeography • Molecular ...
... • Direct observation of evolutionary changes. • Fossils • Homology • Convergent Evolution • Biogeography • Molecular ...
Amino Acid Sequence-indicators of evolution
... molecular level. DNA and proteins, the genes and the products of genes, provide powerful evidence for descent with modification. As DNA changes over time, the proteins that are produced by the DNA change too. The result is that many organisms have similar, but not identical, versions of a given prot ...
... molecular level. DNA and proteins, the genes and the products of genes, provide powerful evidence for descent with modification. As DNA changes over time, the proteins that are produced by the DNA change too. The result is that many organisms have similar, but not identical, versions of a given prot ...
Willmer_sample chapter_Environmental
... This book is about how animals cope with the problems posed, and exploit the opportunities offered, by their particular environments. Traditionally the mechanisms for coping with the environment have been treated as issues of comparative physiology, which is concerned with investigating both general ...
... This book is about how animals cope with the problems posed, and exploit the opportunities offered, by their particular environments. Traditionally the mechanisms for coping with the environment have been treated as issues of comparative physiology, which is concerned with investigating both general ...
Genome and sex 10-29
... high rates of sexual reproduction are sustained (graph, right). If frozen parasite stocks to reinfect each new generation of the host with a fixed, nonevolving ancestral strain of the parasite (p0 bottom series of boxes), rates of sexual reproduction can decline. Science 333: 166-7; 2011. When coevo ...
... high rates of sexual reproduction are sustained (graph, right). If frozen parasite stocks to reinfect each new generation of the host with a fixed, nonevolving ancestral strain of the parasite (p0 bottom series of boxes), rates of sexual reproduction can decline. Science 333: 166-7; 2011. When coevo ...
Natural Selection and Genetic Variety
... wrote Principles of Geology and popularized the theory of uniformitarianism, which is the belief that the present is the only key to the past and all things continue by a natural process at the same rates as they have always done. Darwin applied this idea to the variety of different plants and anima ...
... wrote Principles of Geology and popularized the theory of uniformitarianism, which is the belief that the present is the only key to the past and all things continue by a natural process at the same rates as they have always done. Darwin applied this idea to the variety of different plants and anima ...
Genetics
... DNA copying is a blind process It can be hijacked, e.g. by viruses It makes mistakes Mistakes accumulate over (lots of) time ...
... DNA copying is a blind process It can be hijacked, e.g. by viruses It makes mistakes Mistakes accumulate over (lots of) time ...
Selecting for Evolvability
... ABSTRACT Evolutionary theory posits that over time both genetic drift and natural selection lead to a decrease in variation within a population. Variation is maintained by other processes such as gene flow, mutation, and sexual reproduction. However, mutation is not only a exogenous phenomenon. Rate ...
... ABSTRACT Evolutionary theory posits that over time both genetic drift and natural selection lead to a decrease in variation within a population. Variation is maintained by other processes such as gene flow, mutation, and sexual reproduction. However, mutation is not only a exogenous phenomenon. Rate ...
Quiz # 1 Chapters 1 and 2
... 7. Sediments can be used to deduce past landscapes and climate. True Or False? 8. Charles Darwin suggested mechanisms for changes in anatomy over many generations, a process he called "Natural Selection". True Or False? 9. Larmarckian evolution was based on inheritance of acquired characteristics. T ...
... 7. Sediments can be used to deduce past landscapes and climate. True Or False? 8. Charles Darwin suggested mechanisms for changes in anatomy over many generations, a process he called "Natural Selection". True Or False? 9. Larmarckian evolution was based on inheritance of acquired characteristics. T ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.