Classification Booklet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
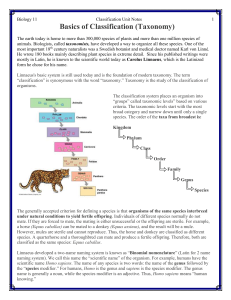
... The classification system places an organism into “groups” called taxonomic levels” based on various criteria. The taxonomic levels start with the most broad category and narrow down until only a single species. The order of the taxa from broadest is: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species ...
... The classification system places an organism into “groups” called taxonomic levels” based on various criteria. The taxonomic levels start with the most broad category and narrow down until only a single species. The order of the taxa from broadest is: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species ...
SMART Notebook
... of the card should be a colored picture, « the of the card should be the word and definition. Crossing Over Independent Assortment Random Fertilization ...
... of the card should be a colored picture, « the of the card should be the word and definition. Crossing Over Independent Assortment Random Fertilization ...
here
... You can determine omega for the whole dataset; however, usually not all sites in a sequence are under selection all the time. PAML (and other programs) allow to either determine omega for each site over the whole tree, ...
... You can determine omega for the whole dataset; however, usually not all sites in a sequence are under selection all the time. PAML (and other programs) allow to either determine omega for each site over the whole tree, ...
Pathways for making unisexual flowers and unisexual
... sexes within the same groups.” In spite of the sparse genetic and phylogenetic evidence for transitions from gynodioecy to dioecy, this pathway has received vast attention. Determining whether some dioecious angiosperms perhaps do have male and female sex-determining genes linked in a recombination- ...
... sexes within the same groups.” In spite of the sparse genetic and phylogenetic evidence for transitions from gynodioecy to dioecy, this pathway has received vast attention. Determining whether some dioecious angiosperms perhaps do have male and female sex-determining genes linked in a recombination- ...
Nature, red in tooth and claw, so what?
... most of nature’s mayhem is indiscriminate. If life is tragic, it’s largely a universal tragedy. ...
... most of nature’s mayhem is indiscriminate. If life is tragic, it’s largely a universal tragedy. ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Migrated to Asia and Europe and displaced other hominin species that had colonized those areas earlier. Homo erectus migrated and then evolved into H. sapiens. Various subgroups of H. erectus existed throughout Africa, Asia and Europe and interbred to give rise to the races we ...
... Migrated to Asia and Europe and displaced other hominin species that had colonized those areas earlier. Homo erectus migrated and then evolved into H. sapiens. Various subgroups of H. erectus existed throughout Africa, Asia and Europe and interbred to give rise to the races we ...
Student handout - Inquiry-Based Activities in Genomics and
... This activity is intended to be completed after AP Biology Investigation 2, “Mathematical Modeling: Hardy-Weinberg”. Please see the AP Biology Lab Manual for background information. Installing Populus—Populus is a population modeling program developed at the University of Minnesota. If you are doing ...
... This activity is intended to be completed after AP Biology Investigation 2, “Mathematical Modeling: Hardy-Weinberg”. Please see the AP Biology Lab Manual for background information. Installing Populus—Populus is a population modeling program developed at the University of Minnesota. If you are doing ...
Evolution of Populations
... The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem The frequencies of alleles in the population will remain constant if Mendelian segregation is the only process that affects the gene pool. ...
... The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem The frequencies of alleles in the population will remain constant if Mendelian segregation is the only process that affects the gene pool. ...
The Evolutionary Role of Wildfire in the Northern Rockies and
... Major wildfires in the Northern Rockies leave islands of live trees partially or wholly isolated from external pollen sources. I conclude that trees in these small, presumably random mating, populations serve as the parents for most of the ensuing natural regeneration (except for serotinous-cone spe ...
... Major wildfires in the Northern Rockies leave islands of live trees partially or wholly isolated from external pollen sources. I conclude that trees in these small, presumably random mating, populations serve as the parents for most of the ensuing natural regeneration (except for serotinous-cone spe ...
Do Now: Answer these 2 questions in your notebook.
... show how the physical traits of living things are handed down and modified from one generation to the next. By comparing the DNA of many organisms, scientists can map the relationships between species. This map is in remarkable agreement with Darwin’s predictions. The structure of chromosomes and pa ...
... show how the physical traits of living things are handed down and modified from one generation to the next. By comparing the DNA of many organisms, scientists can map the relationships between species. This map is in remarkable agreement with Darwin’s predictions. The structure of chromosomes and pa ...
Chapter 27 (Genetic Monitoring) - Laboratory Animal Boards Study
... 6. Many inbred strains were initially developed to study the role of genes in ? a. Infectious disease b. Pharmacology c. Genetics d. Cancer 7. What is a common chemical agent used to generate mice carrying point mutations? a. ANTU b. ENU c. FETAX d. MS222 8. At F20 the number of loci that remained ...
... 6. Many inbred strains were initially developed to study the role of genes in ? a. Infectious disease b. Pharmacology c. Genetics d. Cancer 7. What is a common chemical agent used to generate mice carrying point mutations? a. ANTU b. ENU c. FETAX d. MS222 8. At F20 the number of loci that remained ...
Thesis
... the genetic determinants of the adaptation is to analyze the nucleotide differentiation between populations submitted to contrasted environment by whole genome sequencing of pooled individuals. Pools allow estimating allele frequencies of polymorphisms within and between populations useful for a gen ...
... the genetic determinants of the adaptation is to analyze the nucleotide differentiation between populations submitted to contrasted environment by whole genome sequencing of pooled individuals. Pools allow estimating allele frequencies of polymorphisms within and between populations useful for a gen ...
Ploidy, sex and crossing over in an evolutionary aging model
... removed the antagonistic pleiotropy restriction of the Partridge–Barton model and Heumann and Hötzel [12] tried to generalize it to a many ages structured population model. They tried but failed. Even on starting with several ages (11, in their work), the final stationary regime ended with only 3 ag ...
... removed the antagonistic pleiotropy restriction of the Partridge–Barton model and Heumann and Hötzel [12] tried to generalize it to a many ages structured population model. They tried but failed. Even on starting with several ages (11, in their work), the final stationary regime ended with only 3 ag ...
Document
... • Genetic information is stored in the chromosomes • Each chromosome is build of DNA • Chromosomes in humans form pairs • There are 23 pairs • The chromosome is divided in parts: genes • Genes code for properties • The posibilities of the genes for one property is called: allele • Every gene has an ...
... • Genetic information is stored in the chromosomes • Each chromosome is build of DNA • Chromosomes in humans form pairs • There are 23 pairs • The chromosome is divided in parts: genes • Genes code for properties • The posibilities of the genes for one property is called: allele • Every gene has an ...
Mendel_and_the_genetic_engine
... • Natural selection favors organisms that have traits that are “good enough”; and usually acts on just a few characteristics – Extremes are rarely selected for ...
... • Natural selection favors organisms that have traits that are “good enough”; and usually acts on just a few characteristics – Extremes are rarely selected for ...
Evolutionary Computing A Practical Introduction
... More reproduction leads to more of the “new improved” genetic “Good” sets of genes get reproduced more “Bad” sets of genes get reproduce less Organisms as a whole get better and better at surviving in their environment Evolutionists claim that this slow changing of genetic material through reproduct ...
... More reproduction leads to more of the “new improved” genetic “Good” sets of genes get reproduced more “Bad” sets of genes get reproduce less Organisms as a whole get better and better at surviving in their environment Evolutionists claim that this slow changing of genetic material through reproduct ...
Define inheritance as the transmission of
... offspring and the production of genetically dissimilar offspring Meiosis Define meiosis as reduction division in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid (details of stages are not required) State that gametes are the result of meiosis State that meiosis results in genetic ...
... offspring and the production of genetically dissimilar offspring Meiosis Define meiosis as reduction division in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid (details of stages are not required) State that gametes are the result of meiosis State that meiosis results in genetic ...
hybrid zone
... Fusion: Weakening Reproductive Barriers • If hybrids are as fit as parents, there can be substantial gene flow between species • If gene flow is great enough, the parent species can fuse into a single species • For example, researchers think that pollution in Lake Victoria has reduced the ability o ...
... Fusion: Weakening Reproductive Barriers • If hybrids are as fit as parents, there can be substantial gene flow between species • If gene flow is great enough, the parent species can fuse into a single species • For example, researchers think that pollution in Lake Victoria has reduced the ability o ...
Slightly beyond Turing`s computability for studying Genetic
... GP is typically solving approximately problems in 0’ A lot of work about approximating NP-complete problems, but not a lot about 0’ We provide a mathematical analysis of GP ...
... GP is typically solving approximately problems in 0’ A lot of work about approximating NP-complete problems, but not a lot about 0’ We provide a mathematical analysis of GP ...
8-7 Power Point
... Mutations can be caused by several factors. • Replication errors can cause mutations. • Mutagens, such as UV ray and chemicals, can cause mutations. • Some cancer drugs use mutagenic properties to kill ...
... Mutations can be caused by several factors. • Replication errors can cause mutations. • Mutagens, such as UV ray and chemicals, can cause mutations. • Some cancer drugs use mutagenic properties to kill ...
World.GeographyWeek2Extension
... When the study of human origins intensified in the 20th century, two main theories emerged to explain the archaeological and fossil record: one, known as the multi-regional hypothesis, suggested that a species of human ancestor dispersed throughout the globe, and modern humans evolved from this pred ...
... When the study of human origins intensified in the 20th century, two main theories emerged to explain the archaeological and fossil record: one, known as the multi-regional hypothesis, suggested that a species of human ancestor dispersed throughout the globe, and modern humans evolved from this pred ...
The Hardy-Weinberg equation can test whether a population is
... explanation of descent with modification, evolution by the mechanism of natural selection – It noted that as organisms spread into various habitats over millions of years, they accumulated diverse adaptations that fit them to specific ways of life in these ...
... explanation of descent with modification, evolution by the mechanism of natural selection – It noted that as organisms spread into various habitats over millions of years, they accumulated diverse adaptations that fit them to specific ways of life in these ...
The Evolution of Populations CHAPTER 23 Microevolution Change
... The average percentage of loci that are heterozygous ...
... The average percentage of loci that are heterozygous ...
Blueprint of Life #2
... the scientific community that supported evolution. What was missing was a plausible mechanism to explain how evolution was occurring. Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace independently arrived at evolution as a result of natural selection. By the early 1840s, he had documented the main points of his ...
... the scientific community that supported evolution. What was missing was a plausible mechanism to explain how evolution was occurring. Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace independently arrived at evolution as a result of natural selection. By the early 1840s, he had documented the main points of his ...
Factors Affecting Gene Frequency handout - Mr. Lesiuk
... -If a small group of individuals is separated from the main group, they may have a different frequency of alleles in their gene pool. -As the population grows, this frequency may be much different from the main group. Frequency CHANGED 5. Random Genetic Drift: -Occurs in small populations -Chance ma ...
... -If a small group of individuals is separated from the main group, they may have a different frequency of alleles in their gene pool. -As the population grows, this frequency may be much different from the main group. Frequency CHANGED 5. Random Genetic Drift: -Occurs in small populations -Chance ma ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.























