Earthquakes: fault classification, terminology, stress
... Japan was prepared. The earthquake and tsunami caused so much destruction that emergency services and education of population were not enough to save many lives. ...
... Japan was prepared. The earthquake and tsunami caused so much destruction that emergency services and education of population were not enough to save many lives. ...
Weathering and Erosion
... True or False: The Earth’s surface has stayed the same for thousands of years. Think about the statement in the box above. Do you think it is a true statement or a false statement? Circle True or False on Journal Jam #10. ...
... True or False: The Earth’s surface has stayed the same for thousands of years. Think about the statement in the box above. Do you think it is a true statement or a false statement? Circle True or False on Journal Jam #10. ...
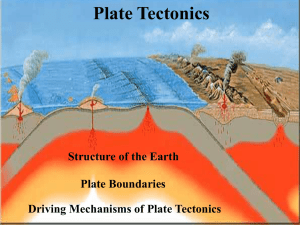
Modern Plate Tectonics
... slope to drive the plates laterally. Once the crust has cooled, having been pushed away form the ridge, it sinks into the upper mantle and helps to pull adjacent crust along. This pushing and pulling provides the forces that drive ...
... slope to drive the plates laterally. Once the crust has cooled, having been pushed away form the ridge, it sinks into the upper mantle and helps to pull adjacent crust along. This pushing and pulling provides the forces that drive ...
Modern Plate Tectonics
... The types of boundary between plates are distinguished by the type of relative plate motion along the boundary: Oceanic Ridge – Divergence ...
... The types of boundary between plates are distinguished by the type of relative plate motion along the boundary: Oceanic Ridge – Divergence ...
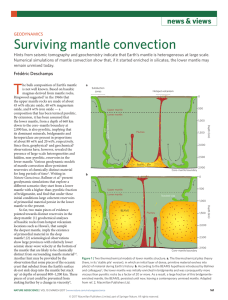
Geodynamics: Surviving mantle convection
... mantle with a higher-than-pyrolitic fraction of bridgmanite, and find that under these initial conditions large coherent reservoirs of primordial material persist in the lower mantle to the present. So far, two main pieces of evidence pointed towards distinct reservoirs in the deep mantle: (1) geoch ...
... mantle with a higher-than-pyrolitic fraction of bridgmanite, and find that under these initial conditions large coherent reservoirs of primordial material persist in the lower mantle to the present. So far, two main pieces of evidence pointed towards distinct reservoirs in the deep mantle: (1) geoch ...
A seismic refraction study of the Cocos plate offshore Nicaragua and
... Water budget of subduc?on zones ...
... Water budget of subduc?on zones ...
Mode of opening of pull-‐apart basins
... long distance correlaCon with an ODP Site Ø Consistent with the age of the OFZ ...
... long distance correlaCon with an ODP Site Ø Consistent with the age of the OFZ ...
Plate Tectonics Rock Powerpoint
... • Oceanic plate colliding with a less dense continental plate • Oceanic plate moves beneath the continental plate; it melts into mantle. • Volcanoes (mountains), trenches, earthquakes occur at ...
... • Oceanic plate colliding with a less dense continental plate • Oceanic plate moves beneath the continental plate; it melts into mantle. • Volcanoes (mountains), trenches, earthquakes occur at ...
Inside Earth Notes
... Africa, India, Australia, and Antarctica. The seeds would be to large to have been carried to the continents as they are today. ...
... Africa, India, Australia, and Antarctica. The seeds would be to large to have been carried to the continents as they are today. ...
Review for Exam 32 & 33
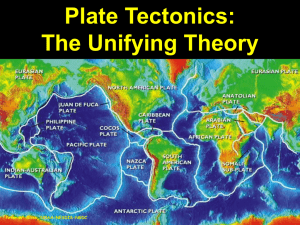
... The plates move in conveyor-belt fashion as new crust is generated at the continental margins and destroyed at the mid-ocean ridge The lithosphere is broken up into large palates that move as the result of convection within the asthenosphere Earthquakes & volcanic activity results from convection mo ...
... The plates move in conveyor-belt fashion as new crust is generated at the continental margins and destroyed at the mid-ocean ridge The lithosphere is broken up into large palates that move as the result of convection within the asthenosphere Earthquakes & volcanic activity results from convection mo ...
File - Mr Vincent Science
... mixed in the trench by the faulting and folding caused as they are scraped from the down-going oceanic plate. The southern line of islands of the Indonesian Archipelago is a good example of this type. 2. Those formed of chains of explosive volcanoes. These volcanoes form from andesitic magmas that a ...
... mixed in the trench by the faulting and folding caused as they are scraped from the down-going oceanic plate. The southern line of islands of the Indonesian Archipelago is a good example of this type. 2. Those formed of chains of explosive volcanoes. These volcanoes form from andesitic magmas that a ...
Chapter 20 PowerPoint
... • Orogeny is the cycle of processes that form mountain belts. Most mountain belts are associated with plate boundaries. • Island arc complexes are volcanic mountains that form as a result of the convergence of two oceanic plates. • Highly deformed mountains with deep roots may form as a result of th ...
... • Orogeny is the cycle of processes that form mountain belts. Most mountain belts are associated with plate boundaries. • Island arc complexes are volcanic mountains that form as a result of the convergence of two oceanic plates. • Highly deformed mountains with deep roots may form as a result of th ...
Geology
... D is for Deposition: There are three kinds of rocks. Igneous rocks are formed from molten rock. Metamorphic rocks are formed as a result of great pressure. Sedimentary rock is formed as a result of heating and cooling and eroding of soil and rock, as a result of temperature changes, as a result of ...
... D is for Deposition: There are three kinds of rocks. Igneous rocks are formed from molten rock. Metamorphic rocks are formed as a result of great pressure. Sedimentary rock is formed as a result of heating and cooling and eroding of soil and rock, as a result of temperature changes, as a result of ...
CHAPTER 19 - PLATE TECTONICS
... indicate that earthquakes only occur between offset sections of ridge crests, called transform faults, that exhibit motion away from the crests, exactly opposite of their apparent strike-slip offset. Discussion moves to the detailed description of plate boundaries. Diverging plate boundaries create ...
... indicate that earthquakes only occur between offset sections of ridge crests, called transform faults, that exhibit motion away from the crests, exactly opposite of their apparent strike-slip offset. Discussion moves to the detailed description of plate boundaries. Diverging plate boundaries create ...
Unit 7 Lesson 1 Forces that Change the Earth
... divergent plate boundary under the ocean sea-floor spreading: the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor deep-ocean trench: a deep valley along the ocean floor beneath which oceanic crust slowly sinks toward the mantle subduction: the process by which oceanic crus ...
... divergent plate boundary under the ocean sea-floor spreading: the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor deep-ocean trench: a deep valley along the ocean floor beneath which oceanic crust slowly sinks toward the mantle subduction: the process by which oceanic crus ...
MS Word file ()
... Due date: see greensheet or information at top of your learning group discussion for this activity in Canvas. Parts of this exercise were adapted from the Natural Sciences 412D class at SDSU, which is available at http://www.showmegeology.org/seismic-eruption_1.htm) Objective: (a) Understand about t ...
... Due date: see greensheet or information at top of your learning group discussion for this activity in Canvas. Parts of this exercise were adapted from the Natural Sciences 412D class at SDSU, which is available at http://www.showmegeology.org/seismic-eruption_1.htm) Objective: (a) Understand about t ...
Divergent Margins
... Earth is broken into various plates. These plates drift on the asthenosphere at very slow rates. As plates move away from each other the lithosphere thins and tears. At these divergent plate boundaries new oceanic lithosphere is created in the gaps from upwelling magma from the mantle. This upwellin ...
... Earth is broken into various plates. These plates drift on the asthenosphere at very slow rates. As plates move away from each other the lithosphere thins and tears. At these divergent plate boundaries new oceanic lithosphere is created in the gaps from upwelling magma from the mantle. This upwellin ...
Plate Tectonics Scavenger Hunt
... Name the four layers of Earth and classify each one as solid or liquid. Layer Solid or Liquid ...
... Name the four layers of Earth and classify each one as solid or liquid. Layer Solid or Liquid ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... When two plates of continental crust collide and crumple up, tall mountain ranges may form. Earthquakes are common at these convergent boundaries. Volcanoes do not form, however, because there is little or no subduction when two continental plates collide. ...
... When two plates of continental crust collide and crumple up, tall mountain ranges may form. Earthquakes are common at these convergent boundaries. Volcanoes do not form, however, because there is little or no subduction when two continental plates collide. ...
Lec-07 - nptel
... Most of the Earth's mass is in the mantle, which is composed of iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O) silicate compounds. At over 1000 degrees C, the mantle is solid but can deform slowly in a plastic manner. The crust is much thinner than any of the other layers, an ...
... Most of the Earth's mass is in the mantle, which is composed of iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O) silicate compounds. At over 1000 degrees C, the mantle is solid but can deform slowly in a plastic manner. The crust is much thinner than any of the other layers, an ...
Student Study Guide
... - Densities in the interior of Earth must be very high since the average density of Earth is almost twice as great as the average density of the crust. - The interior must consist of roughly spherical homogeneous layers since Earth doesn’t wobble much as it rotates and the value of gravity over the ...
... - Densities in the interior of Earth must be very high since the average density of Earth is almost twice as great as the average density of the crust. - The interior must consist of roughly spherical homogeneous layers since Earth doesn’t wobble much as it rotates and the value of gravity over the ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.