7th Grade Science Unit 3 Vocabulary Uniformitarianism
... Trace Fossil- A fossilized structure, such as a footprint or coprolite, that formed in sedimentary rock by animal activity on or within soft sediment. ...
... Trace Fossil- A fossilized structure, such as a footprint or coprolite, that formed in sedimentary rock by animal activity on or within soft sediment. ...
Chapter One – Fire and Ice
... and heavier from new snowfall. Snow is compressed by its own weight. Weight changes the structure of the snow. Snow crystals will start to fit tightly together to form layers of ice. As this ice thickens, its weight increases changing the layers into a solid mass of ice. Gravity begins to move the t ...
... and heavier from new snowfall. Snow is compressed by its own weight. Weight changes the structure of the snow. Snow crystals will start to fit tightly together to form layers of ice. As this ice thickens, its weight increases changing the layers into a solid mass of ice. Gravity begins to move the t ...
Weathering, Erosion, & Deposition
... The movement of weathered earth materials by moving water, wind, gravity or ice (glaciers) ...
... The movement of weathered earth materials by moving water, wind, gravity or ice (glaciers) ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Chapter 9: Plate Tectonics Section 9.1
... Rift Valley- deep vaulted structure found along the axes of divergent plate boundaries; rift valleys can develop on the seafloor or on land Seafloor Spreading- the process by which plate tectonics produces new oceanic lithosphere at ocean ridges Subduction Zone- a destructive plate margin where ocea ...
... Rift Valley- deep vaulted structure found along the axes of divergent plate boundaries; rift valleys can develop on the seafloor or on land Seafloor Spreading- the process by which plate tectonics produces new oceanic lithosphere at ocean ridges Subduction Zone- a destructive plate margin where ocea ...
The Sea Floor
... Matter expanded into space. Earth and Solar system originated from a cloud or clouds of dust. Dust particles collided with each other – those larger particles collided with one another – then those larger particles collided with one another, and so on… ...
... Matter expanded into space. Earth and Solar system originated from a cloud or clouds of dust. Dust particles collided with each other – those larger particles collided with one another – then those larger particles collided with one another, and so on… ...
Oceanography Final Exam Review Guide Fall Semester Name Date
... 87. The largest fish on the planet is actually the _________________________. 88. The largest shark on the planet is the _____________________________. 89. Turtles named for the color of their fat - ________________________. 90. Turtle shells used for jewelry - ___________________________. 91. These ...
... 87. The largest fish on the planet is actually the _________________________. 88. The largest shark on the planet is the _____________________________. 89. Turtles named for the color of their fat - ________________________. 90. Turtle shells used for jewelry - ___________________________. 91. These ...
Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
... The pattern of convection for internal heating is different from bottom heating. ...
... The pattern of convection for internal heating is different from bottom heating. ...
End Of Course Exam 7th Grade Review Answer Key
... 18. Describe the three types of plate boundaries. Divergent moves away, Convergent comes together, transform slides past each other. 19. What boundary would create mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes? Convergent ...
... 18. Describe the three types of plate boundaries. Divergent moves away, Convergent comes together, transform slides past each other. 19. What boundary would create mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes? Convergent ...
7-1 Inside the Earth RG
... 5. Oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust because it contains more of which three elements? ...
... 5. Oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust because it contains more of which three elements? ...
For the Student
... It seems that the more we know about the earth, the more questions we have. It is difficult to visualize a three dimensional earth on two-dimensional paper. In this activity, you will construct a three dimensional model of part of the earth’s surface. Recall that scientists now think that the earth’ ...
... It seems that the more we know about the earth, the more questions we have. It is difficult to visualize a three dimensional earth on two-dimensional paper. In this activity, you will construct a three dimensional model of part of the earth’s surface. Recall that scientists now think that the earth’ ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes Page
... Indian & Asian plates -> HIMALAYAS One plate may move beneath Transform Boundary: Plates slide past each other •Lithosphere isn’t created or destroyed •Rock shatters •Many shallow earthquakes (San Andreas Fault) •Separates Pacific & North American Plates Paleomagnetism Confirms Plate Tectonics•Mag ...
... Indian & Asian plates -> HIMALAYAS One plate may move beneath Transform Boundary: Plates slide past each other •Lithosphere isn’t created or destroyed •Rock shatters •Many shallow earthquakes (San Andreas Fault) •Separates Pacific & North American Plates Paleomagnetism Confirms Plate Tectonics•Mag ...
Read extract - Diane Mitchell
... Complicating things is the relatively small Juan de Fuca oceanic plate which sits between the North American and Pacific plates (west of British Columbia, Washington and Oregon). This small plate collides with, and sinks beneath, North America. The plate boundary lies offshore. When earthquakes hit ...
... Complicating things is the relatively small Juan de Fuca oceanic plate which sits between the North American and Pacific plates (west of British Columbia, Washington and Oregon). This small plate collides with, and sinks beneath, North America. The plate boundary lies offshore. When earthquakes hit ...
Coasts – Chapter 10
... Changes in sea level: eustatic • Several factors can influence global, or eustatic sea level variations – Sea level is lower during periods of glaciation (more water held up in ice) and higher during warm periods (when glaciers are smaller) – High rates of seafloor spreading produce larger rises, d ...
... Changes in sea level: eustatic • Several factors can influence global, or eustatic sea level variations – Sea level is lower during periods of glaciation (more water held up in ice) and higher during warm periods (when glaciers are smaller) – High rates of seafloor spreading produce larger rises, d ...
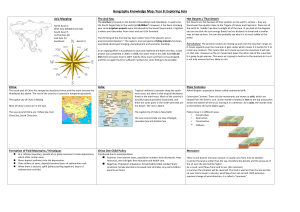
Geography Knowledge Map: Year 8: Exploring Asia
... In winter the land is colder than the sea, therefore the density and the pressure of the air over the land will be higher. As a result, wind flows from land to sea. (No monsoon) In summer the situation will be reversed. The land is warmer than the sea and the air over land is lower in density; wind ...
... In winter the land is colder than the sea, therefore the density and the pressure of the air over the land will be higher. As a result, wind flows from land to sea. (No monsoon) In summer the situation will be reversed. The land is warmer than the sea and the air over land is lower in density; wind ...
calaisgsa
... stopped, although at a slow and decaying rate Maximum stress that can be transferred into the upper crust from viscoelastic relaxation following a large earthquake more than one order of magnitude less than typical stress drop value ...
... stopped, although at a slow and decaying rate Maximum stress that can be transferred into the upper crust from viscoelastic relaxation following a large earthquake more than one order of magnitude less than typical stress drop value ...
Recent Rapid Uplift of Today`s Mountains
... volcanism, and erosion that sculpt mountains. In their book they repeatedly relate how geological features they and other fellow geomorphologists observe in the field fail to match the explanations of their theorist colleagues. Yet in the end they offer no suggestion as to how the disparity between ...
... volcanism, and erosion that sculpt mountains. In their book they repeatedly relate how geological features they and other fellow geomorphologists observe in the field fail to match the explanations of their theorist colleagues. Yet in the end they offer no suggestion as to how the disparity between ...
Rocks and Glaciers A Story of Sedimentation
... Overthrust Fault, pushed rocks in some places as much as 50 to 60 miles from west to east. The old rocks ended up on top of much younger rocks. Over millions of years, running water, and the passage of large Ice Age glaciers, carved the rugged peaks and deep valleys of Glacier National Park. This is ...
... Overthrust Fault, pushed rocks in some places as much as 50 to 60 miles from west to east. The old rocks ended up on top of much younger rocks. Over millions of years, running water, and the passage of large Ice Age glaciers, carved the rugged peaks and deep valleys of Glacier National Park. This is ...
UNIT C - apel slice
... surface looks. In dry areas and along sandy coasts, soil is dry and loose. There aren't many plants. Wind lifts particles and carries them. Wind slams sand into rocky surfaces. The wind-blown sand makes pits and grooves in rock. Wind also carries sand and deposits it in dunes, as you learned in Less ...
... surface looks. In dry areas and along sandy coasts, soil is dry and loose. There aren't many plants. Wind lifts particles and carries them. Wind slams sand into rocky surfaces. The wind-blown sand makes pits and grooves in rock. Wind also carries sand and deposits it in dunes, as you learned in Less ...
Plate Tectonics U2L4 Cloze Name: ______ 1. The supercontinent
... 1. The supercontinent called ________ formed 300 million years ago and began to break up 200 million years ago. 2. The process by which new oceanic lithosphere sea floor forms when magma rises to Earth’s surface, called ________ _________, occurs at mid-ocean ridges and solidifies, as older existing ...
... 1. The supercontinent called ________ formed 300 million years ago and began to break up 200 million years ago. 2. The process by which new oceanic lithosphere sea floor forms when magma rises to Earth’s surface, called ________ _________, occurs at mid-ocean ridges and solidifies, as older existing ...
Unit 5 - mrhebert.org
... India was once part of Antarctica, which broke off and collided with Eurasia, putting the fossils of trilobites, from the bottom of the sea, high into the Himalayans! ...
... India was once part of Antarctica, which broke off and collided with Eurasia, putting the fossils of trilobites, from the bottom of the sea, high into the Himalayans! ...
Ice Sheets: Lithosphere
... glacial erosion and deposition. Troughs, hanging valleys, narrow rock peaks, cirques, high relief mountains, and lakes are just some of the specific land features that Sugden described. A>E>L With the increase in global warming, the rate of ice sheet melting also increases. Greenland's ice, for exam ...
... glacial erosion and deposition. Troughs, hanging valleys, narrow rock peaks, cirques, high relief mountains, and lakes are just some of the specific land features that Sugden described. A>E>L With the increase in global warming, the rate of ice sheet melting also increases. Greenland's ice, for exam ...
Document
... The Colorado River has cut down through these gently uplifted sedimentary layers to form the Grand Canyon, which is a mile deep. c. Removal of immense weight from the crustal surface results in an upward adjustment of the continental crust known as isostatic rebound. Remember, the crust floats in up ...
... The Colorado River has cut down through these gently uplifted sedimentary layers to form the Grand Canyon, which is a mile deep. c. Removal of immense weight from the crustal surface results in an upward adjustment of the continental crust known as isostatic rebound. Remember, the crust floats in up ...
Printer-friendly Version - Solid Earth Discussions
... Swedan also gives ridge push of 1.61*10ˆ12 N/m, again of the same order of magnitude as earlier work. That is of course about 1/3 of his own slab pull, so I do not understand why he implies (p.137 l.3 and l.22, p.139 l.3) that ridge push is what drives plate tectonics. In line 3 he also says it will ...
... Swedan also gives ridge push of 1.61*10ˆ12 N/m, again of the same order of magnitude as earlier work. That is of course about 1/3 of his own slab pull, so I do not understand why he implies (p.137 l.3 and l.22, p.139 l.3) that ridge push is what drives plate tectonics. In line 3 he also says it will ...
Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics
... Subduction – when one tectonic plate can sink under another platecrust gets recycled back into the mantle ...
... Subduction – when one tectonic plate can sink under another platecrust gets recycled back into the mantle ...
Plate Tectonics
... •1. Away from each other –Found underneath oceans •2. Towards each other •3. Side by side ...
... •1. Away from each other –Found underneath oceans •2. Towards each other •3. Side by side ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.