Chapter 3 Test Review
... continental drift? • A. the existence of convection currents • B. the matching of glacial grooves on ...
... continental drift? • A. the existence of convection currents • B. the matching of glacial grooves on ...
Day Starter Quizzes
... where an oceanic plate is forced beneath a second plate where an oceanic plate grinds past a second plate where a continental plate grinds past a second plate where an oceanic plate moves away from a second plate ...
... where an oceanic plate is forced beneath a second plate where an oceanic plate grinds past a second plate where a continental plate grinds past a second plate where an oceanic plate moves away from a second plate ...
The Dynamic Earth Section 1
... can occur on land or in the sea. • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are either colliding or separating from one another. • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean. ...
... can occur on land or in the sea. • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are either colliding or separating from one another. • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean. ...
A Model of Earth`s Interior
... The studies of seismic waves indicate that the Earth is composed of many layers. The crust is the outermost part of the Earth below the atmosphere or hydrosphere. This layer is mostly solid rock, but includes soil and eroded/weathered rock. ~ The crust is divided into two major divisions: continenta ...
... The studies of seismic waves indicate that the Earth is composed of many layers. The crust is the outermost part of the Earth below the atmosphere or hydrosphere. This layer is mostly solid rock, but includes soil and eroded/weathered rock. ~ The crust is divided into two major divisions: continenta ...
Plate Tectonics
... If oceanic crust is pulling apart from oceanic crust then new crust will made. This means that in some places the sea floor is actually growing! This is a process called sea floor spreading. This is happening along the midAtlantic ridge between the UK and America too. Small chains of islands are cre ...
... If oceanic crust is pulling apart from oceanic crust then new crust will made. This means that in some places the sea floor is actually growing! This is a process called sea floor spreading. This is happening along the midAtlantic ridge between the UK and America too. Small chains of islands are cre ...
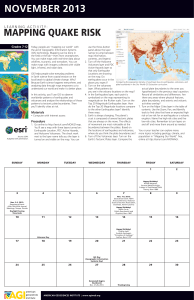
Earthquake risk - EdCommunity
... risk or low risk for an earthquake or a volcanic crust is composed of several tectonic plates eruption. Name five high-risk cities and five that are always on the move. The effects low-risk cities. Remember to turn layers on of movement are most noticeable at the and off and move them around as need ...
... risk or low risk for an earthquake or a volcanic crust is composed of several tectonic plates eruption. Name five high-risk cities and five that are always on the move. The effects low-risk cities. Remember to turn layers on of movement are most noticeable at the and off and move them around as need ...
How Diamonds Are Formed
... Formation of diamond requires very high temperature and pressure. These conditions occur in limited zone of the Earth’s mantle about 90 miles below the surface where the temperatures are at least 2000 degrees Fahrenheit. This environment is thought to be present in the mantle only beneath the stabl ...
... Formation of diamond requires very high temperature and pressure. These conditions occur in limited zone of the Earth’s mantle about 90 miles below the surface where the temperatures are at least 2000 degrees Fahrenheit. This environment is thought to be present in the mantle only beneath the stabl ...
Tectonic Map of the World
... If oceanic crust is pulling apart from oceanic crust then new crust will made. This means that in some places the sea floor is actually growing! This is a process called sea floor spreading. This is happening along the midAtlantic ridge between the UK and America too. Small chains of islands are cre ...
... If oceanic crust is pulling apart from oceanic crust then new crust will made. This means that in some places the sea floor is actually growing! This is a process called sea floor spreading. This is happening along the midAtlantic ridge between the UK and America too. Small chains of islands are cre ...
SECTION II The Physical World: The Earth, Climate and Water
... - with the earthquakes layer on top of the others, the plate boundaries are obscured; to allow us to see these boundaries more clearly, drag the earthquakes layer to the bottom of the list of layers in the TOC; the earthquakes that you found in the query building step should remain on top and be eas ...
... - with the earthquakes layer on top of the others, the plate boundaries are obscured; to allow us to see these boundaries more clearly, drag the earthquakes layer to the bottom of the list of layers in the TOC; the earthquakes that you found in the query building step should remain on top and be eas ...
Geochemistry and petrogenesis of extrusive rocks, dykes and high
... The MgO content of the metabasalts ranges from 5.6 to 7.9 wt%, with the majority (93.8%) in the 6.1 to 7.3 wt% interval (Fig. 4). The concentrations of other elements vary significantly at a given MgO content. The regression lines (least squares linear) of the major and trace elements, all definin � ...
... The MgO content of the metabasalts ranges from 5.6 to 7.9 wt%, with the majority (93.8%) in the 6.1 to 7.3 wt% interval (Fig. 4). The concentrations of other elements vary significantly at a given MgO content. The regression lines (least squares linear) of the major and trace elements, all definin � ...
File - tallisA2units
... You need to draw together a selection of detailed information about the causes of tectonic activity, and subsequently about a range of different landscape features that they create over time. It is vital that you have real world examples of these features which you can describe and name. You will be ...
... You need to draw together a selection of detailed information about the causes of tectonic activity, and subsequently about a range of different landscape features that they create over time. It is vital that you have real world examples of these features which you can describe and name. You will be ...
APS Continental Crust RLR.pptx
... Felsic crustal material removed from upper plate by subduction erosion is relaminated to the ...
... Felsic crustal material removed from upper plate by subduction erosion is relaminated to the ...
Wednesday Sept 8th
... YES!! The density of the plates determines which will be on top after a collision. More dense sinks Less dense goes on top ...
... YES!! The density of the plates determines which will be on top after a collision. More dense sinks Less dense goes on top ...
Metamorphic Notes
... Prevalent in intensely deformed mountain ranges May occur over wide temperature range Higher pressure and temperature will produce increased metamorphic grade – Prograde metamorphism of shale produces: • slate • phyllite • schist • gneiss ...
... Prevalent in intensely deformed mountain ranges May occur over wide temperature range Higher pressure and temperature will produce increased metamorphic grade – Prograde metamorphism of shale produces: • slate • phyllite • schist • gneiss ...
What Earth Scientists Do
... climate; solar radiation and its effects; and the role of atmospheric chemistry in ozone depletion, climate change, and pollution. Economic geologists explore for and develop metallic and nonmetallic resources; they study mineral deposits and find environmentally safe ways to dispose of waste materi ...
... climate; solar radiation and its effects; and the role of atmospheric chemistry in ozone depletion, climate change, and pollution. Economic geologists explore for and develop metallic and nonmetallic resources; they study mineral deposits and find environmentally safe ways to dispose of waste materi ...
Slide 1
... • As the plate sinks into the mantle, it melts and becomes magma. The magma rises through the continental plate and forms a volcanic chain ...
... • As the plate sinks into the mantle, it melts and becomes magma. The magma rises through the continental plate and forms a volcanic chain ...
File
... Earth’s surface. Most volcanic rock is extrusive. Contains either very small crystals or none at all because it cools quickly 3 examples of Extrusive Igneous Rocks are Pumice; Obsidian; Basalt Fissures – long cracks in the Earth’s surface form which lava sometimes flows Lava plateau – when a ...
... Earth’s surface. Most volcanic rock is extrusive. Contains either very small crystals or none at all because it cools quickly 3 examples of Extrusive Igneous Rocks are Pumice; Obsidian; Basalt Fissures – long cracks in the Earth’s surface form which lava sometimes flows Lava plateau – when a ...
Moving and Shaking: Tectonic Plates and Geological Events
... 3. Push your hands slowly towards each while observing what occurs at the plate boundary. 4. Draw and record your observations ...
... 3. Push your hands slowly towards each while observing what occurs at the plate boundary. 4. Draw and record your observations ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.