Earth Science Chapter 5 - alisa25k
... • Blasts from the Earth have brought rocks from 100 ft to the surface ...
... • Blasts from the Earth have brought rocks from 100 ft to the surface ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... There are places on Earth that are so hot that rocks melt to form magma. Because magma is liquid and usually less dense than surrounding solid rock, it moves upward to cooler regions of the Earth. As the magma loses heat, it cools and crystallizes into an igneous rock. Magma can cool on the Earth's ...
... There are places on Earth that are so hot that rocks melt to form magma. Because magma is liquid and usually less dense than surrounding solid rock, it moves upward to cooler regions of the Earth. As the magma loses heat, it cools and crystallizes into an igneous rock. Magma can cool on the Earth's ...
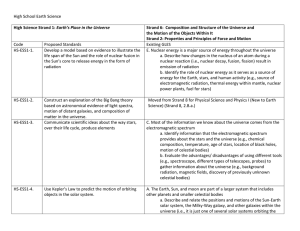
HS Earth Science Crosswalk
... a. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer b. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer 2. Earth’s Systems (geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) interact with one another as they undergo change by co ...
... a. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer b. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer 2. Earth’s Systems (geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) interact with one another as they undergo change by co ...
Igneous Environments
... 6. Magma that reaches the surface erupts as lava (molten rock that flows on the surface) or as volcanic ash. Volcanic ash forms when dissolved gases in the magma expand and blow the magma apart into small fragments of volcanic glass. Any igneous rock that forms on the surface is called an extrusive r ...
... 6. Magma that reaches the surface erupts as lava (molten rock that flows on the surface) or as volcanic ash. Volcanic ash forms when dissolved gases in the magma expand and blow the magma apart into small fragments of volcanic glass. Any igneous rock that forms on the surface is called an extrusive r ...
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
... body under the influence of deforming stress • Usually occurs along sub-planar surfaces that separate zones of coherent material ...
... body under the influence of deforming stress • Usually occurs along sub-planar surfaces that separate zones of coherent material ...
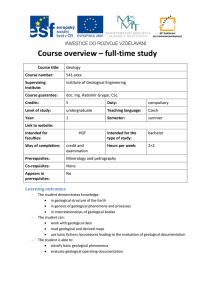
Course overview – full
... Earth. Earth's continental and oceanic crust, its origin and development. Fundamentals of the theory of isostasy. The pressure in the Earth’s body. Natural stress field, stress redistribution. Thermal field of the Earth. 3) The theory of lithospheric plates. 4) The theory of the layer and strata - L ...
... Earth. Earth's continental and oceanic crust, its origin and development. Fundamentals of the theory of isostasy. The pressure in the Earth’s body. Natural stress field, stress redistribution. Thermal field of the Earth. 3) The theory of lithospheric plates. 4) The theory of the layer and strata - L ...
Forces of Change
... breaks down rocks Erosion- Ground surface moved from one place to another (wind /water /glaciers) Human Factors – Entertainment, Urbanization, Mining, Deforestation Volcanism - ...
... breaks down rocks Erosion- Ground surface moved from one place to another (wind /water /glaciers) Human Factors – Entertainment, Urbanization, Mining, Deforestation Volcanism - ...
Earth`s Spheres - Warren Hills Regional School District
... like the plates of Earth’s crust. These plates move about 2 to 15 centimeters (1 to 6 inches) per year. This movement has influenced Earth’s climate and life’s evolution as the continents have combined, separated, and recombined. By studying ancient rock formations throughout the world, geologists h ...
... like the plates of Earth’s crust. These plates move about 2 to 15 centimeters (1 to 6 inches) per year. This movement has influenced Earth’s climate and life’s evolution as the continents have combined, separated, and recombined. By studying ancient rock formations throughout the world, geologists h ...
File
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be _____Denser_______ and ____Thinner_________ than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or _______subducted_________, beneat ...
... Subduction Zones and Volcanoes At some convergent boundaries, an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust tends to be _____Denser_______ and ____Thinner_________ than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or _______subducted_________, beneat ...
Ch7 Atmospheric Energy and Moisture Pt1
... more rapidly and will not condense. • Cold air holds less water vapor because the water molecules are moving less and are more likely to condense. ...
... more rapidly and will not condense. • Cold air holds less water vapor because the water molecules are moving less and are more likely to condense. ...
m5zn_f0d6cf6f44fce87
... A seismic survey is usually the last exploration step before drilling the well. It is the most expensive exploration method. Seismic surveys account for 90% of the budget spent in petroleum exploration. It provides precise details on the formations beneath the earth surface. ...
... A seismic survey is usually the last exploration step before drilling the well. It is the most expensive exploration method. Seismic surveys account for 90% of the budget spent in petroleum exploration. It provides precise details on the formations beneath the earth surface. ...
Igneous Petrology
... Magma: a mixture of a melt (predominantly silicate) ± crystals ± volatiles which occurs at depths and has the ability to migrate to shallower levels where it either crystallizes at depth giving rise to igneous intrusions, or erupts at the surface to form volcanic rocks. The magma occur in equilibriu ...
... Magma: a mixture of a melt (predominantly silicate) ± crystals ± volatiles which occurs at depths and has the ability to migrate to shallower levels where it either crystallizes at depth giving rise to igneous intrusions, or erupts at the surface to form volcanic rocks. The magma occur in equilibriu ...
- mrsolson.com
... I can draw a cross section of each of the 3 types of volcanoes and can describe how each was formed (lava flow or ash & cinders). I can identify and describe the types of intrusive igneous rocks that can form (sill, dike, volcanic neck, batholith). I can describe how a hot spot can create volcanoes ...
... I can draw a cross section of each of the 3 types of volcanoes and can describe how each was formed (lava flow or ash & cinders). I can identify and describe the types of intrusive igneous rocks that can form (sill, dike, volcanic neck, batholith). I can describe how a hot spot can create volcanoes ...
7th Grade Study Guide for Semester Test
... 19. A scientific __law__ is a statement that describes what scientists expect to happen every time under a particular set of conditions. ...
... 19. A scientific __law__ is a statement that describes what scientists expect to happen every time under a particular set of conditions. ...
File
... Fog Fog is defined as a cloud with its base at or very near the ground. Fog Caused by Cooling • As the air cools, it becomes denser and drains into low areas such as river valleys, where thick fog accumulations may occur. ...
... Fog Fog is defined as a cloud with its base at or very near the ground. Fog Caused by Cooling • As the air cools, it becomes denser and drains into low areas such as river valleys, where thick fog accumulations may occur. ...
chapter8_ARCHEAN
... Many geologists think that Archean plates moved faster than plates do now because Earth possessed more radiogenic heat. Small cratons would have grown more rapidly to become larger continents. Several small cratons existed, 30-40% of present continental crust existed. We did not however, have si ...
... Many geologists think that Archean plates moved faster than plates do now because Earth possessed more radiogenic heat. Small cratons would have grown more rapidly to become larger continents. Several small cratons existed, 30-40% of present continental crust existed. We did not however, have si ...
Ontstaan en hoogtepunten
... Through this time, Gondwana experienced a number of climate changes, due in part to the movement of Earth's techtonic plates which formed and ultimately broke it up. Africa broke off first, followed by South America and India I always thought that New Zealand broke away from Australia - they seem to ...
... Through this time, Gondwana experienced a number of climate changes, due in part to the movement of Earth's techtonic plates which formed and ultimately broke it up. Africa broke off first, followed by South America and India I always thought that New Zealand broke away from Australia - they seem to ...
RP 3E2 Land and Water Features
... depleted, making it more and more difficult and expensive to obtain those minerals. Fresh water is an essential resource for daily life and industrial processes. We obtain our water from rivers and lakes and from water that moves below the earth's surface. This groundwater, which is a major source f ...
... depleted, making it more and more difficult and expensive to obtain those minerals. Fresh water is an essential resource for daily life and industrial processes. We obtain our water from rivers and lakes and from water that moves below the earth's surface. This groundwater, which is a major source f ...
Chapter 2
... moving away from mid-ocean ridges • As oceanic crust gets older, it cools and becomes denser, therefore sinking a little lower into mantle • Weight of sediments on plate also cause it to sink a little into mantle Figure 2.22 ...
... moving away from mid-ocean ridges • As oceanic crust gets older, it cools and becomes denser, therefore sinking a little lower into mantle • Weight of sediments on plate also cause it to sink a little into mantle Figure 2.22 ...
Test 3, 2nd Quarter: Rocks
... 13. The holes within an igneous rock, if present, are caused by a. Small worms burrowing through the rock b. The contraction of the rock during cooling c. The expansion and release of hot gases as the rock is cooling d. Parts of the rock dissolving after it forms e. None of the above 14. An igneous ...
... 13. The holes within an igneous rock, if present, are caused by a. Small worms burrowing through the rock b. The contraction of the rock during cooling c. The expansion and release of hot gases as the rock is cooling d. Parts of the rock dissolving after it forms e. None of the above 14. An igneous ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.