Climate
... NH is tilted most toward the Sun – longest day of the year and shortest night (Summer Solstice – June 21st) NH is tilted most away from the sun – longest night of the year and shortest day (Winter Solstice – December 21st) Day and night are = o Autumnal Equinox – September 21st o Vernal Equinox – Ma ...
... NH is tilted most toward the Sun – longest day of the year and shortest night (Summer Solstice – June 21st) NH is tilted most away from the sun – longest night of the year and shortest day (Winter Solstice – December 21st) Day and night are = o Autumnal Equinox – September 21st o Vernal Equinox – Ma ...
Weather and Climate - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets
... 11. The state of the earth's atmosphere at a certain time and place is called http://www.helpteaching.com/tests/159771/weather-and-climate ...
... 11. The state of the earth's atmosphere at a certain time and place is called http://www.helpteaching.com/tests/159771/weather-and-climate ...
ESCI 106 – Weather and Climate Lecture 1
... “air”. The molecules have lots of energy and that energy is not necessarily in ‘heat’ energy. Thus, the temperature is high due to the interactions of the energized molecules bumping into one ...
... “air”. The molecules have lots of energy and that energy is not necessarily in ‘heat’ energy. Thus, the temperature is high due to the interactions of the energized molecules bumping into one ...
Science 10 - TheScienceWoman
... 2. Explain the movement of three types of seismic waves (primary, secondary, and surface waves) through the layers of the earth’s crust 3. � describe tectonic plate boundaries, including - transform boundaries - divergent boundaries - convergent boundaries (oceanic-oceanic, oceanic-continental, and ...
... 2. Explain the movement of three types of seismic waves (primary, secondary, and surface waves) through the layers of the earth’s crust 3. � describe tectonic plate boundaries, including - transform boundaries - divergent boundaries - convergent boundaries (oceanic-oceanic, oceanic-continental, and ...
Chapter 10 Resources: The Atmosphere in Motion
... Directions: Correctly complete each sentence by underlining the best of the three choices in parentheses. 2. During evaporation, water (loses, gains, absorbs) energy. 3. When warm air rises and cool air sinks, it is called (conduction, convection, clouds). ...
... Directions: Correctly complete each sentence by underlining the best of the three choices in parentheses. 2. During evaporation, water (loses, gains, absorbs) energy. 3. When warm air rises and cool air sinks, it is called (conduction, convection, clouds). ...
Earth Interior and Plate tectonics
... from 1-16 cm (0.4-6.3in) per year. • Some plates move toward each other, some moves away from each other, and others move alongside each other. • The theory of plate tectonics help scientists study and sometimes predict volcanic eruptions and has provided information on earthquakes. • Mid-oceanic ri ...
... from 1-16 cm (0.4-6.3in) per year. • Some plates move toward each other, some moves away from each other, and others move alongside each other. • The theory of plate tectonics help scientists study and sometimes predict volcanic eruptions and has provided information on earthquakes. • Mid-oceanic ri ...
Document
... currents (or currents in a liquid) is called a. radiation. b. conduction. c. convection. d. condensation. ...
... currents (or currents in a liquid) is called a. radiation. b. conduction. c. convection. d. condensation. ...
CH. 1-3 Exam Review
... Essay: Two of the following will be on the exam 1. How does the Earth’s rotation, revolution, and tilt affect the amount of solar energy it receives? ...
... Essay: Two of the following will be on the exam 1. How does the Earth’s rotation, revolution, and tilt affect the amount of solar energy it receives? ...
6th Regular Study Guide-Canu
... 33. How many millimeters are there in 10 centimeters? 34. How many meters in one kilometer? 35. How many meters would 3.5 km be equal to? 36. How does erosion move stuff? 37. What are the two types of weathering? 38. What is the process by which rock is worn away over time? 39. In which part of a la ...
... 33. How many millimeters are there in 10 centimeters? 34. How many meters in one kilometer? 35. How many meters would 3.5 km be equal to? 36. How does erosion move stuff? 37. What are the two types of weathering? 38. What is the process by which rock is worn away over time? 39. In which part of a la ...
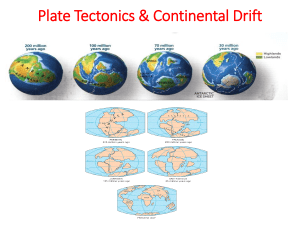
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... ___________pushing up from the mantle. The best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This submerged mountain range, which extends from the Arctic Ocean to beyond the southern tip of Africa, is but one segment of the global mid-ocean ridge system that encircles the Earth. b.__ ...
... ___________pushing up from the mantle. The best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This submerged mountain range, which extends from the Arctic Ocean to beyond the southern tip of Africa, is but one segment of the global mid-ocean ridge system that encircles the Earth. b.__ ...
Global Climate - Cloudfront.net
... -amphibians, ozone forms, mammals, anaerobic prokaryotes (photosynthetic cyanobacteria), earth forms, fishies, eukaryotes, largest mass extinction in history, reptiles, coal forming swamps form (carboniferous period), oxygen levels rise, pangaea 2. What do you know about plate tectonics???? (brain s ...
... -amphibians, ozone forms, mammals, anaerobic prokaryotes (photosynthetic cyanobacteria), earth forms, fishies, eukaryotes, largest mass extinction in history, reptiles, coal forming swamps form (carboniferous period), oxygen levels rise, pangaea 2. What do you know about plate tectonics???? (brain s ...
Essay- choose ONE
... apart and slowly moved to there present positions. ___The theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle is broken up into sections. ___The process that explains how continents move and where new crust is made. ___The name of the giant landmass that was formed 250 million years ago. ___This theo ...
... apart and slowly moved to there present positions. ___The theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle is broken up into sections. ___The process that explains how continents move and where new crust is made. ___The name of the giant landmass that was formed 250 million years ago. ___This theo ...
ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL
... Let’s start by reading pages 16-17 in our Atlas 1. What are “plates” 2. What impact can colliding plates have on the earth? 3. Define Subduction 4. What can subduction cause? 5. What causes earthquakes? 6. What happens when plates pull apart? 7. Define Pangea ...
... Let’s start by reading pages 16-17 in our Atlas 1. What are “plates” 2. What impact can colliding plates have on the earth? 3. Define Subduction 4. What can subduction cause? 5. What causes earthquakes? 6. What happens when plates pull apart? 7. Define Pangea ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.