The SNC meteorites: basaltic igneous processes on Mars
... see mineral compositions of SNCs in Table 3). There is a large overall range: En1–71 Wo0–30 Fs1–94 , with Los Angeles containing the most Fe-rich pyroxenes. The other basaltic shergottites show more restricted ranges of pyroxene compositions; for instance, Shergotty augites and pigeonites are En30–7 ...
... see mineral compositions of SNCs in Table 3). There is a large overall range: En1–71 Wo0–30 Fs1–94 , with Los Angeles containing the most Fe-rich pyroxenes. The other basaltic shergottites show more restricted ranges of pyroxene compositions; for instance, Shergotty augites and pigeonites are En30–7 ...
Deformation of the Plates
... Quartz and Feldspar The behaviour of quartz and feldspar is important because the continental crust is dominated by these minerals. Fully plastic flow in quartz appears at about 300◦ C and for feldspar at about 450–500◦ C. Between these two states quartzofeldspathic rocks behave as composite materia ...
... Quartz and Feldspar The behaviour of quartz and feldspar is important because the continental crust is dominated by these minerals. Fully plastic flow in quartz appears at about 300◦ C and for feldspar at about 450–500◦ C. Between these two states quartzofeldspathic rocks behave as composite materia ...
Magmatic Apatite: A Powerful, Yet Deceptive
... Thermodynamic Relations and Modeling of Apatite–Melt–Fluid(s) Systems What is the relationship between F, Cl, and OH in apatite and the volatile contents of the melt from which it crystallized? Does the presence of high-Cl apatite indicate that it crystallized from a high-Cl system? Not necessarily. ...
... Thermodynamic Relations and Modeling of Apatite–Melt–Fluid(s) Systems What is the relationship between F, Cl, and OH in apatite and the volatile contents of the melt from which it crystallized? Does the presence of high-Cl apatite indicate that it crystallized from a high-Cl system? Not necessarily. ...
The Dynamic Earth - Betavak-NLT
... An example of a rock that has cooled quickly is basalt. It is a black rock that has very few visible crystals. Basalt often forms at the bottom of the ocean, where the heat dissipates quickly in the cold seawater. When molten material cools slowly there is time for a greater number of crystals to fo ...
... An example of a rock that has cooled quickly is basalt. It is a black rock that has very few visible crystals. Basalt often forms at the bottom of the ocean, where the heat dissipates quickly in the cold seawater. When molten material cools slowly there is time for a greater number of crystals to fo ...
Folds, Faults and Mountain Belts (Con`t.)
... Produced metamorphic rocks found in the Alps, Himalaya, and Appalachian Mountains. Also produced the greatly eroded metamorphic rocks in the Great Lakes region. These rocks are exposed by uplift (faulting) and rapid erosion. The process doesn’t reverse itself. ...
... Produced metamorphic rocks found in the Alps, Himalaya, and Appalachian Mountains. Also produced the greatly eroded metamorphic rocks in the Great Lakes region. These rocks are exposed by uplift (faulting) and rapid erosion. The process doesn’t reverse itself. ...
Microbes and volcanoes: A tale from the oceans, ophiolites, and
... the biological mechanism for generating these void textures remains unchallenged even though it was proposed more than a decade ago. The textures of bioalteration have important consequences for the development of surface area during alteration. Abiotic alteration progressively decreases surface are ...
... the biological mechanism for generating these void textures remains unchallenged even though it was proposed more than a decade ago. The textures of bioalteration have important consequences for the development of surface area during alteration. Abiotic alteration progressively decreases surface are ...
tectonic hazards - 2015-Sec3-Geog
... e. What are the different types of plate boundaries? 1. Oceanic–oceanic plate convergence • When two oceanic plates converge, one subducts under the other. • A subduction zone forms, creating a deep oceanic trench. • The subduction of the oceanic plate causes the solid mantle material to melt and m ...
... e. What are the different types of plate boundaries? 1. Oceanic–oceanic plate convergence • When two oceanic plates converge, one subducts under the other. • A subduction zone forms, creating a deep oceanic trench. • The subduction of the oceanic plate causes the solid mantle material to melt and m ...
How a Barometer works: A barometer is an instrument for measuring
... A barometer's main use, however, is not to measure altitude, but to measure the actual changes in the pressure of air at a particular place. High and low pressure systems in the atmosphere move around the earth's surface, and the movements shown on the face of a barometer attached to the wall of you ...
... A barometer's main use, however, is not to measure altitude, but to measure the actual changes in the pressure of air at a particular place. High and low pressure systems in the atmosphere move around the earth's surface, and the movements shown on the face of a barometer attached to the wall of you ...
ISCI 2001 Final Exam Review
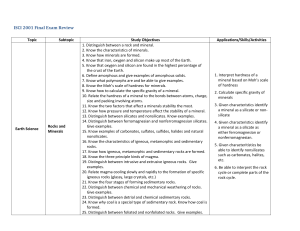
... 1. Distinguish between a rock and mineral. 2. Know the characteristics of minerals. 3. Know how minerals are formed. 4. Know that iron, oxygen and silicon make up most of the Earth. 5. Know that oxygen and silicon are found in the highest percentage of the crust of the Earth. 6. Define amorphous and ...
... 1. Distinguish between a rock and mineral. 2. Know the characteristics of minerals. 3. Know how minerals are formed. 4. Know that iron, oxygen and silicon make up most of the Earth. 5. Know that oxygen and silicon are found in the highest percentage of the crust of the Earth. 6. Define amorphous and ...
Crustal thickening in an extensional regime: application to the mid
... rift axis was not located here but instead jumped westward with respect to the earlier rift axes locations. The modeling study predicts that local crustal thickening during extension can be expected when large lateral thermal variations are present in the lithosphere at the onset of extension. Negat ...
... rift axis was not located here but instead jumped westward with respect to the earlier rift axes locations. The modeling study predicts that local crustal thickening during extension can be expected when large lateral thermal variations are present in the lithosphere at the onset of extension. Negat ...
Origin of the modern Chiapanecan Volcanic arc in southern México
... characterized by two Neogene volcanic arcs: the ancestral Miocene Sierra Madre arc and the modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc (Fig. 1). The Miocene Sierra Madre arc was abandoned between 9 and 3 Ma, when the modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc was formed (Damon and Montesinos, 1978). There are a series of ...
... characterized by two Neogene volcanic arcs: the ancestral Miocene Sierra Madre arc and the modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc (Fig. 1). The Miocene Sierra Madre arc was abandoned between 9 and 3 Ma, when the modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc was formed (Damon and Montesinos, 1978). There are a series of ...
the origin of modern chiapanecan volcanic arc in southern mexico
... 1999; Engdahl and Villaseñor, 2002), convergence rate (DeMets et al., 1994) and oceanic plate age at the MAT (Manea et al., 2004-B; Kanjorsky, 2003; Klitgord and Mammerickx, 1982) (Figure 3). The first profile was chosen just above TR because of the subhorizontal shape of the subducting Cocos slab. ...
... 1999; Engdahl and Villaseñor, 2002), convergence rate (DeMets et al., 1994) and oceanic plate age at the MAT (Manea et al., 2004-B; Kanjorsky, 2003; Klitgord and Mammerickx, 1982) (Figure 3). The first profile was chosen just above TR because of the subhorizontal shape of the subducting Cocos slab. ...
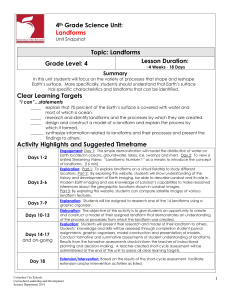
Landforms - Columbus City Schools
... processes include erosion, deposition, volcanic activity, earthquakes, glacial movement and weathering. Beginning to recognize common landforms or features through field investigations, field trips, topographic maps, remote sensing data, aerial photographs, physical geography maps and/or photographs ...
... processes include erosion, deposition, volcanic activity, earthquakes, glacial movement and weathering. Beginning to recognize common landforms or features through field investigations, field trips, topographic maps, remote sensing data, aerial photographs, physical geography maps and/or photographs ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.