bYTEBoss Platinum & Gold Prospects Choco
... Chocó is an area of oceanic crust placed in western Colombia. It is part of an islands arc which continues along Panamá to Northwest and to the South along the Pacific shelf to Ecuador territory. The parts of the islands arc in Chocó are well defined, the subduction zone is along the Baudó coast, w ...
... Chocó is an area of oceanic crust placed in western Colombia. It is part of an islands arc which continues along Panamá to Northwest and to the South along the Pacific shelf to Ecuador territory. The parts of the islands arc in Chocó are well defined, the subduction zone is along the Baudó coast, w ...
Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks
... The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international ...
... The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international ...
plate tectonic mapping
... INTRODUCTION & BACKGROUND: The data below represent worldwide earthquake and volcano locations given by their latitude and longitude. The goal of this investigation is to map the locations of these tectonic events to see what relationships can be deduced. PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions on t ...
... INTRODUCTION & BACKGROUND: The data below represent worldwide earthquake and volcano locations given by their latitude and longitude. The goal of this investigation is to map the locations of these tectonic events to see what relationships can be deduced. PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions on t ...
Document
... b. metamorphic c. metasedimentary d. sedimentary 22. Which rock’s texture is determined by the pressure and temperature the rock was exposed to? a. metasedimentary b. metamorphic c. igneous d. sedimentary ...
... b. metamorphic c. metasedimentary d. sedimentary 22. Which rock’s texture is determined by the pressure and temperature the rock was exposed to? a. metasedimentary b. metamorphic c. igneous d. sedimentary ...
Review for CFE-answers
... Convergent (move together), divergent (move apart), transform (slide horizontally along each other). The boundary type tells the type of movement of those two plates. 10. Identify features that result from moving tectonic plates to the major processes of plate tectonics. (may include diagrams) NS9, ...
... Convergent (move together), divergent (move apart), transform (slide horizontally along each other). The boundary type tells the type of movement of those two plates. 10. Identify features that result from moving tectonic plates to the major processes of plate tectonics. (may include diagrams) NS9, ...
plate tectonics review game!!!!
... currents within the Earth are due primarily to the fact that fluids will rise if the surrounding fluid is a greater... ...
... currents within the Earth are due primarily to the fact that fluids will rise if the surrounding fluid is a greater... ...
Plate Boundaries
... How tall are these mountains? Some are taller than Mt. Everest, the tallest Mountain in the world. ...
... How tall are these mountains? Some are taller than Mt. Everest, the tallest Mountain in the world. ...
Thehazardspresentedhavethegreatestimpactonthepoorestpeople
... world’s poorest people'. To what extent do you agree with this view? Answer 1. Tectonic hazards such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur across the surface of the globe, but many argue that they have the greatest impact on the poorest people – the inhabitants of LEDCs. However, there are man ...
... world’s poorest people'. To what extent do you agree with this view? Answer 1. Tectonic hazards such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur across the surface of the globe, but many argue that they have the greatest impact on the poorest people – the inhabitants of LEDCs. However, there are man ...
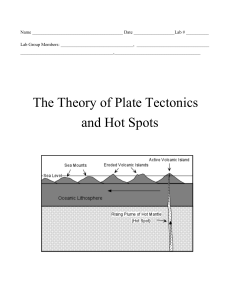
Hot Spot LAB 2017 - eat, sleep, breathe science
... millions of years before the present. Calculate the age difference between the islands and enter the data in the table on page 3. 2. Make distance measurements between the “dots” of each circle using the scale on the diagram. 3. Convert the distance from kilometers to “land” or “real” centimeters (N ...
... millions of years before the present. Calculate the age difference between the islands and enter the data in the table on page 3. 2. Make distance measurements between the “dots” of each circle using the scale on the diagram. 3. Convert the distance from kilometers to “land” or “real” centimeters (N ...
Astronomy Test - The Summer Science Safari Summer Camp
... 1. Describe the contributions of the 7 astronomers described in Chapter 22 Section 1. 2. According to the big bang theory, the age of the universe is about: 3. Astronomers often place telescopes on mountaintops because: 4. Describe the two types of telescopes. Include a description of the advantages ...
... 1. Describe the contributions of the 7 astronomers described in Chapter 22 Section 1. 2. According to the big bang theory, the age of the universe is about: 3. Astronomers often place telescopes on mountaintops because: 4. Describe the two types of telescopes. Include a description of the advantages ...
Study Guide! Which of the following is homozygous and has a
... A. Erosion moves rocks and weathering doesn’t B. Erosion makes lava and weathering does not C. Weathering moves rocks and erosion doesn’t D. Weathering makes lava and Erosion doesn’t 15. The small particles that make up rocks are: A. Magma B. Fusion C. Sediments D. Volcano 16. This type of Rock is k ...
... A. Erosion moves rocks and weathering doesn’t B. Erosion makes lava and weathering does not C. Weathering moves rocks and erosion doesn’t D. Weathering makes lava and Erosion doesn’t 15. The small particles that make up rocks are: A. Magma B. Fusion C. Sediments D. Volcano 16. This type of Rock is k ...
Chapter 7, Section 1 - Directed Reading B
... _____14. Which of the following is the thickest part of the South American plate? a. the continental crust b. the oceanic crust c. the mantle d. the mid-Atlantic Ocean Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of ...
... _____14. Which of the following is the thickest part of the South American plate? a. the continental crust b. the oceanic crust c. the mantle d. the mid-Atlantic Ocean Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of ...
Plate Tectonics
... the heavier oceanic floor collides into the lighter continental crust, the continental crust is pushed over the oceanic crust. The oceanic crust “dives” under the continental crust creating a subduction zone. Land is lost in this area. The Pacific Ocean is getting smaller because of this process. ...
... the heavier oceanic floor collides into the lighter continental crust, the continental crust is pushed over the oceanic crust. The oceanic crust “dives” under the continental crust creating a subduction zone. Land is lost in this area. The Pacific Ocean is getting smaller because of this process. ...
Geosphere
... Ash clouds from major eruptions can block sunlight & change drop the average global temp. ...
... Ash clouds from major eruptions can block sunlight & change drop the average global temp. ...
THE OCEANS AND THE ATMOSPHERE
... atmosphere’s total mass – Ozone layer • A zone in the stratosphere where ozone is concentrated ...
... atmosphere’s total mass – Ozone layer • A zone in the stratosphere where ozone is concentrated ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.