AIM: OBJ: DN: HW:
... • Hydrosphere: liquid (water) layer of the Earth (e.g., oceans, lakes, rivers, streams, glaciers?) • Atmosphere: gas layer of the Earth • Lithosphere: solid (rock) layer of the Earth (= crust + uppermost mantle) • Cloud Formation: warm air (humid/moist, carries water), rises; why? less dense, cools ...
... • Hydrosphere: liquid (water) layer of the Earth (e.g., oceans, lakes, rivers, streams, glaciers?) • Atmosphere: gas layer of the Earth • Lithosphere: solid (rock) layer of the Earth (= crust + uppermost mantle) • Cloud Formation: warm air (humid/moist, carries water), rises; why? less dense, cools ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... and retains energy from sunlight. • The early atmosphere of Venus contained substantial amounts of water vapor • This caused a runaway greenhouse effect that evaporated Venus’s oceans and drove carbon dioxide out of the rocks and into the atmosphere • Almost all of the water vapor was eventually los ...
... and retains energy from sunlight. • The early atmosphere of Venus contained substantial amounts of water vapor • This caused a runaway greenhouse effect that evaporated Venus’s oceans and drove carbon dioxide out of the rocks and into the atmosphere • Almost all of the water vapor was eventually los ...
Collaborative Research: Testing the Hypothesis of Ocean Core
... segments of the southern Juan de Fuca and Gorda eastern ridge flanks associated with propagating rift traces may be the result of OCC-like processes. To test this assertion, we request support for a pilot field program of geophysical surveys (high resolution 30 kHz multibeam bathymetry, gravity, and ...
... segments of the southern Juan de Fuca and Gorda eastern ridge flanks associated with propagating rift traces may be the result of OCC-like processes. To test this assertion, we request support for a pilot field program of geophysical surveys (high resolution 30 kHz multibeam bathymetry, gravity, and ...
Geology and petrography of Adolerite dyke, Hyderabad granitic
... Both type gray and pink granites were cropped out around the study area. They are courser in grain size. The Hyderabad granitic region (HGR) forms part ofthe Eastern Dharwar Craton (EDC) of southern India and is covered by unclassified granites and granitegneisses of Achaean age (Crawford 1969), whi ...
... Both type gray and pink granites were cropped out around the study area. They are courser in grain size. The Hyderabad granitic region (HGR) forms part ofthe Eastern Dharwar Craton (EDC) of southern India and is covered by unclassified granites and granitegneisses of Achaean age (Crawford 1969), whi ...
Moving Plates: Restless Earth
... Wegener’s theory stated that over the years, Pangaea split into the continents and drifted apart. A problem with Wegener’s theory, though, was that he thought the continents floated on the ocean floor like icebergs. In the 1960’s, scientists used new discoveries about the sea floor to develop a theo ...
... Wegener’s theory stated that over the years, Pangaea split into the continents and drifted apart. A problem with Wegener’s theory, though, was that he thought the continents floated on the ocean floor like icebergs. In the 1960’s, scientists used new discoveries about the sea floor to develop a theo ...
Chapter 22.1: Earth`s Structure
... “taffy-like”; What happens to temps., pressures, and density as you move through layers? ...
... “taffy-like”; What happens to temps., pressures, and density as you move through layers? ...
Chapter 22.1: Earth`s Structure
... “taffy-like”; What happens to temps., pressures, and density as you move through layers? ...
... “taffy-like”; What happens to temps., pressures, and density as you move through layers? ...
Seafloor Spreading notes guide 2015
... 1. During World War I, scientists used underwater (soundwaves/ cameras?) to detect the varying depths of the ocean. This is known as “sonar” today. 2. While using this method of echo location, they discovered an underwater system of _________________ (mountains) and ____________________. 3. In the A ...
... 1. During World War I, scientists used underwater (soundwaves/ cameras?) to detect the varying depths of the ocean. This is known as “sonar” today. 2. While using this method of echo location, they discovered an underwater system of _________________ (mountains) and ____________________. 3. In the A ...
E8C3_CRT_CR_MSTIPS_FinalS
... Part A is a list of, Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core. Part B will include; density and rock type (Granite for Continental, Basalt for Oceanic). Continental crust (primarily granite) is less dense than Oceanic crust (primarily basalt). Part C will include; The core is the source of heat (from r ...
... Part A is a list of, Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core. Part B will include; density and rock type (Granite for Continental, Basalt for Oceanic). Continental crust (primarily granite) is less dense than Oceanic crust (primarily basalt). Part C will include; The core is the source of heat (from r ...
Deep Earth Volatiles Cycle: processes, fluxes and deep mantle
... depths (Fig. 1 shows a simplified simulation of the water cycle in the shallow mantle). Furthermore, it is poorly understood which are the implications of a deep (>300 km) mantle metasomatization that potentially could cause the formation of magma (Fig. 2) and diamonds at depth, and related volcanis ...
... depths (Fig. 1 shows a simplified simulation of the water cycle in the shallow mantle). Furthermore, it is poorly understood which are the implications of a deep (>300 km) mantle metasomatization that potentially could cause the formation of magma (Fig. 2) and diamonds at depth, and related volcanis ...
Mountain Building-Folding and Faulting
... Rock that is put under extreme pressure for long periods of time (thousands or millions of years) will fold like clay. ...
... Rock that is put under extreme pressure for long periods of time (thousands or millions of years) will fold like clay. ...
Plate margin... - Consortium for Ocean Leadership
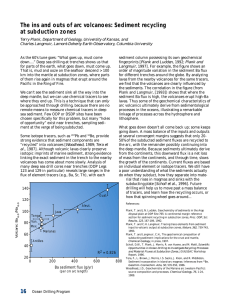
... at several convergent margins suggests that only 2050% of the subducted sediment fluxes are recycled to the arc, with the remainder possibly continuing into the deep mantle. Because sediments ultimately derive from the continents, this downward flux is a net loss of mass from the continents, and thr ...
... at several convergent margins suggests that only 2050% of the subducted sediment fluxes are recycled to the arc, with the remainder possibly continuing into the deep mantle. Because sediments ultimately derive from the continents, this downward flux is a net loss of mass from the continents, and thr ...
Practice 1 - WordPress.com
... 14contacts where plates slide past each other. New oceanic crust is formed along one or 15more margins of each plate by material issuing from deeper layers of the Earth's crust, 16for example, by volcanic eruptions of lava at midocean ridges. If at such a spreading 17contact the two plates support c ...
... 14contacts where plates slide past each other. New oceanic crust is formed along one or 15more margins of each plate by material issuing from deeper layers of the Earth's crust, 16for example, by volcanic eruptions of lava at midocean ridges. If at such a spreading 17contact the two plates support c ...
Plate tectonics web quest Alfred Wegner noticed that Greenland had
... continents didn't move but were "carried" by larger pieces of the earth's crust. Harry worked and led to the development of plate tectonics. More information Harry Hess The four types of divergent boundaries are Divergent boundaries, where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each oth ...
... continents didn't move but were "carried" by larger pieces of the earth's crust. Harry worked and led to the development of plate tectonics. More information Harry Hess The four types of divergent boundaries are Divergent boundaries, where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each oth ...
Plate tectonics 2014
... movement at this type of boundary using two minis and one fun six bar. Then do it. 4. Identify the features each model showed. At the end your group needs to decide which choice (two minis or one fun size) is best and support that with evidence from the lab. ...
... movement at this type of boundary using two minis and one fun six bar. Then do it. 4. Identify the features each model showed. At the end your group needs to decide which choice (two minis or one fun size) is best and support that with evidence from the lab. ...
Hydrothermal vent glossary: elementary
... The most prevalent chemical dissolved in the sea water of vents. It smells like rotten eggs and is produced when seawater reacts with sulfate in the volcanic rock below the ocean floor. The exchange of seawater that seeps through fissures in the ocean's crust; becomes heated, losing and gaining meta ...
... The most prevalent chemical dissolved in the sea water of vents. It smells like rotten eggs and is produced when seawater reacts with sulfate in the volcanic rock below the ocean floor. The exchange of seawater that seeps through fissures in the ocean's crust; becomes heated, losing and gaining meta ...
Review / Study Sheet for the next Big Test: Layers
... Divergent (di – divide) boundaries create trenches, gaps, valleys and cracks in the earth Convergent (con – connect) boundaries cause mountains to rise slightly or create volcanic islands in some cases Convergent Volcanic islands are formed from plates colliding together and magma coming up to the w ...
... Divergent (di – divide) boundaries create trenches, gaps, valleys and cracks in the earth Convergent (con – connect) boundaries cause mountains to rise slightly or create volcanic islands in some cases Convergent Volcanic islands are formed from plates colliding together and magma coming up to the w ...
Plate Tectonics Notes
... According to the _______________________ theory, the uppermost _________, along with the overlying _________, behaves as a strong, rigid layer. This layer is known as the _____________ A _________ is one of numerous rigid sections of the _____________ that move as a unit over the material of the _ _ ...
... According to the _______________________ theory, the uppermost _________, along with the overlying _________, behaves as a strong, rigid layer. This layer is known as the _____________ A _________ is one of numerous rigid sections of the _____________ that move as a unit over the material of the _ _ ...
Unit Objectives
... Explain how plate tectonics account for the features and processes (sea floor spreading, mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, earthquakes and volcanoes, mountain ranges) that occur on or near the Earth’s surface. 7. I can explain the theory of plate tectonics. 8. I can use the theory of plate tectoni ...
... Explain how plate tectonics account for the features and processes (sea floor spreading, mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, earthquakes and volcanoes, mountain ranges) that occur on or near the Earth’s surface. 7. I can explain the theory of plate tectonics. 8. I can use the theory of plate tectoni ...
Y8GeU4A Plate tectonicsPPwk14
... The Eurasian and North American plates moving away from each other – so very slowly Europe is getting further away from America. As the plates move apart (very slowly), magma rises from the mantle. The magma erupts to the surface of the earth. When the magma reaches the surface, it cools and solidif ...
... The Eurasian and North American plates moving away from each other – so very slowly Europe is getting further away from America. As the plates move apart (very slowly), magma rises from the mantle. The magma erupts to the surface of the earth. When the magma reaches the surface, it cools and solidif ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.