Earth`s Changing Surface Review
... He could not identify the force that moves the tectonic plates ...
... He could not identify the force that moves the tectonic plates ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Oceanic crust collides with oceanic crust • Island Arc is formed when: – One plate is subducted, forming a trench – Subducted plate melts – Molten rock rises to surface along trench ...
... • Oceanic crust collides with oceanic crust • Island Arc is formed when: – One plate is subducted, forming a trench – Subducted plate melts – Molten rock rises to surface along trench ...
Plate Tectonics
... Volcanoes and Boundaries (pg 189) • Volcanoes form in a regular pattern along Earth’s plates. One major belt of volcanoes, the Ring of Fire, is found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean. • At divergent boundaries, the crust fractures and magma pushes to the surface. Found along mid-ocean ridges and ...
... Volcanoes and Boundaries (pg 189) • Volcanoes form in a regular pattern along Earth’s plates. One major belt of volcanoes, the Ring of Fire, is found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean. • At divergent boundaries, the crust fractures and magma pushes to the surface. Found along mid-ocean ridges and ...
Plate Tectonics fill
... f. Beneath the volcanoes are large plutons in thickened crust, seen on land as batholiths when exposed by extensive erosion. g. The more buoyant continental plate experiences intense deformation, metamorphism, and melting (1) crust thickens (2) also rises isostatically (3) thrust faults , associated ...
... f. Beneath the volcanoes are large plutons in thickened crust, seen on land as batholiths when exposed by extensive erosion. g. The more buoyant continental plate experiences intense deformation, metamorphism, and melting (1) crust thickens (2) also rises isostatically (3) thrust faults , associated ...
Geology of Washington
... forced onto the North American plate around Spokane • These islands are welded on, and end about where Twisp and the Methow valley is today ...
... forced onto the North American plate around Spokane • These islands are welded on, and end about where Twisp and the Methow valley is today ...
Dynamic Earth Webquest
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
Where the African plate and the South American plate meet is:
... Describe the processes happening at continental collisions ...
... Describe the processes happening at continental collisions ...
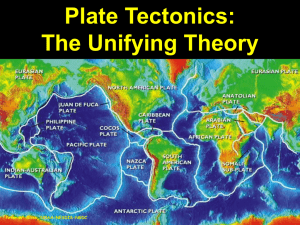
Plate Tectonics “The Grand Unifying Theory”
... • Rift valleys, 1-2 km deep, split the ridge crests. ...
... • Rift valleys, 1-2 km deep, split the ridge crests. ...
Mid-ocean ridges
... As plates moves, they always interact with other plates The ways that plates interact along their boundaries shape geological features of Earth’s surface and the terrain The terrain of the seafloor includes seafloor (abyssal) hills, mountain chains (ridges, islands and seamounts), trenches and great ...
... As plates moves, they always interact with other plates The ways that plates interact along their boundaries shape geological features of Earth’s surface and the terrain The terrain of the seafloor includes seafloor (abyssal) hills, mountain chains (ridges, islands and seamounts), trenches and great ...
Aim #9: Plate Tectonics Theory – Convergent
... lithosphere is broken up into 8 major plates that move relative to one another. ...
... lithosphere is broken up into 8 major plates that move relative to one another. ...
Plate Tectonics - Effingham County Schools
... • A hot spot is an area of volcanic activity that develops above where magma rises in a plume from the mantle. • A hot spot can be used to measure plate movement because it generally stays in one place while the tectonic plate above it keeps ...
... • A hot spot is an area of volcanic activity that develops above where magma rises in a plume from the mantle. • A hot spot can be used to measure plate movement because it generally stays in one place while the tectonic plate above it keeps ...
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
... New seafloor moves away from the ridge, cools, and becomes more dense than the material beneath it. Hot magma which is less dense than surrounding material, is forced toward the crust. New ocean floor forms as the magma hardens. ...
... New seafloor moves away from the ridge, cools, and becomes more dense than the material beneath it. Hot magma which is less dense than surrounding material, is forced toward the crust. New ocean floor forms as the magma hardens. ...
File
... BOUNDARIES •Tectonic plates interact at places called BOUNDARIES. •The continents / oceans do not necessarily resemble the outline of the plate boundaries. •There are three types of boundaries •Divergent •Convergent •Transform ...
... BOUNDARIES •Tectonic plates interact at places called BOUNDARIES. •The continents / oceans do not necessarily resemble the outline of the plate boundaries. •There are three types of boundaries •Divergent •Convergent •Transform ...
Pacific Ring of Fire Plate Tectonics
... - According to plate tectonic theory, the rigid lithosphere (crust + upper most mantle), is divided into differentsized plates (tectonic plates) that drive on top of the liquid asthenosphere (mantle) ...
... - According to plate tectonic theory, the rigid lithosphere (crust + upper most mantle), is divided into differentsized plates (tectonic plates) that drive on top of the liquid asthenosphere (mantle) ...
8.9AB Plate Tectonic Theory
... away from each other; on land creates rift valleys, on the sea floor creates new ocean crust ...
... away from each other; on land creates rift valleys, on the sea floor creates new ocean crust ...
Clouard_new_scientis..
... boundary is interesting, but has some doubts about the mechanism they use to make their case. Like many other geologists, he believes that strain on the Pacific plate on its own would not be enough to prompt hot mantle to well up. There are several places on Earth where oceanic crust is being stretc ...
... boundary is interesting, but has some doubts about the mechanism they use to make their case. Like many other geologists, he believes that strain on the Pacific plate on its own would not be enough to prompt hot mantle to well up. There are several places on Earth where oceanic crust is being stretc ...
Geology 101 chapter2 Plate tectonics
... and oceanic crust move together Seafloor separates at oceanic ridges where new crust forms from upwelling and cooling magma, and the new crust moves laterally away from the ridge ...
... and oceanic crust move together Seafloor separates at oceanic ridges where new crust forms from upwelling and cooling magma, and the new crust moves laterally away from the ridge ...
Plate tectonics note-taker - Tanque Verde Unified School District
... 1. At the subduction zone a ________________________________ is formed where the plate is being forced downwards under the continental plate. 2. Subduction causes rocks to _____________, and magma _____________ to surface to form _____________________. 3. Example: ____________________ in US, _______ ...
... 1. At the subduction zone a ________________________________ is formed where the plate is being forced downwards under the continental plate. 2. Subduction causes rocks to _____________, and magma _____________ to surface to form _____________________. 3. Example: ____________________ in US, _______ ...
End of unit exam study guide
... hypothesis of continental drift? Fossil and plant evidence far away from each other on different continents • Sea-floor spreading occurs at which type of boundary? divergent ...
... hypothesis of continental drift? Fossil and plant evidence far away from each other on different continents • Sea-floor spreading occurs at which type of boundary? divergent ...
Plate Tectonics Unit - the E-Portfolio of Jessica Mann B.Com., RED
... understand how and why the earth’s surface is continually changing. On the west coast of Canada we live in a subduction zone that causes earthquakes and volcanic activity, the students are affected by this plate tectonic movement in building code restrictions and the need for earthquake preparedn ...
... understand how and why the earth’s surface is continually changing. On the west coast of Canada we live in a subduction zone that causes earthquakes and volcanic activity, the students are affected by this plate tectonic movement in building code restrictions and the need for earthquake preparedn ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Earthquakes and volcanic activity occur primarily at the location of plate boundaries. – Plate boundaries are where 2 plates are pushing toward, pulling away, or sliding past each other. The strain and friction causes fractures in the earth, where earthquakes occur and where the fractures allow mol ...
... Earthquakes and volcanic activity occur primarily at the location of plate boundaries. – Plate boundaries are where 2 plates are pushing toward, pulling away, or sliding past each other. The strain and friction causes fractures in the earth, where earthquakes occur and where the fractures allow mol ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.