PART 1 - earth science!
... 2. The continental shelf is the section of the continental crust that extends under the water. 3. The continental slope is the steep incline section of the continental crust. It connects the continental shelf to the abyssal plain. 4. The abyssal plain is a large, flat, almost level of the ocean flo ...
... 2. The continental shelf is the section of the continental crust that extends under the water. 3. The continental slope is the steep incline section of the continental crust. It connects the continental shelf to the abyssal plain. 4. The abyssal plain is a large, flat, almost level of the ocean flo ...
Continental Margins and Ocean Basins - Cal State LA
... Covers about 30% of Earth’s surface Begins at base of continental rise Sedimentation: Passive and turbidity currents Contain abyssal plains, deep sea trenches, and seamounts ...
... Covers about 30% of Earth’s surface Begins at base of continental rise Sedimentation: Passive and turbidity currents Contain abyssal plains, deep sea trenches, and seamounts ...
Exam 1
... 20. When magma rises toward the surface from deep in the mantle, a. the decrease in pressure promotes further melting b. the pressure increases and causes the rock to solidify c. no change in pressure can occur d. the decrease in pressure usually prevents volcanism 21. A rock with large amphibole ph ...
... 20. When magma rises toward the surface from deep in the mantle, a. the decrease in pressure promotes further melting b. the pressure increases and causes the rock to solidify c. no change in pressure can occur d. the decrease in pressure usually prevents volcanism 21. A rock with large amphibole ph ...
Key Points on the Earth`s Layers - Greenville Public School District
... 1. Boundaries are the spots were two plates meet 2. Convergent Boundaries: where two tectonic plates are moving toward one another A. The word converge means come together. 3. There are three different types of convergent boundaries. The types are based on the two types of lithosphere colliding. A. ...
... 1. Boundaries are the spots were two plates meet 2. Convergent Boundaries: where two tectonic plates are moving toward one another A. The word converge means come together. 3. There are three different types of convergent boundaries. The types are based on the two types of lithosphere colliding. A. ...
Geodynamics
... • Generation of new plate material occurs by seafloor spreading; that is, new material is generated along mid-ocean ridges. • The new oceanic lithosphere, once created, forms part of a rigid plate. • The Earth’s surface area remains constant; therefore seafloor spreading must be balanced by consu ...
... • Generation of new plate material occurs by seafloor spreading; that is, new material is generated along mid-ocean ridges. • The new oceanic lithosphere, once created, forms part of a rigid plate. • The Earth’s surface area remains constant; therefore seafloor spreading must be balanced by consu ...
Mechanisms of Plate Motion
... to slide down the sides of the oceanic ridge as a result of gravity. • Ridge-push an slab-pull are acting together moving ocean lithosphere from mid-ocean ridges toward subduction zones and then down into the mantle. • Downward flow of subducted ocean lithosphere must be equal to upward flow of rock ...
... to slide down the sides of the oceanic ridge as a result of gravity. • Ridge-push an slab-pull are acting together moving ocean lithosphere from mid-ocean ridges toward subduction zones and then down into the mantle. • Downward flow of subducted ocean lithosphere must be equal to upward flow of rock ...
Plate Tectonics - THS Aquatic Science
... • No single idea explains everything but we can identify several forces that contribute to the movement of the plates. – Slab pull • The sinking of the cooled dense oceanic plates pulls on the rest of the plate ...
... • No single idea explains everything but we can identify several forces that contribute to the movement of the plates. – Slab pull • The sinking of the cooled dense oceanic plates pulls on the rest of the plate ...
Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory
... continent, Pangaea began to split apart, around 200 million years ago. These continents are still on the move today. ...
... continent, Pangaea began to split apart, around 200 million years ago. These continents are still on the move today. ...
10.2 Dir. Reading Plate Tectonics
... b. It slopes downward away from the ridge. c. It slides down the slope between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. d. It exerts force on the plate. 51. The force on the rest of the plate from the asthenosphere below cooling, sliding rock is called _________________________________. 52. What happe ...
... b. It slopes downward away from the ridge. c. It slides down the slope between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. d. It exerts force on the plate. 51. The force on the rest of the plate from the asthenosphere below cooling, sliding rock is called _________________________________. 52. What happe ...
Plate Tectonic Model Rubric
... Concept Model Relating to Physical Characteristics of Earth and Seafloor Topic: Types of plate boundaries, tectonic plates and their movement, Pangaea and Continental Drift Theory, Layers of the Earth, Seafloor formation, Parts of the Ocean floor, Theory of Plate Tectonics ...
... Concept Model Relating to Physical Characteristics of Earth and Seafloor Topic: Types of plate boundaries, tectonic plates and their movement, Pangaea and Continental Drift Theory, Layers of the Earth, Seafloor formation, Parts of the Ocean floor, Theory of Plate Tectonics ...
Plate boundaries: study information from class only
... Map and crosssection views of the subduction zone The oceanic Juan de Fuca plate subducts under the continental North American Plate ...
... Map and crosssection views of the subduction zone The oceanic Juan de Fuca plate subducts under the continental North American Plate ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... Similar geologic features (similar rocks) were found on different continents, matching fossils on different continents, evidence of different climates (such as coal in Antarctica) ...
... Similar geologic features (similar rocks) were found on different continents, matching fossils on different continents, evidence of different climates (such as coal in Antarctica) ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... What geologic features form at convergent plate boundaries? 1. Collision between oceanic crust and continental crust – basalt (oceanic crust) more dense than granite (continental crust) – forms deep ocean trenches where ocean crust is subducted into mantle – forms volcanoes on continent due to melt ...
... What geologic features form at convergent plate boundaries? 1. Collision between oceanic crust and continental crust – basalt (oceanic crust) more dense than granite (continental crust) – forms deep ocean trenches where ocean crust is subducted into mantle – forms volcanoes on continent due to melt ...
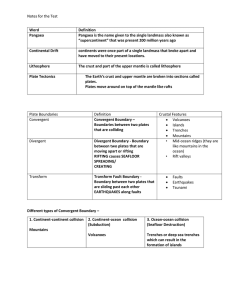
Notes for the Test Word Definition Pangaea Pangaea is the name
... Notes for the Test Word Pangaea ...
... Notes for the Test Word Pangaea ...
GTPlate Tectonics, Continental Drift and Seafloor Spreading
... other and crash/crunch against each other. Two types are subduction zone (under the ocean) and collision zone. 2. Divergent – where plates split and move apart. 3. Transform – plates slide along or past each other due to shear force. ...
... other and crash/crunch against each other. Two types are subduction zone (under the ocean) and collision zone. 2. Divergent – where plates split and move apart. 3. Transform – plates slide along or past each other due to shear force. ...
Plate Tectonics - maxwellsciencenfhs
... of ancient rocks with the location of magnetic poles at the time the rocks were formed) revealed the following: – Motion of continents relative to magnetic poles – Magnetic polarity reversals in rock corresponding to the Earth’s polarity reversals over time ...
... of ancient rocks with the location of magnetic poles at the time the rocks were formed) revealed the following: – Motion of continents relative to magnetic poles – Magnetic polarity reversals in rock corresponding to the Earth’s polarity reversals over time ...
class outline - WordPress.com
... the center of most ocean basins. An oceanic ridge would have the youngest ocean floor in a typical ocean basin. As the oceanic lithosphere spreads away from the divergent boundary, the age of rocks on the ocean floor get older and older. Oceanic lithosphere is another name for the rocks of the ocean ...
... the center of most ocean basins. An oceanic ridge would have the youngest ocean floor in a typical ocean basin. As the oceanic lithosphere spreads away from the divergent boundary, the age of rocks on the ocean floor get older and older. Oceanic lithosphere is another name for the rocks of the ocean ...
Plate Tectonics
... To the west of the fault is the Pacific plate, which is moving northwest. To the east is the North American Plate, which is moving southeast. Los Angeles, located on the Pacific plate, is now 340 miles south of San Francisco, located on the North American plate. In 16 million years, the plat ...
... To the west of the fault is the Pacific plate, which is moving northwest. To the east is the North American Plate, which is moving southeast. Los Angeles, located on the Pacific plate, is now 340 miles south of San Francisco, located on the North American plate. In 16 million years, the plat ...
key - Scioly.org
... 14. The San Andreas fautt cred'tes the tectonic boundary between which two plates? Pacific ...
... 14. The San Andreas fautt cred'tes the tectonic boundary between which two plates? Pacific ...
Plate Worksheet - Scarsdale Schools
... of Africa, are examples of rift zones.The island nation of Iceland is now being pulled apart by rifting. 2. Subduction zones occur where plates collide and one plate (usually an oceanic plate) is diving beneath another. In the oceans, subduction zones are usually found at the deep ocean trenches. An ...
... of Africa, are examples of rift zones.The island nation of Iceland is now being pulled apart by rifting. 2. Subduction zones occur where plates collide and one plate (usually an oceanic plate) is diving beneath another. In the oceans, subduction zones are usually found at the deep ocean trenches. An ...
Unit 1 – Studying the Earth Topics
... normal fault reverse fault thrust fault strike-slip fault mountain range mountain system mountain belt folded mountain plateau fault-block mountain dome mountain volcanic mountain ...
... normal fault reverse fault thrust fault strike-slip fault mountain range mountain system mountain belt folded mountain plateau fault-block mountain dome mountain volcanic mountain ...
Part B - Bakersfield College
... • thinner and more dense plate subducts • subducted plates melt (160 km) below the surface, and magma rises • EQ’s occur along the subduction zone, and magma plumes rise • typically, the older plate will subduct (more dense) beneath younger plate material ...
... • thinner and more dense plate subducts • subducted plates melt (160 km) below the surface, and magma rises • EQ’s occur along the subduction zone, and magma plumes rise • typically, the older plate will subduct (more dense) beneath younger plate material ...
inner core
... • SEDIMENTARY ROCKS are formed from pieces of other rocks (sediments) carried by water, wind, or ice. Sedimentary rocks are easy to find on the ground beneath our feet – the uppermost portion of Earth crust. Sedimentary rocks cover more than two-thirds of the Earth’s surface. Sandstone, shale, and l ...
... • SEDIMENTARY ROCKS are formed from pieces of other rocks (sediments) carried by water, wind, or ice. Sedimentary rocks are easy to find on the ground beneath our feet – the uppermost portion of Earth crust. Sedimentary rocks cover more than two-thirds of the Earth’s surface. Sandstone, shale, and l ...
Skinner Chapter 4
... d. continental slope. 27. A collision zone marks a. the disappearance of an ocean. b. the convergence of two plates capped by continental crust. c. the tectonic setting in which spectacular mountain ranges are uplifted. d. All of these are true. 28. The increase in temperature with increasing depth ...
... d. continental slope. 27. A collision zone marks a. the disappearance of an ocean. b. the convergence of two plates capped by continental crust. c. the tectonic setting in which spectacular mountain ranges are uplifted. d. All of these are true. 28. The increase in temperature with increasing depth ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.