Layers of the Earth
... the outer core is hotter than the mantle. It is so hot that the iron and nickel that make up this layer have melted. This is the Earth’s only liquid layer. ...
... the outer core is hotter than the mantle. It is so hot that the iron and nickel that make up this layer have melted. This is the Earth’s only liquid layer. ...
Sinking Slabs and Convection Connections
... • 7b. About 53 hotspots are shown. • 7c. In general, plates pass over hot spots. There is little, if any, correlation between hot spots and plate direction. For a relatively small number of hot spots on spreading ridges, the plate moves away from the hot spots (e.g., Iceland, Galapagos, or Afar at ...
... • 7b. About 53 hotspots are shown. • 7c. In general, plates pass over hot spots. There is little, if any, correlation between hot spots and plate direction. For a relatively small number of hot spots on spreading ridges, the plate moves away from the hot spots (e.g., Iceland, Galapagos, or Afar at ...
isostasy - UMSL.edu
... Continental Crust is thicker and has a lower density than Oceanic Crust. Therefore, it floats higher and has a deeper "root" than Oceanic Crust. This phenomenon can be compared with the behavior of floating wood blocks, all with the same density (see figure). The thicker blocks stand higher but have ...
... Continental Crust is thicker and has a lower density than Oceanic Crust. Therefore, it floats higher and has a deeper "root" than Oceanic Crust. This phenomenon can be compared with the behavior of floating wood blocks, all with the same density (see figure). The thicker blocks stand higher but have ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere
... oceanic plate- a tectonic plate containing ocean water ...
... oceanic plate- a tectonic plate containing ocean water ...
Splitting continents - Workspace
... According to this theory, if hot mantle is present, for example due to an underlying plume rising from deeper in the Earth, then a volcanic margin will form. This has been the cornerstone of our understanding for 20 years. The emphasis on mantle temperature as the main control on what happens when y ...
... According to this theory, if hot mantle is present, for example due to an underlying plume rising from deeper in the Earth, then a volcanic margin will form. This has been the cornerstone of our understanding for 20 years. The emphasis on mantle temperature as the main control on what happens when y ...
The Earth`s Layers
... • The upper mantle made of the lithosphere and asthenosphere. Therefor it is more solid than the lower mantle • The lower mantle is softer than the upper mantle. Although it is not completely liquid. ...
... • The upper mantle made of the lithosphere and asthenosphere. Therefor it is more solid than the lower mantle • The lower mantle is softer than the upper mantle. Although it is not completely liquid. ...
6th Grade Earth Science – Inside Earth Vocabulary 1. crust – the
... and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface 11. sea-floor spreading – the process ...
... and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface 11. sea-floor spreading – the process ...
Stratigraphy & geochemistry of the Nipigon basin
... Ga but still evidence of arc magmatism • Increasing evidence for Phanerozoic processes from 2.8 to 2.9 Ga • By 2.7 Ga plate tectonic processes similar to those of the Phanerozoic generate comparable suites of rocks ...
... Ga but still evidence of arc magmatism • Increasing evidence for Phanerozoic processes from 2.8 to 2.9 Ga • By 2.7 Ga plate tectonic processes similar to those of the Phanerozoic generate comparable suites of rocks ...
Convection Currents - Effingham County Schools
... lithosphere and has a different composition under land than it does on the ocean floor. ...
... lithosphere and has a different composition under land than it does on the ocean floor. ...
Earth`s interior volc eq1
... • A layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the ocean floor. – Very thin compared to the other layers, like the skin of an apple. – Thickest under high mountains, thinnest under the ocean floor. – 5-100 km thick – Oceanic crust is denser than continental. ...
... • A layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the ocean floor. – Very thin compared to the other layers, like the skin of an apple. – Thickest under high mountains, thinnest under the ocean floor. – 5-100 km thick – Oceanic crust is denser than continental. ...
What is “magnetic reversal?”
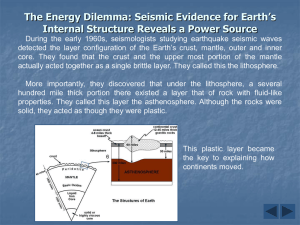
... During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion of the mantle actually acted together as a single brittle layer. They called this the lith ...
... During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion of the mantle actually acted together as a single brittle layer. They called this the lith ...
1. 1. Draw a subduction zone in which an oceanic plate collides with
... 1. 1. Draw a subduction zone in which an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Label the following on your sketch: the oceanic plate, the continental plate, location of seismicity (if any), location of volcanism (if any). Draw the boundary between the crust and the mantle and the boundary ...
... 1. 1. Draw a subduction zone in which an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Label the following on your sketch: the oceanic plate, the continental plate, location of seismicity (if any), location of volcanism (if any). Draw the boundary between the crust and the mantle and the boundary ...
Reviewing Vocabulary Reviewing Key Concepts
... c. the thickest layer of hot rock d. the thinnest and hottest layer 8. Tectonic plates make up Earth’s a. lower mantle c. asthenosphere b. lithosphere d. inner core 9. Why did many scientists reject Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis? a. He could not explain how the continents moved. b. The geol ...
... c. the thickest layer of hot rock d. the thinnest and hottest layer 8. Tectonic plates make up Earth’s a. lower mantle c. asthenosphere b. lithosphere d. inner core 9. Why did many scientists reject Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis? a. He could not explain how the continents moved. b. The geol ...
Mantle & Crust
... •At divergent plate margins (mid ocean ridges) – magma rises from asthenosphere decompression melting at low pressure - tholeiitic basalt •At hot spot (intra-plate volcanoes) – magma rises from deep mantle - decompression melting at high pressure - alkali basalt •At convergent plate margins (volcani ...
... •At divergent plate margins (mid ocean ridges) – magma rises from asthenosphere decompression melting at low pressure - tholeiitic basalt •At hot spot (intra-plate volcanoes) – magma rises from deep mantle - decompression melting at high pressure - alkali basalt •At convergent plate margins (volcani ...
Layers of Earth`s Interior Continental Drift/Seafloor
... ■ Shear forces cause plates to grind/slide past each other ■ Effects: shallow earthquakes ○ Earthquakes, along with volcanoes, mountains, ridges, and trenches occur at the boundary between two plates. ...
... ■ Shear forces cause plates to grind/slide past each other ■ Effects: shallow earthquakes ○ Earthquakes, along with volcanoes, mountains, ridges, and trenches occur at the boundary between two plates. ...
layers-of-the-earth-d-rl-2016
... _____ 6. Large pieces of the lithosphere that move around on the asthenosphere are called a. mantle pieces. b. crust pieces. c. tectonic plates. d. puzzle pieces. 7. Why are tectonic plates like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle? _______________________________________________________________ __________ ...
... _____ 6. Large pieces of the lithosphere that move around on the asthenosphere are called a. mantle pieces. b. crust pieces. c. tectonic plates. d. puzzle pieces. 7. Why are tectonic plates like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle? _______________________________________________________________ __________ ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.