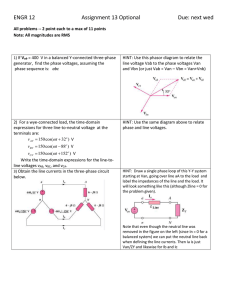
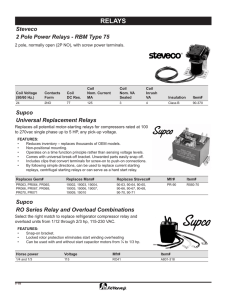
glossary of power terms
... reactive power to be applied to an AC network for power factor correction; adding capacitance in order to bring the voltage and current waveform in phase. Reactive power (kvar) — power which is actually “borrowed” from the load and returned to the power source each cycle; unused power. Resolution — ...
... reactive power to be applied to an AC network for power factor correction; adding capacitance in order to bring the voltage and current waveform in phase. Reactive power (kvar) — power which is actually “borrowed” from the load and returned to the power source each cycle; unused power. Resolution — ...
COMBOLIGHT New Construction Recessed Trimless - 12V MR16 - 6 Light
... plus one snoot or cross baffle. Optional retractable arm is available for lamp pulldown and extreme aiming. ...
... plus one snoot or cross baffle. Optional retractable arm is available for lamp pulldown and extreme aiming. ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... 1. Remember resistance occurs anytime current is sent thru a wire. 2. Power companies have found that very high voltages can travel more efficiently thru the wires 3. Once electricity is generated, it is transformed (in a step up transformer) to a very high voltage ( up to 750,000 volts) then sent a ...
... 1. Remember resistance occurs anytime current is sent thru a wire. 2. Power companies have found that very high voltages can travel more efficiently thru the wires 3. Once electricity is generated, it is transformed (in a step up transformer) to a very high voltage ( up to 750,000 volts) then sent a ...
1)______ types of Induction Motor are widely used. A. SlipringIM B
... 9) For a 3φ transmission line transmission efficiency of a line decreases with A. increase in load p.f. B. Does not vary with power factor C. increase in load current. D. decrease in load p.f. 10) Which combination is true for any transmission line A. A⃗ = 52, B⃗ = 0.8, C⃗ = 25, D⃗ = 0.385 B. . A⃗ = ...
... 9) For a 3φ transmission line transmission efficiency of a line decreases with A. increase in load p.f. B. Does not vary with power factor C. increase in load current. D. decrease in load p.f. 10) Which combination is true for any transmission line A. A⃗ = 52, B⃗ = 0.8, C⃗ = 25, D⃗ = 0.385 B. . A⃗ = ...
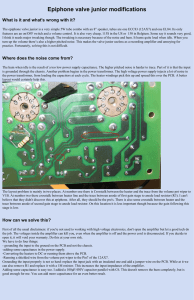
svokke_epi_valve_jr_..
... believe that they didn't discover this at epiphone. After all, they should be the pro's. There is also some crosstalk between heater and the trace between anode of second gain stage to anode load resistor. On this location it is less important though because the gain following this stage is low. ...
... believe that they didn't discover this at epiphone. After all, they should be the pro's. There is also some crosstalk between heater and the trace between anode of second gain stage to anode load resistor. On this location it is less important though because the gain following this stage is low. ...
ComboLight New Construction Recessed Trimless - 12V AR111 - 1 Light
... edge of the fixture opening. Includes a beveled “knife-edge” lips to ensure a clean edge. Can accommodate 0.50" (13mm) to 1.25" (32mm) ceiling thickness. Optional Chicago Plenum configuration available. ...
... edge of the fixture opening. Includes a beveled “knife-edge” lips to ensure a clean edge. Can accommodate 0.50" (13mm) to 1.25" (32mm) ceiling thickness. Optional Chicago Plenum configuration available. ...
Ignition system lecture
... the secondary winding.When the trailing edge of the magnets the flywheel reaches the trigger coil, a second small current is induced in the trigger coil and that current tells the transistor to "turn off", effectively breaking the circuit of the primary winding to ground (Figure 3), the sudden break ...
... the secondary winding.When the trailing edge of the magnets the flywheel reaches the trigger coil, a second small current is induced in the trigger coil and that current tells the transistor to "turn off", effectively breaking the circuit of the primary winding to ground (Figure 3), the sudden break ...
Transformer types
A variety of types of electrical transformer are made for different purposes. Despite their design differences, the various types employ the same basic principle as discovered in 1831 by Michael Faraday, and share several key functional parts.