5. Matching of impedances___________2007__17
... Available power (H. T. Friis, 1944) is defined as the maximum power that can be delivered to a load from a source having fixed nonzero resistance ...
... Available power (H. T. Friis, 1944) is defined as the maximum power that can be delivered to a load from a source having fixed nonzero resistance ...
Three Phase Transmission lines fault Detection, Classification and
... Faults occurrence can be easily detected with abrupt decrease in impedance of the line due to high current during fault. Next problem is its classification that is the type of fault which has occurred. Out of these five the LLL and LLLG faults are symmetrical faults and are indistinguishable. The vo ...
... Faults occurrence can be easily detected with abrupt decrease in impedance of the line due to high current during fault. Next problem is its classification that is the type of fault which has occurred. Out of these five the LLL and LLLG faults are symmetrical faults and are indistinguishable. The vo ...
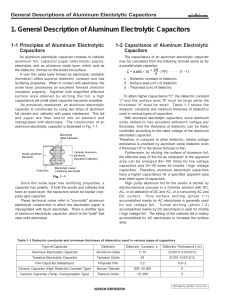
1. General Description of Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
... ε : Dielectric constant of dielectric S : Surface area (cm2) of dielectric d : Thickness (cm) of dielectric To attain higher capacitance "C", the dielectric constant " ε " and the surface area "S" must be large while the thickness "d" must be small. Table 1-1 shows the dielectric constants and minim ...
... ε : Dielectric constant of dielectric S : Surface area (cm2) of dielectric d : Thickness (cm) of dielectric To attain higher capacitance "C", the dielectric constant " ε " and the surface area "S" must be large while the thickness "d" must be small. Table 1-1 shows the dielectric constants and minim ...
Loading Considerations when Paralleling Transformers
... Loading considerations for paralleling transformers are simple unless kVA, percent impedances or ratios are different. When paralleled transformer turn ratios, and percent impedances are the same, there will be equal load division on each transformers. When paralleled transformer kVA ratings are the ...
... Loading considerations for paralleling transformers are simple unless kVA, percent impedances or ratios are different. When paralleled transformer turn ratios, and percent impedances are the same, there will be equal load division on each transformers. When paralleled transformer kVA ratings are the ...
An End Fed Half Wave Length Antenna is a variation of the much
... impedance is high designing a choke balun with enough impedance to be effective may be difficult anyway. However, if this setup is being used in the field with very short or no coax (direct attachment to rig) then any common mode currents that do exist will be negligible. Only when the "counterpoise ...
... impedance is high designing a choke balun with enough impedance to be effective may be difficult anyway. However, if this setup is being used in the field with very short or no coax (direct attachment to rig) then any common mode currents that do exist will be negligible. Only when the "counterpoise ...
Distance Protection for Half Wavelength Transmission Lines
... an alternating current (AC link) option with some particular characteristics might be the most economical one, having much less dependence on the Power Electronics technology. In the 1960s [1]-[2], the first studies were done showing that the AC line has an interesting behavior in terms of voltage, ...
... an alternating current (AC link) option with some particular characteristics might be the most economical one, having much less dependence on the Power Electronics technology. In the 1960s [1]-[2], the first studies were done showing that the AC line has an interesting behavior in terms of voltage, ...
Glossary - Priority Wire
... Breakdown Voltage: The voltage at which the insulation between two conductors is destroyed. Breakout: The point at which a conductor or group of conductors is separated from a multiconductor cable to complete circuits at various points along the main cable. ...
... Breakdown Voltage: The voltage at which the insulation between two conductors is destroyed. Breakout: The point at which a conductor or group of conductors is separated from a multiconductor cable to complete circuits at various points along the main cable. ...
Signal Integrity Analysis of Package and PCB for High Speed Data
... factors like tighter packaging space, circuit boards and increasing clock frequencies, packaging issues and system-level performance issues such as crosstalk and transmission lines are becoming increasingly significant. Multi-chip packages and increased IO counts are forcing package design to become ...
... factors like tighter packaging space, circuit boards and increasing clock frequencies, packaging issues and system-level performance issues such as crosstalk and transmission lines are becoming increasingly significant. Multi-chip packages and increased IO counts are forcing package design to become ...
A Novel High-Frequency Voltage Standing-Wave Ratio
... electrode line, and improvement measures were proposed to enhance the reliability of the existing unbalanced current protection strategy [8]. The authors in [9] proposed a fast tripping scheme by inserting DC breakers into both grounding electrode lines. The control and protection strategies were re ...
... electrode line, and improvement measures were proposed to enhance the reliability of the existing unbalanced current protection strategy [8]. The authors in [9] proposed a fast tripping scheme by inserting DC breakers into both grounding electrode lines. The control and protection strategies were re ...
Advanced Control Architectures for Intelligent MicroGrids, Part I
... sources inject control signals into the network at a frequency which droops as the shared quantity increases. PLLs in remote units extract this information and adjust their output. Although interesting, this approach has not yet been investigated fully to study the issues of voltage distortion and n ...
... sources inject control signals into the network at a frequency which droops as the shared quantity increases. PLLs in remote units extract this information and adjust their output. Although interesting, this approach has not yet been investigated fully to study the issues of voltage distortion and n ...
TRI`ACE WW `
... de?ection of the oscilloscope will trigger the horizontal 40, and resistor 52. Transducer 30 is connected to terminal 24 through high pass ?lter means 42, ampli?er means 44, 55 sweep of the scope. Further, only one type of signal is used, with all of the signals being from a transducer or and resist ...
... de?ection of the oscilloscope will trigger the horizontal 40, and resistor 52. Transducer 30 is connected to terminal 24 through high pass ?lter means 42, ampli?er means 44, 55 sweep of the scope. Further, only one type of signal is used, with all of the signals being from a transducer or and resist ...
PCB Design Guidelines For Reduced EMI
... not a teaching aid. The reader is cautioned against making the assumption that although on a prior design a given technique was not applied and the unit had acceptable performance, that the technique is not useful. Over time, as IC devices increase in speed and density, every method to isolate and r ...
... not a teaching aid. The reader is cautioned against making the assumption that although on a prior design a given technique was not applied and the unit had acceptable performance, that the technique is not useful. Over time, as IC devices increase in speed and density, every method to isolate and r ...
Practical Approach in Designing Conducted EMI Filter to Mitigate
... CM consist of high frequency impulses, there is a high probability that the noise will see the high frequency transformer just as a coupling capacitor and pass through unobstructed. Stray capacitor paths may exist within SMPS because they are smaller in physical size and more densely packaged as com ...
... CM consist of high frequency impulses, there is a high probability that the noise will see the high frequency transformer just as a coupling capacitor and pass through unobstructed. Stray capacitor paths may exist within SMPS because they are smaller in physical size and more densely packaged as com ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.