MAX2034 Quad-Channel, Ultra-Low-Noise Amplifier with Digitally Programmable Input Impedance General Description
... Channel 2 LNA Analog Input. Single-ended input for channel 2 amplifier. Connect the analog input to the source circuit through a series capacitor. ...
... Channel 2 LNA Analog Input. Single-ended input for channel 2 amplifier. Connect the analog input to the source circuit through a series capacitor. ...
Design Example –7.1.
... conventional way to satisfy (at least to approach to) this condition is to use a low loss (high Q) resonance circuit as the resonator of the oscillator. For on-chip resonance circuits there is a possibility to equate ω(max) and ω(Re). It can be seen from (7.4) that for rC rL , ω(Re) becomes equal ...
... conventional way to satisfy (at least to approach to) this condition is to use a low loss (high Q) resonance circuit as the resonator of the oscillator. For on-chip resonance circuits there is a possibility to equate ω(max) and ω(Re). It can be seen from (7.4) that for rC rL , ω(Re) becomes equal ...
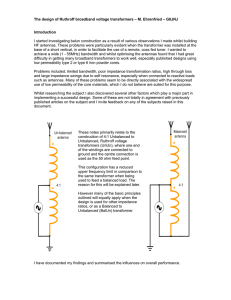
Development of Ultra-Multilayer Printed Circuit Board
... with the thicker boards and smaller diameter holes. At the time of introducing new electroplating equipment, we simulated current distribution in the plating tank and developed the plating equipment. Additionally, by introducing new plating solution and optimizing plating conditions, we were able to ...
... with the thicker boards and smaller diameter holes. At the time of introducing new electroplating equipment, we simulated current distribution in the plating tank and developed the plating equipment. Additionally, by introducing new plating solution and optimizing plating conditions, we were able to ...
JohnAnalog
... stability and noise immunity. Each MDT connects to a “signal” preamp with an associated “dummy” preamp. This in turn connects to the mezzanine card but goes no further. It provides dc balance to the subsequent stages as well as some degree of common mode rejection from noise pickup, substrate coupli ...
... stability and noise immunity. Each MDT connects to a “signal” preamp with an associated “dummy” preamp. This in turn connects to the mezzanine card but goes no further. It provides dc balance to the subsequent stages as well as some degree of common mode rejection from noise pickup, substrate coupli ...
Chapter 2
... transition is proportional to Q. For example, if a filter allows a 50 kHz channel spacing at 1 MHz center frequency, then with the same Q at 1 GHz the minimum channel spacing would be 50 MHz. Most protocols of communication do not require more than a couple MHz of bandwidth to contain all the inform ...
... transition is proportional to Q. For example, if a filter allows a 50 kHz channel spacing at 1 MHz center frequency, then with the same Q at 1 GHz the minimum channel spacing would be 50 MHz. Most protocols of communication do not require more than a couple MHz of bandwidth to contain all the inform ...
Chapter 1 : Introduction to Electronic Communications
... when Z0 = ZL, all the incident power is absorbed by the load. This is called a matched line. when Z0 ≠ ZL, some of the incident power is absorbed by the load and some is returned (reflected) to the source. This is called an unmatched or mismatched line. with a mismatched line, there are 2 electromag ...
... when Z0 = ZL, all the incident power is absorbed by the load. This is called a matched line. when Z0 ≠ ZL, some of the incident power is absorbed by the load and some is returned (reflected) to the source. This is called an unmatched or mismatched line. with a mismatched line, there are 2 electromag ...
Antennas and propagation
... These antennas find applications where low profile or flush installations are required. eg High Speed Aircraft. Relation of slot and their complimentary dipole forms. Any slot has its complementary form in wires or strips. Pattern and impedance data can be used to predict the pattern and impedance o ...
... These antennas find applications where low profile or flush installations are required. eg High Speed Aircraft. Relation of slot and their complimentary dipole forms. Any slot has its complementary form in wires or strips. Pattern and impedance data can be used to predict the pattern and impedance o ...
S-Parameters and Related Quantities
... The signal A reaching the DUT at terminal 1 is called the incident signal. Part of that signal is reflected as B, and part of it is transmitted as C out of terminal 2. The ratio of the reflected signal, B, to the incident signal, A, is the reflection coefficient. The ratio of the transmitted signal, ...
... The signal A reaching the DUT at terminal 1 is called the incident signal. Part of that signal is reflected as B, and part of it is transmitted as C out of terminal 2. The ratio of the reflected signal, B, to the incident signal, A, is the reflection coefficient. The ratio of the transmitted signal, ...
Feasibility study
... behavior there is no circuit with input impedance that matches to the function W() for all frequencies. The characteristic impedance goes to the value of 300Ohm at high frequencies, so resistive part of the electronic input impedance must go to the value as well. A serial capacitor in front of it d ...
... behavior there is no circuit with input impedance that matches to the function W() for all frequencies. The characteristic impedance goes to the value of 300Ohm at high frequencies, so resistive part of the electronic input impedance must go to the value as well. A serial capacitor in front of it d ...
High Frequency Modeling for Cable and Induction Motor Over
... program, one chooses the number of lumped sections as well as the simulation time step. The whole system can be simulated in a two-axes ( – ) approach, which reduces the number of differential equations. The numerical integration is realized using Runge–Kutta Method order 4 [4]. Simulation results w ...
... program, one chooses the number of lumped sections as well as the simulation time step. The whole system can be simulated in a two-axes ( – ) approach, which reduces the number of differential equations. The numerical integration is realized using Runge–Kutta Method order 4 [4]. Simulation results w ...
Touch Current Basics.ppt [Compatibility Mode]
... The input voltage and the output voltage (or milli-amperes milli as indicated on the meter) are measured at various frequencies and the ratios compared to the data in tables as appropriate. The input voltages used should be such as to produce output indications in the range of the TOUCH CURRENT valu ...
... The input voltage and the output voltage (or milli-amperes milli as indicated on the meter) are measured at various frequencies and the ratios compared to the data in tables as appropriate. The input voltages used should be such as to produce output indications in the range of the TOUCH CURRENT valu ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.




















![Touch Current Basics.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007899503_2-89947630ac5049138593ad1d5ba74dfa-300x300.png)