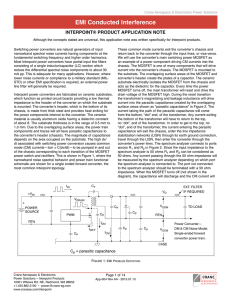
Modified droop control scheme for load sharing
... type control, and circular chain control (Chadorkar et al. 1993, Duan et al. 1999, Wu et al. 2000, Zong 2013) to achieve the rigid control on the voltage/current for load sharing. However, due to the long communication lines between the distantly placed DRs, such wired control approaches face the is ...
... type control, and circular chain control (Chadorkar et al. 1993, Duan et al. 1999, Wu et al. 2000, Zong 2013) to achieve the rigid control on the voltage/current for load sharing. However, due to the long communication lines between the distantly placed DRs, such wired control approaches face the is ...
"Arctic" cable - IET Electrical
... common theme - i.e. can bluesheathed cable, made to BS 6500, be used for 230 V a.c. single-phase supplies to equipment in temporary use? The answer is yes but not at temperatures lower than +5°C. The following is intended to clarify. ...
... common theme - i.e. can bluesheathed cable, made to BS 6500, be used for 230 V a.c. single-phase supplies to equipment in temporary use? The answer is yes but not at temperatures lower than +5°C. The following is intended to clarify. ...
Designing With TPS7H3301-SP Double Data Rate (DDR) Termination
... DDR Memory and SSTL Basics In commercial applications, there are two forms of memory that are commonly used in computer systems non-Volatile memory and volatile memory. Whereas non-volatile memory is memory that can retain the stored information even when not powered. Example of non-volatile memory ...
... DDR Memory and SSTL Basics In commercial applications, there are two forms of memory that are commonly used in computer systems non-Volatile memory and volatile memory. Whereas non-volatile memory is memory that can retain the stored information even when not powered. Example of non-volatile memory ...
Vector Receiver Load Pull
... It is possible to build 3 tuners in 1 box, but it becomes 2-3x longer and 2-3x more expensive 23 ...
... It is possible to build 3 tuners in 1 box, but it becomes 2-3x longer and 2-3x more expensive 23 ...
EL2082 Datasheet
... op-amps, the pole caused by these capacitances can make the amplifier less stable and even cause oscillations in amplifiers whose gain-bandwidth is greater than 5MHz. A typical cure is to add a capacitor C F in the 2pF-10pF range. This will reduce overall bandwidth, so a capacitor C IN can be added ...
... op-amps, the pole caused by these capacitances can make the amplifier less stable and even cause oscillations in amplifiers whose gain-bandwidth is greater than 5MHz. A typical cure is to add a capacitor C F in the 2pF-10pF range. This will reduce overall bandwidth, so a capacitor C IN can be added ...
Further Development of a High Gain Microphone
... utilizes two feed resistors, typically having resistance of 6.8k . These resistors have to be closely matched (within 0.4%) to achieve good common mode performance, however the actual value of these resistors is not critical. The drawback with this method is the fact that the maximum input impedance ...
... utilizes two feed resistors, typically having resistance of 6.8k . These resistors have to be closely matched (within 0.4%) to achieve good common mode performance, however the actual value of these resistors is not critical. The drawback with this method is the fact that the maximum input impedance ...
System Impact Assessment Application
... A detailed single-line diagram showing the equipment and the protection and telemetry points. The locations of the proposed connections on to existing lines, or into existing transformer/ switching stations, are also to be included. Details are to be included of any existing facilities that are to b ...
... A detailed single-line diagram showing the equipment and the protection and telemetry points. The locations of the proposed connections on to existing lines, or into existing transformer/ switching stations, are also to be included. Details are to be included of any existing facilities that are to b ...
A Test Bench for Differential Circuits
... impedance. (If Rid were not 0 Ω, then the input impedance would be equal to the voltage on d divided by the current through d.) Similarly, one measures the common-mode input impedance during the common-mode gain test by taking the reciprocal of the current through terminal c of Bi. To measure the di ...
... impedance. (If Rid were not 0 Ω, then the input impedance would be equal to the voltage on d divided by the current through d.) Similarly, one measures the common-mode input impedance during the common-mode gain test by taking the reciprocal of the current through terminal c of Bi. To measure the di ...
Signal Types and Terminations
... CMOS signals are distributed across a backplane having 50 ohm impedance traces, into one or more high impedance receivers. As such, there is an impedance mismatch. There are ways to deal with this impedance match, but between this and the inherit limits of the “rail to rail” swing, CMOS outputs are ...
... CMOS signals are distributed across a backplane having 50 ohm impedance traces, into one or more high impedance receivers. As such, there is an impedance mismatch. There are ways to deal with this impedance match, but between this and the inherit limits of the “rail to rail” swing, CMOS outputs are ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.