Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... The potassium gates close relatively slowly, therefore, hyperpolarization occurs, and the cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory p ...
... The potassium gates close relatively slowly, therefore, hyperpolarization occurs, and the cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory p ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... Rapid propagation of action potentials is important for survival, especially in situations that require rapid, reflexive responses. In squids, evolution solved the problem of how to send fast-moving signals from one end of the body to the other by making giant axons, 1000 times fatter than our axons ...
... Rapid propagation of action potentials is important for survival, especially in situations that require rapid, reflexive responses. In squids, evolution solved the problem of how to send fast-moving signals from one end of the body to the other by making giant axons, 1000 times fatter than our axons ...
ppt
... 1. Connect the flow of neurotransmitters through an axon to the mechanism of its potential effect on another neuron 2. Outine the steps in chemical synaptic transmission and predict changes in the efficacy of transmission when the system is perturbed (e.g. changes in ion concentrations or addition ...
... 1. Connect the flow of neurotransmitters through an axon to the mechanism of its potential effect on another neuron 2. Outine the steps in chemical synaptic transmission and predict changes in the efficacy of transmission when the system is perturbed (e.g. changes in ion concentrations or addition ...
THE NERVE OF IT ALL
... – Schwann – form neurolemma and myelin sheath only on neurons OUTSIDE of CNS = PNS – Ependymal – line central canal and ventricles; help produce and circulate CSF in choroid ...
... – Schwann – form neurolemma and myelin sheath only on neurons OUTSIDE of CNS = PNS – Ependymal – line central canal and ventricles; help produce and circulate CSF in choroid ...
Neurons
... the axon versus how much continues down the axon core. The larger the diameter, the more easily current flows down the core and the farther ahead of itself the AP can reach to depolarize fresh membrane. ...
... the axon versus how much continues down the axon core. The larger the diameter, the more easily current flows down the core and the farther ahead of itself the AP can reach to depolarize fresh membrane. ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... a. Purkinje cell (cerebellum). b. Alpha-motoneuron (spinal cord). c. Spiny neuron (striatum). d. Axonless interneuron (locust nervous ...
... a. Purkinje cell (cerebellum). b. Alpha-motoneuron (spinal cord). c. Spiny neuron (striatum). d. Axonless interneuron (locust nervous ...
Summary Sodium pump.
... • The plasma membrane of neurons, like all other cells, has an unequal distribution of ions and electrical charges between the two sides of the membrane. The outside of the membrane has a positive charge, inside has a negative charge. This charge difference is a resting potential and is measured in ...
... • The plasma membrane of neurons, like all other cells, has an unequal distribution of ions and electrical charges between the two sides of the membrane. The outside of the membrane has a positive charge, inside has a negative charge. This charge difference is a resting potential and is measured in ...
Chapter 7 Part 1 Nervous Tissue
... Nodes of Ranvier • Are gaps in the myelin sheath formed by spaces between successive oligodendrocytes (in CNS) or Schwann cells (in PNS) along the length of the axon. • Nodes of Ranvier contain Na+ ion channels, and are sites where action potentials are generated by membrane depolarizations. • The ...
... Nodes of Ranvier • Are gaps in the myelin sheath formed by spaces between successive oligodendrocytes (in CNS) or Schwann cells (in PNS) along the length of the axon. • Nodes of Ranvier contain Na+ ion channels, and are sites where action potentials are generated by membrane depolarizations. • The ...
Neurones & the Action Potential
... threshold, then an action potential and hence an impulse are not produced. This is called the All-or-None Principle. A threshold stimulus must be applied to get an action potential. ...
... threshold, then an action potential and hence an impulse are not produced. This is called the All-or-None Principle. A threshold stimulus must be applied to get an action potential. ...
Nervous System and Neuron
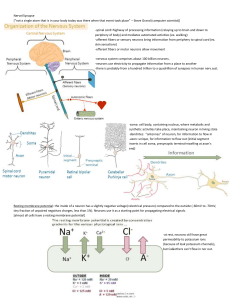
... The Anatomy of a Neuron The nervous system is composed of specialized cells called neurons. Neurons are specialized for the transmission of information at rapid rates. Maintenance of homeostasis depends on this transmission and response. A neuron consists of the following basic parts: Dendrites - ...
... The Anatomy of a Neuron The nervous system is composed of specialized cells called neurons. Neurons are specialized for the transmission of information at rapid rates. Maintenance of homeostasis depends on this transmission and response. A neuron consists of the following basic parts: Dendrites - ...
Anatomy and Physiology 241 Lecture Objectives The Nervous
... Compare and contrast the nervous and the endocrine systems. Describe the organization of the nervous system. Define CNS, PNS-afferent and efferent divisions, somatic nervous system, automatic nervous system. Name the 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system. What are where are ganglia found? Diff ...
... Compare and contrast the nervous and the endocrine systems. Describe the organization of the nervous system. Define CNS, PNS-afferent and efferent divisions, somatic nervous system, automatic nervous system. Name the 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system. What are where are ganglia found? Diff ...
Nerve
... -neurons synapse on cell bodies, dendrites, or axons of other neurons -neurons integrate, conduct, and transmit coded information B. Cell Body (Perikaryon) -contains the nucleus, ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and other cellular organelles -the ER synthesizes neurotransmitter and contains the ribos ...
... -neurons synapse on cell bodies, dendrites, or axons of other neurons -neurons integrate, conduct, and transmit coded information B. Cell Body (Perikaryon) -contains the nucleus, ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and other cellular organelles -the ER synthesizes neurotransmitter and contains the ribos ...
Neural_Tissue_notes
... falling phase of act. pot., period of hyperpolarization. What properties of the nerve cell membrane cause or account for each of the phases? Voltage-gated Na and K channels play key roles. APs are self-propagating – meaning what? They have an all-or-none quality – meaning what? Relationship between ...
... falling phase of act. pot., period of hyperpolarization. What properties of the nerve cell membrane cause or account for each of the phases? Voltage-gated Na and K channels play key roles. APs are self-propagating – meaning what? They have an all-or-none quality – meaning what? Relationship between ...
Chapter 3
... Chapter 2 Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Module 2.1 The Cells of the Nervous System 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barr ...
... Chapter 2 Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Module 2.1 The Cells of the Nervous System 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barr ...
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Chapter 11
... outside cell- negative proteins in also, Na+ higher outside than inside – At equilibrium there is very little movement of K+ or other ions across plasma membrane ...
... outside cell- negative proteins in also, Na+ higher outside than inside – At equilibrium there is very little movement of K+ or other ions across plasma membrane ...
Internet Structure
... The Internet as a graph • Remember: the Internet is a collection of networks called autonomous systems (ASs) • The Internet graph: – The AS graph • Nodes: ASs, links: AS peering ...
... The Internet as a graph • Remember: the Internet is a collection of networks called autonomous systems (ASs) • The Internet graph: – The AS graph • Nodes: ASs, links: AS peering ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in cluste ...
... • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in cluste ...
Nervous System
... cells where myelin is not complete. Saltatory conduction= jump from node to node. ...
... cells where myelin is not complete. Saltatory conduction= jump from node to node. ...
Learning Objectives
... Understand the competing forces of the electrical and concentration gradients on potassium ions and how this competition produces the resting potential. ...
... Understand the competing forces of the electrical and concentration gradients on potassium ions and how this competition produces the resting potential. ...
LESSON 2.3 WORKBOOK How fast do our neurons signal?
... We can immediately see two advantages of saltatory conduction. The first is it saves energy. Sodium ions that enter axons during the action potential must eventually be removed. You’ll remember that the Na+ ions are removed by Na+/K+ pumps, which use significant amounts of energy. As we mentioned be ...
... We can immediately see two advantages of saltatory conduction. The first is it saves energy. Sodium ions that enter axons during the action potential must eventually be removed. You’ll remember that the Na+ ions are removed by Na+/K+ pumps, which use significant amounts of energy. As we mentioned be ...
Schwann cells - Mayfield City Schools
... wrapping its plasma membrane loosely around it in successive layers. ...
... wrapping its plasma membrane loosely around it in successive layers. ...
Motor Neuron - tekkieoldteacher
... • Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane. • When materials move into and out of a cell at equal rates, the cell is balanced, or in dynamic equilibrium. An isotonic solution has a concentration of materials the same as the inside of a cell. If a cell is placed in an isoton ...
... • Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane. • When materials move into and out of a cell at equal rates, the cell is balanced, or in dynamic equilibrium. An isotonic solution has a concentration of materials the same as the inside of a cell. If a cell is placed in an isoton ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.