ESS 202 - Earthquakes
... • There are about 15 major plates. • Their boundaries are the sites of earthquakes and volcanoes. Why? • Three types of plate boundaries – convergent -> subduction -> destruction of plate (oceanic plate) – divergent -> sea-floor spreading -> creation of plate (oceanic plate) ...
... • There are about 15 major plates. • Their boundaries are the sites of earthquakes and volcanoes. Why? • Three types of plate boundaries – convergent -> subduction -> destruction of plate (oceanic plate) – divergent -> sea-floor spreading -> creation of plate (oceanic plate) ...
Snelling book geology - creationapologetics.net
... Amer. Indians and Aborigines(who practiced circumcisim) existed longer that the 3000 yr preflood history and people could not have all dispersed from Asia-Mesopotamia. However it is not clearly proven that they are that old as some of the carbon dating is flawed. If Noah’s sons and daughters had som ...
... Amer. Indians and Aborigines(who practiced circumcisim) existed longer that the 3000 yr preflood history and people could not have all dispersed from Asia-Mesopotamia. However it is not clearly proven that they are that old as some of the carbon dating is flawed. If Noah’s sons and daughters had som ...
sequence-of-geologic-events
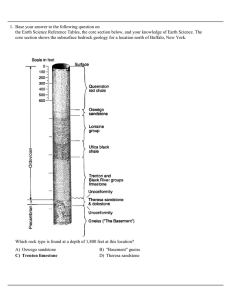
... 3. Based on the given rock and fossil which two letters most likely indicate parts of the same layer? A) A and F B) B and D C) C and E D) D and A 4. Which processes were directly involved in the formation of these rock layers? A) melting and solidification B) heating and pressure C) compaction and c ...
... 3. Based on the given rock and fossil which two letters most likely indicate parts of the same layer? A) A and F B) B and D C) C and E D) D and A 4. Which processes were directly involved in the formation of these rock layers? A) melting and solidification B) heating and pressure C) compaction and c ...
Chapter 9—The Proterozoic: Dawn of a More Modern World
... b. fossils may look like modern forms, but are really not related; some may not have modern equivalents Appearance may have followed soon after the end of global glaciation (the “snowball Earth” hypothesis) ...
... b. fossils may look like modern forms, but are really not related; some may not have modern equivalents Appearance may have followed soon after the end of global glaciation (the “snowball Earth” hypothesis) ...
Plate-Tectonics Teaching Slides
... • Rocks found further away from ridge proves that new sea floor is created continuously • Example of divergent plate boundary : Mid-Atlantic ...
... • Rocks found further away from ridge proves that new sea floor is created continuously • Example of divergent plate boundary : Mid-Atlantic ...
Part 4 - NSW Department of Education
... of tectonic processes. Every year, news reports of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes remind us of the tectonic forces at work inside the Earth, and we can see on television some of the catastrophic effects these forces have had on local areas of the Earth’s surface. In Australia, earthquakes do occ ...
... of tectonic processes. Every year, news reports of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes remind us of the tectonic forces at work inside the Earth, and we can see on television some of the catastrophic effects these forces have had on local areas of the Earth’s surface. In Australia, earthquakes do occ ...
rock
... Large variety of igneous rocks is produced by large variety of magma compositions Mafic magmas will crystallize into basalt or gabbro if early-formed minerals are not removed from the magma Intermediate magmas will similarly crystallize into diorite or andesite if minerals are not removed Separation ...
... Large variety of igneous rocks is produced by large variety of magma compositions Mafic magmas will crystallize into basalt or gabbro if early-formed minerals are not removed from the magma Intermediate magmas will similarly crystallize into diorite or andesite if minerals are not removed Separation ...
Chapter 1 Introduction and review of literature
... Every day there are about fifty earthquakes worldwide that are strong enough to be felt locally, and every few days an earthquake occurs that is capable of damaging structures. Each event radiates seismic waves that travel throughout Earth, and several earthquakes per day produce distant ground moti ...
... Every day there are about fifty earthquakes worldwide that are strong enough to be felt locally, and every few days an earthquake occurs that is capable of damaging structures. Each event radiates seismic waves that travel throughout Earth, and several earthquakes per day produce distant ground moti ...
Plate Tectonics and Landform Evolution
... that continents could move apart by the mechanism of sea floor spreading. This means that a new oceanic crust is continuously generated from molten mantle material advecting below mid-oceanic ridges, and progressively ages during its retreat from the ridge, the crust adjacent to continental margins ...
... that continents could move apart by the mechanism of sea floor spreading. This means that a new oceanic crust is continuously generated from molten mantle material advecting below mid-oceanic ridges, and progressively ages during its retreat from the ridge, the crust adjacent to continental margins ...
Earthquakes
... marks the boundary between the Earth’s crust and mantle. The shadow zone is an area on the Earth’s Surface where no direct seismic waves from a particular earthquake can be detected. This discovery suggested that the Earth has a liquid core. The solid inner core was discovered in 1936. Before this ...
... marks the boundary between the Earth’s crust and mantle. The shadow zone is an area on the Earth’s Surface where no direct seismic waves from a particular earthquake can be detected. This discovery suggested that the Earth has a liquid core. The solid inner core was discovered in 1936. Before this ...
Lab handout - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... crystals and a coarse texture, while quick cooling produces small crystals and a fine texture. Igneous rocks erupted from volcanoes cool quickly on the surface of the Earth, while others cool slowly in the Earth’s interior. As you saw in the thymol experiment, crystals nucleate and grow, producing a ...
... crystals and a coarse texture, while quick cooling produces small crystals and a fine texture. Igneous rocks erupted from volcanoes cool quickly on the surface of the Earth, while others cool slowly in the Earth’s interior. As you saw in the thymol experiment, crystals nucleate and grow, producing a ...
3rd Qtr Syllabus
... Show your answer to Mr. Shoop for score and assessment. In your journal create a data chart that Lists; Activity 2, 3 & 4. As each activity is completed, Mr. Shoop will give you several questions to answer as an assessment. Mr. Shoop will record each score in your journal in this chart. Activity 2 B ...
... Show your answer to Mr. Shoop for score and assessment. In your journal create a data chart that Lists; Activity 2, 3 & 4. As each activity is completed, Mr. Shoop will give you several questions to answer as an assessment. Mr. Shoop will record each score in your journal in this chart. Activity 2 B ...
Deep Focus Earthquake
... whole number step in the magnitude scale corresponds to the release of about 31.7 times more energy than the amount associated with the preceding whole number value. ...
... whole number step in the magnitude scale corresponds to the release of about 31.7 times more energy than the amount associated with the preceding whole number value. ...
Mercury - GEOCITIES.ws
... continuous ejecta blanket. These restrictions also reduce the effect on Mercury of proximity erosion, in which ejecta from one crater lands on and covers or degrades an adjacent crater. The number of craters on various surfaces on Mercury also shows remarkable similarities to lunar cratering. The ag ...
... continuous ejecta blanket. These restrictions also reduce the effect on Mercury of proximity erosion, in which ejecta from one crater lands on and covers or degrades an adjacent crater. The number of craters on various surfaces on Mercury also shows remarkable similarities to lunar cratering. The ag ...
Background Knowledge – Layers of the Earth 1. List the layers of the
... The oceanic crust will be subducted because it is more dense. When the plates collide, friction creates a pulling effect on both pieces of crust and a deep oceanic trench is formed. 10. What feature is formed when two pieces of oceanic crust collide? One piece of oceanic crust will be subducted. Whe ...
... The oceanic crust will be subducted because it is more dense. When the plates collide, friction creates a pulling effect on both pieces of crust and a deep oceanic trench is formed. 10. What feature is formed when two pieces of oceanic crust collide? One piece of oceanic crust will be subducted. Whe ...
Granitization of the Basic Volcanic Rocks in the Contact Aureole of
... (Iruneiskaya Formation); (3) terrigenous–volcanic–pyroclastic complex (Stenovaya Group); (4–6) Ganalskaya Group: (4) D’yavolskaya Sequence, (5) Voevodskaya Sequence, (6) Vakhtalkinskaya Sequence; (7) zone of intense hornfelsing, metasomatism, and magmatic replacement of the rocks of the Vakhtalkinsk ...
... (Iruneiskaya Formation); (3) terrigenous–volcanic–pyroclastic complex (Stenovaya Group); (4–6) Ganalskaya Group: (4) D’yavolskaya Sequence, (5) Voevodskaya Sequence, (6) Vakhtalkinskaya Sequence; (7) zone of intense hornfelsing, metasomatism, and magmatic replacement of the rocks of the Vakhtalkinsk ...
Glossary of Terms - Department of Natural Resources
... CALDERA: a large-scale, roughly circular volcanic depression, formed near the top of a volcano when huge eruptions empties the magma chamber under the volcano. The caldera can then be filled with sediments and volcanics and intruded by younger intrusions. More than one caldera can form in any one ar ...
... CALDERA: a large-scale, roughly circular volcanic depression, formed near the top of a volcano when huge eruptions empties the magma chamber under the volcano. The caldera can then be filled with sediments and volcanics and intruded by younger intrusions. More than one caldera can form in any one ar ...
ES 104 Midterm Exam Study Guide 1
... Know that the lithosphere includes the crust and the upper most mantle rocks. Know that the asthenosphere is solid but is soft and capable of gradual flow. Know that the only layer that is completely molten is the outer core. Know the differences between continental crust and oceanic crust (thicknes ...
... Know that the lithosphere includes the crust and the upper most mantle rocks. Know that the asthenosphere is solid but is soft and capable of gradual flow. Know that the only layer that is completely molten is the outer core. Know the differences between continental crust and oceanic crust (thicknes ...
Earth`s Lithosphere System – Rock Cycle
... related to chemical composition and atomic structure; these properties do not change with mineral size or shape. CLEAVAGE AND FRACTURE: how a mineral tends to break. Cleavage: splitting of a mineral along planar (flat) surfaces; determined by planes of weakness in its atomic structure. The number, q ...
... related to chemical composition and atomic structure; these properties do not change with mineral size or shape. CLEAVAGE AND FRACTURE: how a mineral tends to break. Cleavage: splitting of a mineral along planar (flat) surfaces; determined by planes of weakness in its atomic structure. The number, q ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.