The Geological Time Scale
... 350 mya: first trees appear; period of intense global warming and coal formation 300 mya: first true reptiles 275 mya: super continent of “Pangaea” forms 250 mya: largest mass extinction ever kills off 95% of ocean life; end of Paleozoic Major events of the Mesozoic Era 250 mya: first true dinosaurs ...
... 350 mya: first trees appear; period of intense global warming and coal formation 300 mya: first true reptiles 275 mya: super continent of “Pangaea” forms 250 mya: largest mass extinction ever kills off 95% of ocean life; end of Paleozoic Major events of the Mesozoic Era 250 mya: first true dinosaurs ...
INVITED REVIEW Petit-spot volcanism: A new type of volcanic zone
... by ROV KAIKO (of the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, JAMSTEC) in the Japan Trench, was unexpected because nobody had anticipated such volcanism on the Cretaceous Pacific Plate. The dive revealed continuous outcrops and collapsed angular blocks of basalt for 50 m along a steep c ...
... by ROV KAIKO (of the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, JAMSTEC) in the Japan Trench, was unexpected because nobody had anticipated such volcanism on the Cretaceous Pacific Plate. The dive revealed continuous outcrops and collapsed angular blocks of basalt for 50 m along a steep c ...
Erratum - Forward
... systematically with water content and the a axis decreases systematically with increasing water content. Although there is also a clear positive volume of hydration (i.e. volume increases with water content), by using b / a individual measurements are not subject to absolute uncertainty in the volum ...
... systematically with water content and the a axis decreases systematically with increasing water content. Although there is also a clear positive volume of hydration (i.e. volume increases with water content), by using b / a individual measurements are not subject to absolute uncertainty in the volum ...
DAY 2 Key VocabularyDEFINE WORDSIN NOTEBOOKSWATCH
... lithosphere is broken into solid sections called tectonic plates. These solid sections float on top of the asthenosphere. The movement and flow of heat within the asthenosphere cause the plates to move. ● Which natural processes occur as a result of tectonic plate movement? ...
... lithosphere is broken into solid sections called tectonic plates. These solid sections float on top of the asthenosphere. The movement and flow of heat within the asthenosphere cause the plates to move. ● Which natural processes occur as a result of tectonic plate movement? ...
Meteorite Impacts as Triggers to Large Igneous Provinces
... explain the differentiated melts of the Sudbury Igneous LIP, where underlain by oceanic mantle, was ultramafic (e.g. Complex, including the currently unfavoured idea that the high-magnesium basalt or picrite). Such an impact event nickel-rich deposits are cosmogenic (Dietz 1972). Hot melt- preceding ...
... explain the differentiated melts of the Sudbury Igneous LIP, where underlain by oceanic mantle, was ultramafic (e.g. Complex, including the currently unfavoured idea that the high-magnesium basalt or picrite). Such an impact event nickel-rich deposits are cosmogenic (Dietz 1972). Hot melt- preceding ...
sedimentary rocks
... In some cases, only an impression remains where the majority of, or all of, the organic material was completely destroyed by decay or mineral dissolution (see Figure 5.6d, page 113). Only a very few organisms become fossils upon death. Shell, bone, teeth, and soft tissue are all subject to destructi ...
... In some cases, only an impression remains where the majority of, or all of, the organic material was completely destroyed by decay or mineral dissolution (see Figure 5.6d, page 113). Only a very few organisms become fossils upon death. Shell, bone, teeth, and soft tissue are all subject to destructi ...
hydrothe~mal alteration of basaltic andesite and other rocks in drill
... Sinter Hill prove that high-temperature, silica-bearing waters discharged in the past at -altitudes at least 148 feet nbove the present water table. The different types and -ages of the hot-spring sinters have been described in detail by White and others (1964). I-Iydrothermal alteration of the rock ...
... Sinter Hill prove that high-temperature, silica-bearing waters discharged in the past at -altitudes at least 148 feet nbove the present water table. The different types and -ages of the hot-spring sinters have been described in detail by White and others (1964). I-Iydrothermal alteration of the rock ...
The Origin of Alkaline Lavas
... this question was first addressed theoretically decades ago. The direct core hole calculation of O2 within the Hartree-Fock approximation supported a localized core hole picture. The energy of a symmetry-broken ionic state of O2, in which a core hole is localized and thus the O atoms are inequivalen ...
... this question was first addressed theoretically decades ago. The direct core hole calculation of O2 within the Hartree-Fock approximation supported a localized core hole picture. The energy of a symmetry-broken ionic state of O2, in which a core hole is localized and thus the O atoms are inequivalen ...
Chapter 9: Weathering and Erosion
... Time It takes time for rocks to weather. It can take thousands of years for some soils to form. As soils develop, they become less like the rock from which they formed. In young soils, the parent rock determines the soil characteristics. As weathering continues, however, the soil resembles the paren ...
... Time It takes time for rocks to weather. It can take thousands of years for some soils to form. As soils develop, they become less like the rock from which they formed. In young soils, the parent rock determines the soil characteristics. As weathering continues, however, the soil resembles the paren ...
Wegener Reading [Biography]
... have to be prepared always for the possibility that each new discovery, no matter what science furnishes it, may modify the conclusions we draw." Alfred Wegener. The Origins of Continents and Oceans (4th edition) Some truly revolutionary scientific theories may take years or decades to win general a ...
... have to be prepared always for the possibility that each new discovery, no matter what science furnishes it, may modify the conclusions we draw." Alfred Wegener. The Origins of Continents and Oceans (4th edition) Some truly revolutionary scientific theories may take years or decades to win general a ...
GSA-Charlotte 2012
... friend and colleage, Tom Worsley, whom some of you may know, but many, I suspect, do not. It is particularly fitting that I should do so at this time, since this year marks both his retirement from academia and the 30th anniversary of his debut paper on the existence of a supercontinent cycle, which ...
... friend and colleage, Tom Worsley, whom some of you may know, but many, I suspect, do not. It is particularly fitting that I should do so at this time, since this year marks both his retirement from academia and the 30th anniversary of his debut paper on the existence of a supercontinent cycle, which ...
Загрузить этот файл PDF - Геодинамика и тектонофизика
... делимость литосферы, ячеи Релея‐Бенара, континенты ...
... делимость литосферы, ячеи Релея‐Бенара, континенты ...
Chapter 17: Plate Tectonics
... climatic changes on some continents. Coal deposits, for example, had been found in Antarctica. Coal forms from dead swamp plants. Swamps are areas of wet, spongy land often covered by water. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica, then, indicated that this frozen land once had a temperate, rainy c ...
... climatic changes on some continents. Coal deposits, for example, had been found in Antarctica. Coal forms from dead swamp plants. Swamps are areas of wet, spongy land often covered by water. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica, then, indicated that this frozen land once had a temperate, rainy c ...
Terra Nova 2012 Jagoutz
... the major element difference between Archean TTG and post-Archean GG. Based on an extensive compilation of experimental melt compositions, Moyen and Stevens (2006), have inferred that the Na concentration of the melt is dependent on the pressure of melting, with high pressure melts have high Na conce ...
... the major element difference between Archean TTG and post-Archean GG. Based on an extensive compilation of experimental melt compositions, Moyen and Stevens (2006), have inferred that the Na concentration of the melt is dependent on the pressure of melting, with high pressure melts have high Na conce ...
Garzione, C. N., P. Molnar, J. C. Libarkin, and B, MacFadden (2006), Rapid Late Miocene rise
... formed in the lower crust in regions of crustal thickening, can greatly enhance the resulting elevation change [4–9]. Depending upon the amount and depth range over which mass is redistributed, the force per unit length that a high terrain applies to surrounding lowlands can change sufficiently to r ...
... formed in the lower crust in regions of crustal thickening, can greatly enhance the resulting elevation change [4–9]. Depending upon the amount and depth range over which mass is redistributed, the force per unit length that a high terrain applies to surrounding lowlands can change sufficiently to r ...
geography - Hitbullseye
... Figure 1: Hubble Space Telescope view of a distant cluster of galaxies near the beginning of time. ...
... Figure 1: Hubble Space Telescope view of a distant cluster of galaxies near the beginning of time. ...
The Geological Concept
... InADictionaryoftheNatural Environment, Monkhouse and Small (1978) define the term "mountain" as follows: "A markedly elevated landform, bounded by steep slopes and rising to prominent ridges or individual summit-peaks. There is no specific altitude, but usually taken to be over 600 m (2000 ft.) in B ...
... InADictionaryoftheNatural Environment, Monkhouse and Small (1978) define the term "mountain" as follows: "A markedly elevated landform, bounded by steep slopes and rising to prominent ridges or individual summit-peaks. There is no specific altitude, but usually taken to be over 600 m (2000 ft.) in B ...
Subduction and collision processes in the Central Andes
... letters to nature together with the smoothed surface topography. Large variations of the depth of the Moho beneath the high plateau indicate strong heterogeneity of the lithospheric thickness, where a thin mantle lithosphere is required to maintain high topography if the crust is thin. This is prob ...
... letters to nature together with the smoothed surface topography. Large variations of the depth of the Moho beneath the high plateau indicate strong heterogeneity of the lithospheric thickness, where a thin mantle lithosphere is required to maintain high topography if the crust is thin. This is prob ...
HS Plate Tectonics
... ultramafic rock peridotite, which is made of the iron- and magnesium-rich silicate minerals (Figure 1.7). Peridotite is rarely found at Earth’s surface. ...
... ultramafic rock peridotite, which is made of the iron- and magnesium-rich silicate minerals (Figure 1.7). Peridotite is rarely found at Earth’s surface. ...
Chapter 5: Mineral Resources of the Western US
... deposits in the West are usually associated with igneous intrusions (formed during mountain building events, rifting, and volcanic activity), which can range in composition from granite (felsic) to gabbro (mafic). Metamorphism may also cause recrystallization of minerals and concentration of rare el ...
... deposits in the West are usually associated with igneous intrusions (formed during mountain building events, rifting, and volcanic activity), which can range in composition from granite (felsic) to gabbro (mafic). Metamorphism may also cause recrystallization of minerals and concentration of rare el ...
Earth Layers
... James Hutton (1726–1797) • Known as the “father of modern geology” • Believed Earth to be internally dynamic, ever-changing, and very old • Originated the concept of Uniformitarianism— that geological forces at work in the present day are the same as those that operated in the past • Great influence ...
... James Hutton (1726–1797) • Known as the “father of modern geology” • Believed Earth to be internally dynamic, ever-changing, and very old • Originated the concept of Uniformitarianism— that geological forces at work in the present day are the same as those that operated in the past • Great influence ...
How Does Earth Work?
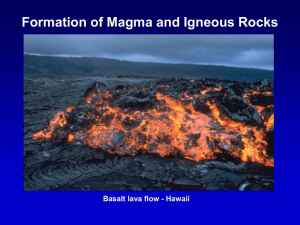
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely silica (45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, C ...
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely silica (45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, C ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.








![Wegener Reading [Biography]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004189784_1-5fd15e1925a2c907481f1ec648102120-300x300.png)