rock-cycle-inro-ppt
... A. Rocks deep below ground rise to the surface, are moved back underground, then rise to the surface again. B. Igneous rock and sedimentary rock change to metamorphic rock. C. The rock cycle has a single pathway from one type of rock to another type of rock. D. Every type of rock can be change ...
... A. Rocks deep below ground rise to the surface, are moved back underground, then rise to the surface again. B. Igneous rock and sedimentary rock change to metamorphic rock. C. The rock cycle has a single pathway from one type of rock to another type of rock. D. Every type of rock can be change ...
Plate Tectonics
... • All continents were once connected as one large landmass called Pangaea. • Landmass broke apart and drifted to their present positions. ...
... • All continents were once connected as one large landmass called Pangaea. • Landmass broke apart and drifted to their present positions. ...
Lesson 7.1: Volcanoes and Plate Boundaries
... • If two plates move towards each other, one has to give and bend and move underneath. • If the one that bends goes deep enough, the heat from Earth’s interior will melt the rocks and it will float back up again, pushing cooler rocks down. • Volcanoes form on surface and an opening on the earth’s su ...
... • If two plates move towards each other, one has to give and bend and move underneath. • If the one that bends goes deep enough, the heat from Earth’s interior will melt the rocks and it will float back up again, pushing cooler rocks down. • Volcanoes form on surface and an opening on the earth’s su ...
suggested prehistory cross-curricular links
... Rocks and soils: Compare and group together different kinds of rocks on the basis of their appearance and simple physical properties. Recognise that soils are made from rocks and organic matter. Consider the properties of flint, chalk and clay and their use through prehistory for tools, building (wa ...
... Rocks and soils: Compare and group together different kinds of rocks on the basis of their appearance and simple physical properties. Recognise that soils are made from rocks and organic matter. Consider the properties of flint, chalk and clay and their use through prehistory for tools, building (wa ...
Module 4 Processes That Shape the Earth Extended
... boundaries. The source of hot-spot magmas is believed to be well below the lithosphere, probably at the core-mantle boundary. Hot-spot volcanoes often form long chains that result from the relative motion of the lithosphere plate over the hot-spot source. The size of the Earth has not changed signif ...
... boundaries. The source of hot-spot magmas is believed to be well below the lithosphere, probably at the core-mantle boundary. Hot-spot volcanoes often form long chains that result from the relative motion of the lithosphere plate over the hot-spot source. The size of the Earth has not changed signif ...
Chapter 15 Outline
... crust contains igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that are recycled by the rock cycle. 1. Rock is a solid combination of one or more minerals. 2. An ore is a rock that contains a large enough concentration of a particular mineral (often a metal) that the rock can be mined and processed to e ...
... crust contains igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that are recycled by the rock cycle. 1. Rock is a solid combination of one or more minerals. 2. An ore is a rock that contains a large enough concentration of a particular mineral (often a metal) that the rock can be mined and processed to e ...
Processes That Shape the Earth
... boundaries. The source of hot-spot magmas is believed to be well below the lithosphere, probably at the core-mantle boundary. Hot-spot volcanoes often form long chains that result from the relative motion of the lithosphere plate over the hot-spot source. ...
... boundaries. The source of hot-spot magmas is believed to be well below the lithosphere, probably at the core-mantle boundary. Hot-spot volcanoes often form long chains that result from the relative motion of the lithosphere plate over the hot-spot source. ...
You Will Discover
... into cracks in rocks. If this water freezes, it forms ice. Have you ever compared an ice cube in an ice tray to the water that it came from? What did you notice? Just like in the ice tray, ice in rock takes up more space than the water did. The ice forces the sides of the crack outward. The crack go ...
... into cracks in rocks. If this water freezes, it forms ice. Have you ever compared an ice cube in an ice tray to the water that it came from? What did you notice? Just like in the ice tray, ice in rock takes up more space than the water did. The ice forces the sides of the crack outward. The crack go ...
THE EVOLUTION OF MOUNTAIN RANGES AND THE ORIGIN AND
... ( The principles used to interpret cratonic geologic records. ( The sequential evolution of the North American continent beginning with the latest Precambrian, and getting as far as we can before the semester runs out. When we examine the oldest rocks on the earth we observe that most are not signif ...
... ( The principles used to interpret cratonic geologic records. ( The sequential evolution of the North American continent beginning with the latest Precambrian, and getting as far as we can before the semester runs out. When we examine the oldest rocks on the earth we observe that most are not signif ...
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1
... What does a volcano tell us about what is happening in the Earth’s Interior? -The Earth releases tremendous amounts of stored energy from its Inner and Outer Cores in a controlled manner by way of tectonic processes. - These processes create changes to existing land and produce new land formation. - ...
... What does a volcano tell us about what is happening in the Earth’s Interior? -The Earth releases tremendous amounts of stored energy from its Inner and Outer Cores in a controlled manner by way of tectonic processes. - These processes create changes to existing land and produce new land formation. - ...
Curriculum Map
... layers of sedimentary rocks and their fossils in a rock cross section to infer relative ages of rock sequences, past geological events, changes in environmental conditions, ...
... layers of sedimentary rocks and their fossils in a rock cross section to infer relative ages of rock sequences, past geological events, changes in environmental conditions, ...
1 Historical perspective perspective
... far outnumbering the former. Each ridiculed the other’s ideas. The nondrifters emphasized the lack of a plausible mechanism, as we have already noted, both convection and Earth expansion being considered unlikely. The nondrifters had difficulty in explaining the present separation of faunal province ...
... far outnumbering the former. Each ridiculed the other’s ideas. The nondrifters emphasized the lack of a plausible mechanism, as we have already noted, both convection and Earth expansion being considered unlikely. The nondrifters had difficulty in explaining the present separation of faunal province ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... of the Earth: crust, mantle and core. 2. Know what is included by the term “fossil fuels.” 3. Explain how temperatures on Earth have changes over the last century (100 years), and tens of thousands of years. 4. Know ways to reduce your impact on the climate. 5. Understand the greenhouse effect. 6. K ...
... of the Earth: crust, mantle and core. 2. Know what is included by the term “fossil fuels.” 3. Explain how temperatures on Earth have changes over the last century (100 years), and tens of thousands of years. 4. Know ways to reduce your impact on the climate. 5. Understand the greenhouse effect. 6. K ...
Chapter 17- Plate Tectonics
... apparent fit of continents on either side of ocean (matching coastlines) • Continental drift (Wegener)- Earth’s continents had once been joined as Pangaea ...
... apparent fit of continents on either side of ocean (matching coastlines) • Continental drift (Wegener)- Earth’s continents had once been joined as Pangaea ...
Chapter 7 Notes - Wachter Middle School
... 4. Describe Wegener’s theory of continental drift, and explain why it was not accepted at first. 5. Explain how sea-floor spreading provides a way for continents to move. 6. Describe how new oceanic crust forms at mid-ocean ridges. 7. Explain how magnetic reversals provide evidence for sea-floor spr ...
... 4. Describe Wegener’s theory of continental drift, and explain why it was not accepted at first. 5. Explain how sea-floor spreading provides a way for continents to move. 6. Describe how new oceanic crust forms at mid-ocean ridges. 7. Explain how magnetic reversals provide evidence for sea-floor spr ...
7th Grade Targeted TEKS - Texas Regional Collaboratives
... short period of time such as the explosion of Mt. St. Helens (an andesite volcano) or over a longer amount of time such as the development of the Hawaiian Islands (hot spot). No matter how quickly these events happen they represent the result of the same effect. Essentially this is the escape of mol ...
... short period of time such as the explosion of Mt. St. Helens (an andesite volcano) or over a longer amount of time such as the development of the Hawaiian Islands (hot spot). No matter how quickly these events happen they represent the result of the same effect. Essentially this is the escape of mol ...
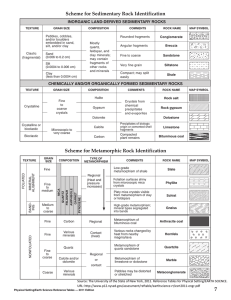
Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification Scheme for
... may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals ...
... may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals ...
Superplumes and single plumes: their magmatic trails on moving
... Institute of Geology, Ufimian Scientific Centre, Russian Federation ([email protected]) ...
... Institute of Geology, Ufimian Scientific Centre, Russian Federation ([email protected]) ...
Week 1
... ► The paper was poorly received. Vic Vacquier (Scripps), Talwani (most Lamont people). ► Le Pichon wrote a paper against plate tectonics explaining that the heat flow measurements are not well-explained by this new theory. ...
... ► The paper was poorly received. Vic Vacquier (Scripps), Talwani (most Lamont people). ► Le Pichon wrote a paper against plate tectonics explaining that the heat flow measurements are not well-explained by this new theory. ...
TYPES OF CRUSTAL MATERIAL
... Because the lithosphere floats on the partially fluid asthenosphere, the denser basaltic ocean crust sinks lower into the asthenosphere than the less dense granitic continental crust. This is the reason why continents are higher than ocean basins; the basins would exist whether or not there was any ...
... Because the lithosphere floats on the partially fluid asthenosphere, the denser basaltic ocean crust sinks lower into the asthenosphere than the less dense granitic continental crust. This is the reason why continents are higher than ocean basins; the basins would exist whether or not there was any ...
DIGGING INTO EARTH`S PAST
... surface. Sedimentary rocks are the most abundant rocks found on the earth. Some are formed from sediments which become cemented together. Metamorphic rocks are created when existing rocks, buried deep within the earth, are changed by tremendous heat and pressure and/or chemical reactions. All rocks ...
... surface. Sedimentary rocks are the most abundant rocks found on the earth. Some are formed from sediments which become cemented together. Metamorphic rocks are created when existing rocks, buried deep within the earth, are changed by tremendous heat and pressure and/or chemical reactions. All rocks ...
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE
... • Volatile siderophiles even more enriched than non-volatile ones. ⇒ 3 possible causes: 1) incomplete equilibration 2) an impure Fe phase 3) addition of a volatile rich component after core formation, aka “late veneer” ...
... • Volatile siderophiles even more enriched than non-volatile ones. ⇒ 3 possible causes: 1) incomplete equilibration 2) an impure Fe phase 3) addition of a volatile rich component after core formation, aka “late veneer” ...
Volcanoes PPT
... • 2 major belts– Circum-Pacific Belt (Ring of Fire)-outlines west coasts of NA, SA, Aleutian Islands, east coast of Asia – Mediterranean Belt- outlines boundaries between Eurasian, African, Arabian plates ...
... • 2 major belts– Circum-Pacific Belt (Ring of Fire)-outlines west coasts of NA, SA, Aleutian Islands, east coast of Asia – Mediterranean Belt- outlines boundaries between Eurasian, African, Arabian plates ...
Plate Tectonics WebQuest
... Earth look like this? 6. What did Alfred Wegener name the continent that existed long ago, and what did this word mean in Greek? 7. The plate tectonics theory states that the Earth’s surface is broken into large slabs called ______________. 8. Under Moving continents, arrange the continents in the ...
... Earth look like this? 6. What did Alfred Wegener name the continent that existed long ago, and what did this word mean in Greek? 7. The plate tectonics theory states that the Earth’s surface is broken into large slabs called ______________. 8. Under Moving continents, arrange the continents in the ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.