DYNAMIC EARTH STATION PACKET Braille Pages 1
... 13. I’m the thin layer of rock that surrounds Earth. 14. I’m the gap that forms as tectonic plates move apart. 15. I occur where plates with continental crust push together. 16. I’m a ball of hot, solid metals at Earth’s center. 17. I’m the transfer of heat within a material. 18. I’m the large and s ...
... 13. I’m the thin layer of rock that surrounds Earth. 14. I’m the gap that forms as tectonic plates move apart. 15. I occur where plates with continental crust push together. 16. I’m a ball of hot, solid metals at Earth’s center. 17. I’m the transfer of heat within a material. 18. I’m the large and s ...
Historical Geology
... understanding how Earth’s various subsystems work and interact – how we consume natural resources and interact with the environment determines our ability to pass on this standard of living to the next generation – our standard of living depends directly on our consumption of natural resources that ...
... understanding how Earth’s various subsystems work and interact – how we consume natural resources and interact with the environment determines our ability to pass on this standard of living to the next generation – our standard of living depends directly on our consumption of natural resources that ...
view this article in PDF format.
... geochronometry from which relatively precise rate calculations are possible, but the near lack of well-constrained fossils in most continental environments confounds our ability to establish the temporal dimension of basin-filling (overburden) strata in which basin history is recorded (Figure 1). Ma ...
... geochronometry from which relatively precise rate calculations are possible, but the near lack of well-constrained fossils in most continental environments confounds our ability to establish the temporal dimension of basin-filling (overburden) strata in which basin history is recorded (Figure 1). Ma ...
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift
... plates. Plate tectonics deals with the nature of these plates, what happens at their boundaries, how and why they move, etc. ...
... plates. Plate tectonics deals with the nature of these plates, what happens at their boundaries, how and why they move, etc. ...
INFORME GEOBRASIL (www.geobrasil.net)
... From an empirical standpoint the mass extinction at the close of the Palaeozoic, 251 Ma ago, links closely with eruption of the largest known flood basalt pile in Siberia, and there is no known extraterrestrial impact that tallies. So it seems likely that the P-T event was generated by the influence ...
... From an empirical standpoint the mass extinction at the close of the Palaeozoic, 251 Ma ago, links closely with eruption of the largest known flood basalt pile in Siberia, and there is no known extraterrestrial impact that tallies. So it seems likely that the P-T event was generated by the influence ...
Earth and Atmosphere
... Scientists think the continents were originally all together in a supercontinent called Pangaea. Over millions of years they have drifted to their present positions on the floating tectonic plates. ...
... Scientists think the continents were originally all together in a supercontinent called Pangaea. Over millions of years they have drifted to their present positions on the floating tectonic plates. ...
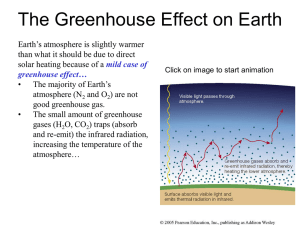
The Greenhouse Effect on Earth
... Earth’s atmosphere is slightly warmer than what it should be due to direct solar heating because of a mild case of greenhouse effect… • The majority of Earth’s atmosphere (N2 and O2) are not good greenhouse gas. • The small amount of greenhouse gases (H2O, CO2) traps (absorb and re-emit) the infrare ...
... Earth’s atmosphere is slightly warmer than what it should be due to direct solar heating because of a mild case of greenhouse effect… • The majority of Earth’s atmosphere (N2 and O2) are not good greenhouse gas. • The small amount of greenhouse gases (H2O, CO2) traps (absorb and re-emit) the infrare ...
Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Earth’s Interior
... Based on the height of the largest wave Familiar but outdated tool A tenfold increase in wave height equals an increase of 1 on the magnitude scale For example: a 5.0 quake is ten times greater than a 4.0 quake ...
... Based on the height of the largest wave Familiar but outdated tool A tenfold increase in wave height equals an increase of 1 on the magnitude scale For example: a 5.0 quake is ten times greater than a 4.0 quake ...
Read Me First - plate tectonics ppt
... a reptile’s plates or scales plate of photographs in a textbook ...
... a reptile’s plates or scales plate of photographs in a textbook ...
What is Earth Science?
... About 200 million years ago, Pangaea began to break apart to form the continents that we know today. ...
... About 200 million years ago, Pangaea began to break apart to form the continents that we know today. ...
Period
... What type of heat transfer is taking place inside the Earth’s asthenosphere right now? Explain WHY this heat transfer is taking place. ...
... What type of heat transfer is taking place inside the Earth’s asthenosphere right now? Explain WHY this heat transfer is taking place. ...
plate tectonic study guide
... 2. Lithosphere (Tectonic Plates)- Crust and rigid upper mantle 3. Asthenosphere (Convection Currents-caused by heat from the core) 4. Mesosphere (Lower Mantle) 5.Outer Core (Liquid Metal- iron and nickel) 6. Inner Core (Solid Metal-iron and nickel) 6. What happens at an oceanic-oceanic convergent bo ...
... 2. Lithosphere (Tectonic Plates)- Crust and rigid upper mantle 3. Asthenosphere (Convection Currents-caused by heat from the core) 4. Mesosphere (Lower Mantle) 5.Outer Core (Liquid Metal- iron and nickel) 6. Inner Core (Solid Metal-iron and nickel) 6. What happens at an oceanic-oceanic convergent bo ...
Collecting Data: Article for Teachers
... collecting? How does this compare to your answer from Passage 1? ...
... collecting? How does this compare to your answer from Passage 1? ...
Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Chapter 1
... planet on which we live, it is easy to forget that Earth is just a tiny object in a vast universe. Indeed, Earth is subject to the same physical laws that govern the many other objects populating the great expanses of space. Thus, to understand explanations of our planet’s origin, it is useful to le ...
... planet on which we live, it is easy to forget that Earth is just a tiny object in a vast universe. Indeed, Earth is subject to the same physical laws that govern the many other objects populating the great expanses of space. Thus, to understand explanations of our planet’s origin, it is useful to le ...
BACKGROUNDINFORMATION
... A transform boundary or transform fault margin is formed when two plates slide past each other, usually moving in opposite directions. For example, one may be moving north while the other moves south; however, they may also move in the same direction, but at different speeds. A fault is a deep crack ...
... A transform boundary or transform fault margin is formed when two plates slide past each other, usually moving in opposite directions. For example, one may be moving north while the other moves south; however, they may also move in the same direction, but at different speeds. A fault is a deep crack ...
Earth Structure
... ray parameter ‘p’ is therefore alternatively referred to as ‘horizontal slowness’ ( p = dT/dX). Further, we note that the ray parameter ‘p’ equals the ‘1/cb’ at the maximum penetration depth ‘z’, for sin i = 1 for horizontal rays, with ‘cb’ as the phase velocity at the bottom (turning point) of the ...
... ray parameter ‘p’ is therefore alternatively referred to as ‘horizontal slowness’ ( p = dT/dX). Further, we note that the ray parameter ‘p’ equals the ‘1/cb’ at the maximum penetration depth ‘z’, for sin i = 1 for horizontal rays, with ‘cb’ as the phase velocity at the bottom (turning point) of the ...
Ch 8 Earth Science PPT
... prediction is to provide an early warning of the location and magnitude of a large earthquake. ...
... prediction is to provide an early warning of the location and magnitude of a large earthquake. ...
Journey to the Center of the Earth
... temperature and pressure conditions within the Earth are so extreme that humans could not survive below a few kilometers depth within the 6371 km radius Earth. Furthermore, we know of no significant openings that would provide access to the deep interior of the planet, and caves or cavities at great ...
... temperature and pressure conditions within the Earth are so extreme that humans could not survive below a few kilometers depth within the 6371 km radius Earth. Furthermore, we know of no significant openings that would provide access to the deep interior of the planet, and caves or cavities at great ...
1 Midterm Exam I September 26, 2:10 HW714
... Earth lost volume because of gravitational compression. High temperatures in the interior turned the inner Earth into a semisolid mass; dense iron (red drops) fell toward the center to form the core, while less dense silicates move outward. Friction generated by this movement heated Earth even more. ...
... Earth lost volume because of gravitational compression. High temperatures in the interior turned the inner Earth into a semisolid mass; dense iron (red drops) fell toward the center to form the core, while less dense silicates move outward. Friction generated by this movement heated Earth even more. ...
Bell Ringer 1-5-10
... 1. Describe how a rock can form by evaporation. What type of rock is it? 2. How do the properties of a rock change when it becomes a metamorphic rock? 3. What are two things that could happen to a metamorphic rock to continue the rock cycle? 4. How are clastic rocks and organic rocks similar? How ar ...
... 1. Describe how a rock can form by evaporation. What type of rock is it? 2. How do the properties of a rock change when it becomes a metamorphic rock? 3. What are two things that could happen to a metamorphic rock to continue the rock cycle? 4. How are clastic rocks and organic rocks similar? How ar ...
Right Side Crust
... relationship between the locations of most active volcanoes and locations of earthquakes: ...
... relationship between the locations of most active volcanoes and locations of earthquakes: ...
rocks!!
... • Sediments (broken bits of rock) are materials that have been transported by air, water or ice. Most sediments are rock, but some can be pieces of animals or plants, and even molecules dissolved in water. When these materials are deposited, they form loose layers, and are then changed into rock lay ...
... • Sediments (broken bits of rock) are materials that have been transported by air, water or ice. Most sediments are rock, but some can be pieces of animals or plants, and even molecules dissolved in water. When these materials are deposited, they form loose layers, and are then changed into rock lay ...
Continents On The Move
... Why do plates move? It is still not very clear what forces cause plates and continents to move around Earth’s surface. The most important motor of plate movement is mantle convection. Mantle convection is the process that continuously stirs the entire mantle as old, cold plates sink at subduction zo ...
... Why do plates move? It is still not very clear what forces cause plates and continents to move around Earth’s surface. The most important motor of plate movement is mantle convection. Mantle convection is the process that continuously stirs the entire mantle as old, cold plates sink at subduction zo ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.