Principles of cell signaling Lecture 2
... Downregulation of GPCR activity GPCRs are removed from cell surface and degraded The affinity of the GPCR for its ligand is in some cases decreased when Ga subunit binds to GTP (= is active). This will limit the number of Ga that can be activated. ...
... Downregulation of GPCR activity GPCRs are removed from cell surface and degraded The affinity of the GPCR for its ligand is in some cases decreased when Ga subunit binds to GTP (= is active). This will limit the number of Ga that can be activated. ...
G-protein
... cell surface receptor or membrane receptor – located on the plasma membrane to bind a ligand outside the cell ...
... cell surface receptor or membrane receptor – located on the plasma membrane to bind a ligand outside the cell ...
Cell Communication Part I
... causing a cellular response. How do concentration levels of signal affect the cellular response? ...
... causing a cellular response. How do concentration levels of signal affect the cellular response? ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
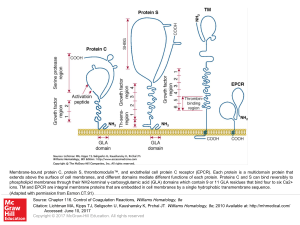
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Principles of Biochemistry
... JAK: = Janus kinases - contiennent 2 domaines Tyrosine Kinase STAT: Signal Transducers and Activators of Transduction ...
... JAK: = Janus kinases - contiennent 2 domaines Tyrosine Kinase STAT: Signal Transducers and Activators of Transduction ...
Prediction of G
... G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) are a well-studied superfamily of proteins in pharmacological research as they are the target of approximately 60% of current drugs on the market (Muller, 2000). Coupling with G-proteins, these receptors regulate much of the signal transduction across the cell memb ...
... G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) are a well-studied superfamily of proteins in pharmacological research as they are the target of approximately 60% of current drugs on the market (Muller, 2000). Coupling with G-proteins, these receptors regulate much of the signal transduction across the cell memb ...
Ch 13
... • Same hormone can elicit different responses in different tissues • Cross‐talk: different hormones elicit same response (fine tuning) ...
... • Same hormone can elicit different responses in different tissues • Cross‐talk: different hormones elicit same response (fine tuning) ...
MB207_14 - MB207Jan2010
... • Upon ligand binding, RTK aggregate and undergo autophosphorylation. • Once a receptor is phosphorylated at tyrosine residues in its cytosolic tails, proteins with SH2 domain such as GRB2 bind to the receptor, recruiting GEF for Ras. • Ras-GEF causes the activation of Ras by helping it to release G ...
... • Upon ligand binding, RTK aggregate and undergo autophosphorylation. • Once a receptor is phosphorylated at tyrosine residues in its cytosolic tails, proteins with SH2 domain such as GRB2 bind to the receptor, recruiting GEF for Ras. • Ras-GEF causes the activation of Ras by helping it to release G ...
GPCR and G Proteins
... - three switch regions of protein - 14% of aa move when tri phosphate present change is brought about by contact of tri phosphate with three aa the N-term of active a is shifted into the protein – increased mobility than when it is tethered into the membrane - βγ do not change (β is a rigid propelle ...
... - three switch regions of protein - 14% of aa move when tri phosphate present change is brought about by contact of tri phosphate with three aa the N-term of active a is shifted into the protein – increased mobility than when it is tethered into the membrane - βγ do not change (β is a rigid propelle ...
Biochemistry Chapter 11 [10-2-13].
... 2. ex. Acetylcholine (acts on nicotinic Ach receptor) a. neurotransmitters secreted in response to electrical stimulus (action potential) caused by changes in Na+ and K+ gradients b. Ca2+ influx causes release of Ach into synaptic cleft c. Ach binds to nicotinic Ach receptor d. causes conformational ...
... 2. ex. Acetylcholine (acts on nicotinic Ach receptor) a. neurotransmitters secreted in response to electrical stimulus (action potential) caused by changes in Na+ and K+ gradients b. Ca2+ influx causes release of Ach into synaptic cleft c. Ach binds to nicotinic Ach receptor d. causes conformational ...
Arrestin - Psychiatry Training
... •Review aspects of chemical transmission and intracellular signalling in the brain •Role of neurotransmitter/signal transduction abnormalities in selected ...
... •Review aspects of chemical transmission and intracellular signalling in the brain •Role of neurotransmitter/signal transduction abnormalities in selected ...
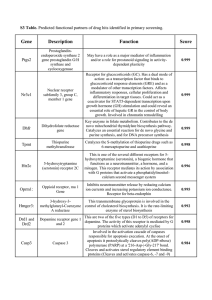
Gene Description Function Score
... This is one of the several different receptors for 5hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. This receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositolcalcium second messenger system ...
... This is one of the several different receptors for 5hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. This receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositolcalcium second messenger system ...
Cell Signaling - Erlenbeck`s Science Room
... transduction pathway which leads to the cellular response. ...
... transduction pathway which leads to the cellular response. ...
邵吉民_Signal_and_dis
... Activates IR -subunit (PTK activity) IR-subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
... Activates IR -subunit (PTK activity) IR-subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
information - GLISTEN: GPCR
... represent the single largest family of cell surface receptors engaged in signal transduction. In humans, it is estimated that several hundreds of distinct members of the GPCR superfamily directly respond to a wide variety of chemical transmitters, such as biogenic amines, amino acids, peptides, lipi ...
... represent the single largest family of cell surface receptors engaged in signal transduction. In humans, it is estimated that several hundreds of distinct members of the GPCR superfamily directly respond to a wide variety of chemical transmitters, such as biogenic amines, amino acids, peptides, lipi ...
An Exploration of the Dynamic-Function
... bodies. Each GPCR has an extracellular ligand binding domain and an intracellular domain which work in tandem to mediate Gprotein coupled interactions. GPCRs are grouped into six classes based on sequence homology and functional similarity [1]. These classes being: Rhodopsin-like, Secretin Receptors ...
... bodies. Each GPCR has an extracellular ligand binding domain and an intracellular domain which work in tandem to mediate Gprotein coupled interactions. GPCRs are grouped into six classes based on sequence homology and functional similarity [1]. These classes being: Rhodopsin-like, Secretin Receptors ...
Biology 52: Problem Set for Lectures 9, 10, and 11
... C. Actin filaments (microfilaments) 2. Receptor-activated G-proteins interact with a variety of downstream effectors such as adenylyl cyclase and Phospholipase C. What second messenger molecule(s) is/are generated by activation of phospholipase C and what is/are the downstream effector(s)? Inositol ...
... C. Actin filaments (microfilaments) 2. Receptor-activated G-proteins interact with a variety of downstream effectors such as adenylyl cyclase and Phospholipase C. What second messenger molecule(s) is/are generated by activation of phospholipase C and what is/are the downstream effector(s)? Inositol ...
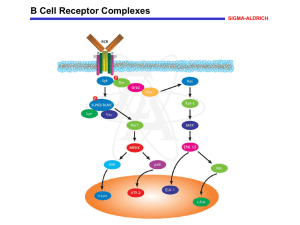
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... homeostasis of reversible tyrosine phosphorylation in the resting B cell. Members of the Src family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads ...
... homeostasis of reversible tyrosine phosphorylation in the resting B cell. Members of the Src family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads ...
038-Signal Transduction Pathways Activity-V Morris
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
Document
... •Ligand binding produces signaling to second messenger by binding to and transducing its signal to a trimeric G protein •G protein has 3 subunits: a, b and g. Ligand-bound receptor interacts with G protein, causing conformational change. Ga subunit exchanges GDP for GTP and dissociates from Gbg. Bot ...
... •Ligand binding produces signaling to second messenger by binding to and transducing its signal to a trimeric G protein •G protein has 3 subunits: a, b and g. Ligand-bound receptor interacts with G protein, causing conformational change. Ga subunit exchanges GDP for GTP and dissociates from Gbg. Bot ...
11 Signal Transduction
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
Lecture 9: Cell signaling
... In the unstimulated state, the α subunit has GDP bound and the G protein is inactive. When stimulated, the α subunit releases its bound GDP, allowing GTP to bind in its place. This exchange causes the trimer to dissociate into active components: α subunit and a βγ complex. ...
... In the unstimulated state, the α subunit has GDP bound and the G protein is inactive. When stimulated, the α subunit releases its bound GDP, allowing GTP to bind in its place. This exchange causes the trimer to dissociate into active components: α subunit and a βγ complex. ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).






![Biochemistry Chapter 11 [10-2-13].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001491986_1-28945f6beadb86fb208c56f0103a35db-300x300.png)