Cell communication
... You should now be able to: 1. Describe the nature of a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligandgated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multistep ...
... You should now be able to: 1. Describe the nature of a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligandgated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multistep ...
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
... • Moving receptors from ER to plasma membrane involves targeting the correct sites on the menbrane. • E.g., GABARAP found primarily in transport sites in Golgi, interacts with NSF (N-ethylamide fusion prot). GABARAP assoc spec with the γ2 subunit proteins of GABAA Rs and also binds tubulin. GABARAP ...
... • Moving receptors from ER to plasma membrane involves targeting the correct sites on the menbrane. • E.g., GABARAP found primarily in transport sites in Golgi, interacts with NSF (N-ethylamide fusion prot). GABARAP assoc spec with the γ2 subunit proteins of GABAA Rs and also binds tubulin. GABARAP ...
Ligand Gated Ion ch8
... • Moving receptors from ER to plasma membrane involves targeting the correct sites on the menbrane. • E.g., GABARAP found primarily in transport sites in Golgi, interacts with NSF (N-ethylamide fusion prot). GABARAP assoc spec with the γ2 subunit proteins of GABAA Rs and also binds tubulin. GABARAP ...
... • Moving receptors from ER to plasma membrane involves targeting the correct sites on the menbrane. • E.g., GABARAP found primarily in transport sites in Golgi, interacts with NSF (N-ethylamide fusion prot). GABARAP assoc spec with the γ2 subunit proteins of GABAA Rs and also binds tubulin. GABARAP ...
Protocol S3 – Proteomic analysis
... probabilities of 0.75 or larger (Table S6). Our reasoning for this threshold score is based on the following observations: (i) a high proportion (71%) of PI verified by reciprocal purification (Table S4) had likelihood scores at or above this threshold (Figure S1A); (ii) the Spearman’s rank correlat ...
... probabilities of 0.75 or larger (Table S6). Our reasoning for this threshold score is based on the following observations: (i) a high proportion (71%) of PI verified by reciprocal purification (Table S4) had likelihood scores at or above this threshold (Figure S1A); (ii) the Spearman’s rank correlat ...
The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence
... storage. However, the cellulose made out of β glucose rings has a different purpose. It has a structural purpose rather than a storage purpose. ...
... storage. However, the cellulose made out of β glucose rings has a different purpose. It has a structural purpose rather than a storage purpose. ...
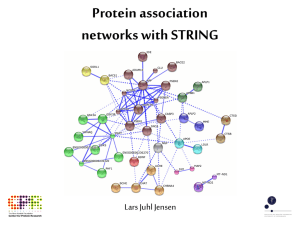
Eukaryotic Protein Networks
... Open http://diseases.jensenlab.org Search for insulin receptor (INSR) What is the strongest associated disease? Inspect the underlying text-mining evidence ...
... Open http://diseases.jensenlab.org Search for insulin receptor (INSR) What is the strongest associated disease? Inspect the underlying text-mining evidence ...
lecture 10
... two major pathways for translocation in bacteria: Sec and SRP pathways both converge at SecYEG translocon and use SecA, a peripherally-bound ATPase that supplies the energy for translocation ...
... two major pathways for translocation in bacteria: Sec and SRP pathways both converge at SecYEG translocon and use SecA, a peripherally-bound ATPase that supplies the energy for translocation ...
Plant hormone perception and action: a role for G-protein
... GA and, similar to GA, its e¡ect is largely overcome by ABA. The inactive mastoparan analogues, MasCP (control peptide), di¡ering from Mas7 by a single amino-acid substitution, and Mas7-COOH, a peptide with the same amino-acid sequence as Mas7, but with a free acid replacing the amine group at the C ...
... GA and, similar to GA, its e¡ect is largely overcome by ABA. The inactive mastoparan analogues, MasCP (control peptide), di¡ering from Mas7 by a single amino-acid substitution, and Mas7-COOH, a peptide with the same amino-acid sequence as Mas7, but with a free acid replacing the amine group at the C ...
RICHARD STANLEY, Ph.D. Positions: Research interests:
... tumor progression. We are also studying the novel CSF-1R ligand interleukin-34 (IL-34), recently showing that both IL-34 and CSF-1 act via the CSF-1R to regulate not only microglial development but also the differentiation of neural progenitor cells. Recently, focusing on the CNS, we have identified ...
... tumor progression. We are also studying the novel CSF-1R ligand interleukin-34 (IL-34), recently showing that both IL-34 and CSF-1 act via the CSF-1R to regulate not only microglial development but also the differentiation of neural progenitor cells. Recently, focusing on the CNS, we have identified ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... Amino Acids Are Joined By Peptide Bonds In Peptides - -carboxyl of one amino acid is joined to -amino of a second amino acid (with removal of water) - only -carboxyl and -amino groups are used, not R-group carboxyl or amino groups ...
... Amino Acids Are Joined By Peptide Bonds In Peptides - -carboxyl of one amino acid is joined to -amino of a second amino acid (with removal of water) - only -carboxyl and -amino groups are used, not R-group carboxyl or amino groups ...
ION CHANNELS AS DRUG TARGETS
... Benzodiazepine tranquillizers: these bind to a region of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor/chloride channel complex (a ligandgated channel; that is distinct from the GABAbinding site; ...
... Benzodiazepine tranquillizers: these bind to a region of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor/chloride channel complex (a ligandgated channel; that is distinct from the GABAbinding site; ...
recovery of whey protein process using chitosan biopolymer
... oxygen demand of 30.000 a 50.000 mg/L. The way protein in the milk have high nutritional value, containing high content of amino acids essential, especially the branched-chain. Also have high levels of calcium and bioactive peptides of the wey that have effects on skeletal muscle protein synthesis, ...
... oxygen demand of 30.000 a 50.000 mg/L. The way protein in the milk have high nutritional value, containing high content of amino acids essential, especially the branched-chain. Also have high levels of calcium and bioactive peptides of the wey that have effects on skeletal muscle protein synthesis, ...
11050-HNAC - Sino Biological Inc.
... As the first one of a series of neurotrophic factors, nerve growth factor (NGF) is important for the development and maintenance of the sympathetic and sensory nervous systems. NGF was identified as a large complex consisting of three non-covalently linked subunits, α, β, and γ, among which, the β s ...
... As the first one of a series of neurotrophic factors, nerve growth factor (NGF) is important for the development and maintenance of the sympathetic and sensory nervous systems. NGF was identified as a large complex consisting of three non-covalently linked subunits, α, β, and γ, among which, the β s ...
Protein Threading Optimization Using
... dRMSD(Tin, Tc) =[(2/n(n-1))Si=1,…,n-1Sj=i+1,…,n(dij(Tin) – dij(Tc))2]1/2 ...
... dRMSD(Tin, Tc) =[(2/n(n-1))Si=1,…,n-1Sj=i+1,…,n(dij(Tin) – dij(Tc))2]1/2 ...
Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria
... Part 1: Electron Flow High G electrons from glycolysis, TCA cycle, AA, and fatty acid oxidation are funneled into universal electron carriers: NADH / NADPH / FADH2 The e- are then transferred to a chain of e- carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. This is called the respiratory chain. ...
... Part 1: Electron Flow High G electrons from glycolysis, TCA cycle, AA, and fatty acid oxidation are funneled into universal electron carriers: NADH / NADPH / FADH2 The e- are then transferred to a chain of e- carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. This is called the respiratory chain. ...
Integral membrane proteins and free electron lasers
... statistically highly underrepresented in the PDB, with only 541 unique structures in the ‘Membrane Proteins of Known Structure Database’ (http://blanco.biomol.uci.edu/ mpstruc/). Why the dearth of structures of such important and fascinating macromolecules? Multiple nontrivial technical obstacles ex ...
... statistically highly underrepresented in the PDB, with only 541 unique structures in the ‘Membrane Proteins of Known Structure Database’ (http://blanco.biomol.uci.edu/ mpstruc/). Why the dearth of structures of such important and fascinating macromolecules? Multiple nontrivial technical obstacles ex ...
Table of Contents
... Counter-regulation by insulin and isoprenaline of a prominent fatassociated phosphoprotein doublet in rat adipocytes Antitrypanosomal effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors correlate with increases in Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-Lmethionine Modulation of the activity of acetyl-CoA car ...
... Counter-regulation by insulin and isoprenaline of a prominent fatassociated phosphoprotein doublet in rat adipocytes Antitrypanosomal effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors correlate with increases in Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-Lmethionine Modulation of the activity of acetyl-CoA car ...
Protein Folding and Quality Control
... Lecture 24 Protein Folding and Quality Control Folding Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up pol ...
... Lecture 24 Protein Folding and Quality Control Folding Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up pol ...
Biochemistry Course #: - College of Pharmacy at Howard University
... Factors affecting the Stability of the α - helices 1. The electrostatic repulsion or attraction between successive amino acid residues with charged R groups. 2. The bulkiness of the adjacent R groups 3. The interactions between R groups spaced 3 or 4 residues apart. 4. The occurrence of Pro and Gly ...
... Factors affecting the Stability of the α - helices 1. The electrostatic repulsion or attraction between successive amino acid residues with charged R groups. 2. The bulkiness of the adjacent R groups 3. The interactions between R groups spaced 3 or 4 residues apart. 4. The occurrence of Pro and Gly ...
Proteins
... 2. Carboxyl group –COOH 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
... 2. Carboxyl group –COOH 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
Small G-protein
... Monomeric G-proteins are activated by proteins which induce a conformational change resulting in reduced affinity to GDP, and thus in GDP release. The general term for such proteins is GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor). The GEFs of the small G-proteins are not the activated receptors, but rat ...
... Monomeric G-proteins are activated by proteins which induce a conformational change resulting in reduced affinity to GDP, and thus in GDP release. The general term for such proteins is GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor). The GEFs of the small G-proteins are not the activated receptors, but rat ...
Promoters
... 2. Tet-on systems: older versions – a significant basal activity; fully active only at high Dox doses novel versions: display a considerably lower basal activity in the OFF state - have codon-optimized sequence – results in improved expression and stability However, tightness of the control may be p ...
... 2. Tet-on systems: older versions – a significant basal activity; fully active only at high Dox doses novel versions: display a considerably lower basal activity in the OFF state - have codon-optimized sequence – results in improved expression and stability However, tightness of the control may be p ...
Cell Signaling: A Molecular View
... • Intracellular receptors – Present in cytoplasm or nucleus – Binds small and hydrophobic ligands (that can pass through the cell membrane) ...
... • Intracellular receptors – Present in cytoplasm or nucleus – Binds small and hydrophobic ligands (that can pass through the cell membrane) ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).