new window
... (medium chain triglycerides do not require bile acids or enzymatic breakdown) E. Immune Enhancing i. Impact: 3 patented ingredient are Arginine, omega-3 fatty acids, and dietary nucleotides. 1 kcal/cc, 56 grams protein/L. • Arginine: conditionally essential amino acid key for wound healing, nitrogen ...
... (medium chain triglycerides do not require bile acids or enzymatic breakdown) E. Immune Enhancing i. Impact: 3 patented ingredient are Arginine, omega-3 fatty acids, and dietary nucleotides. 1 kcal/cc, 56 grams protein/L. • Arginine: conditionally essential amino acid key for wound healing, nitrogen ...
Steps in chemical synaptic transmission and Ca2+ involvement Step
... Step 4: The resulting increase in Ca2+ triggers fusion of the synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft. Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to rece ...
... Step 4: The resulting increase in Ca2+ triggers fusion of the synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft. Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to rece ...
C274/SQP368 Biology NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
... electrophoresis gel. The result of running the gel is shown below. ...
... electrophoresis gel. The result of running the gel is shown below. ...
DOC
... hippocampal slice cultures from mice expressing spectral variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) that are targeted to the membrane and/or synaptic vesicles in neuronal subsets to image identified presynaptic terminals. In mature tissues with no net change in synapse numbers, subpopulations of pr ...
... hippocampal slice cultures from mice expressing spectral variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) that are targeted to the membrane and/or synaptic vesicles in neuronal subsets to image identified presynaptic terminals. In mature tissues with no net change in synapse numbers, subpopulations of pr ...
Protein–protein interactions
... Genome Project to decode the sequence of human DNA, it became clear that we have far fewer genes than previously thought. In 2000 the number was estimated at perhaps 50 000–90 000. The current figure is a little over 20 000. How can organisms so complicated be constructed from so few ‘instructions’? ...
... Genome Project to decode the sequence of human DNA, it became clear that we have far fewer genes than previously thought. In 2000 the number was estimated at perhaps 50 000–90 000. The current figure is a little over 20 000. How can organisms so complicated be constructed from so few ‘instructions’? ...
PS 1 answers
... This website has several links. Those marked “The Amino Acids,” “The Peptide Bond,” “Secondary Structure,” and “Nucleotides and DNA” contain models of each of these things that will help you understand protein and DNA structure. To do the graded problem, click on “7.013 Problems” and do “Problem 1 ( ...
... This website has several links. Those marked “The Amino Acids,” “The Peptide Bond,” “Secondary Structure,” and “Nucleotides and DNA” contain models of each of these things that will help you understand protein and DNA structure. To do the graded problem, click on “7.013 Problems” and do “Problem 1 ( ...
4.5 Regulation and Variability of Signaling by Nuclear Receptors
... 4.3 Classification and Structure of Nuclear Receptors The nuclear receptors display a high degree of homology at the level of amino acid sequence, which indicates that they operate with similar functional principles. For some receptors the cognate hormone and their function in the cell remain u ...
... 4.3 Classification and Structure of Nuclear Receptors The nuclear receptors display a high degree of homology at the level of amino acid sequence, which indicates that they operate with similar functional principles. For some receptors the cognate hormone and their function in the cell remain u ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... complex with the protein of interest. (In fact there is no room on the membrane for the antibody to attach other than on the binding sites of the specific target protein). • Finally the nitrocellulose membrane is incubated with a secondary antibody, which is an antibody-enzyme conjugate that is dire ...
... complex with the protein of interest. (In fact there is no room on the membrane for the antibody to attach other than on the binding sites of the specific target protein). • Finally the nitrocellulose membrane is incubated with a secondary antibody, which is an antibody-enzyme conjugate that is dire ...
Protein
... • Distinguish between high quality and low quality proteins and list sources of each • Describe how 2 low quality proteins can be complementary to each other to provide the required amounts of essential amino acids ...
... • Distinguish between high quality and low quality proteins and list sources of each • Describe how 2 low quality proteins can be complementary to each other to provide the required amounts of essential amino acids ...
Pipe-Cleaner Proteins
... Work with a partner. One partner gets two long pieces of white pipe cleaner from the front, and the other gets 8 felt pens. You’ll need the following 8 colours: red, yellow, brown, green, orange, blue, purple, pink. Each partner will colour 1 of the pipe cleaners & follow instructions #1-6. 2. Start ...
... Work with a partner. One partner gets two long pieces of white pipe cleaner from the front, and the other gets 8 felt pens. You’ll need the following 8 colours: red, yellow, brown, green, orange, blue, purple, pink. Each partner will colour 1 of the pipe cleaners & follow instructions #1-6. 2. Start ...
LC-MRM, a rapid tool for high throughput quantification
... evaluation of any treatment. Traditionally, this has been done using antibody-based methods such as ELISA or Western blots (Matsui et al. 2015, DeRosa et al 2016). These sensitive methods have several limitations. An antibody may not always be available for a particular mRNA target protein, especial ...
... evaluation of any treatment. Traditionally, this has been done using antibody-based methods such as ELISA or Western blots (Matsui et al. 2015, DeRosa et al 2016). These sensitive methods have several limitations. An antibody may not always be available for a particular mRNA target protein, especial ...
Learning Objectives
... “beta sheet”. Almost all proteins contain one or both of these types of structures. Both are stabilized by hydrogen bonding! Alpha helix (-helix) ...
... “beta sheet”. Almost all proteins contain one or both of these types of structures. Both are stabilized by hydrogen bonding! Alpha helix (-helix) ...
No Slide Title
... Five β subunits (mammalian βA, βB, βC, βE, and Xenopus βD) have been cloned. The activin/inhibin nomenclature reflects the subunit composition of the proteins: activin A (βAβA), activin B (βB- βB), activin AB (βA- βB), inhibin A (α- βA), and inhibin B (α- βB). At the amino acid sequence level, the m ...
... Five β subunits (mammalian βA, βB, βC, βE, and Xenopus βD) have been cloned. The activin/inhibin nomenclature reflects the subunit composition of the proteins: activin A (βAβA), activin B (βB- βB), activin AB (βA- βB), inhibin A (α- βA), and inhibin B (α- βB). At the amino acid sequence level, the m ...
Intrinsic Protein Disorder and Protein
... corepressor, leading to the initiation of transcription by the coactivator. Type II NRs include NR subfamily 1, and receptor molecules such as retinoic acid receptor (RAR), retinoid x receptor (RXR), thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and vitamin D receptor (VDR). Peroxisome proliferator-activated recept ...
... corepressor, leading to the initiation of transcription by the coactivator. Type II NRs include NR subfamily 1, and receptor molecules such as retinoic acid receptor (RAR), retinoid x receptor (RXR), thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and vitamin D receptor (VDR). Peroxisome proliferator-activated recept ...
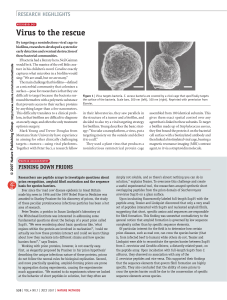
Virus to the rescue
... species, and by using the peptide arrays they were able to observe that the interactions were highly sequence-dependent. “In the case of mammalian prions, the sequences of prion proteins [across species] are actually much more closely related than they are between these two yeast species,” remarks T ...
... species, and by using the peptide arrays they were able to observe that the interactions were highly sequence-dependent. “In the case of mammalian prions, the sequences of prion proteins [across species] are actually much more closely related than they are between these two yeast species,” remarks T ...
Ch 9 and 11 Review Slides
... (c) Hormonal signaling. Specialized endocrine cells secrete hormones into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all body cells. ...
... (c) Hormonal signaling. Specialized endocrine cells secrete hormones into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all body cells. ...
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are
... An example of this process occurs in the kidney. Glucose, water, salts, ions, and amino acids needed by the body are filtered in one part of the kidney. This filtrate, which includes glucose, is then reabsorbed in another part of the kidney. Because there are only a finite number of carrier proteins ...
... An example of this process occurs in the kidney. Glucose, water, salts, ions, and amino acids needed by the body are filtered in one part of the kidney. This filtrate, which includes glucose, is then reabsorbed in another part of the kidney. Because there are only a finite number of carrier proteins ...
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of
... Autophagy is a cellular mechanism by which parts of the cell are digested and the products are used up again by the cell for survival and this may be stimulated under certain conditions such as starvation ...
... Autophagy is a cellular mechanism by which parts of the cell are digested and the products are used up again by the cell for survival and this may be stimulated under certain conditions such as starvation ...
Proteins - e
... pattern can alter in the diseased state. Nevertheless, the race is now on to analyse the structure and function of proteins, many of which are completely new to science, and to see whether they can act as novel drug targets for the future. This is no easy task, and it is made all the more difficult ...
... pattern can alter in the diseased state. Nevertheless, the race is now on to analyse the structure and function of proteins, many of which are completely new to science, and to see whether they can act as novel drug targets for the future. This is no easy task, and it is made all the more difficult ...
Text S6
... are predominantly localized to the nucleus and have been shown to interact with intron-containing transcripts [1,2] and transcribing RNA polymerase II [3,4], respectively. In contrast, Pub1 is predominantly cytoplasmic [5] and has not previously been linked to mRNA processing of intron-containing tr ...
... are predominantly localized to the nucleus and have been shown to interact with intron-containing transcripts [1,2] and transcribing RNA polymerase II [3,4], respectively. In contrast, Pub1 is predominantly cytoplasmic [5] and has not previously been linked to mRNA processing of intron-containing tr ...
Efficient Isolation and Identification of Intracellular Protein
... aspects of the NFκB pathway with one construct ...
... aspects of the NFκB pathway with one construct ...
Peptides and Proteins
... polypeptide subunits held together by non-covalent interaction like H-bonds, ionic or hydrophobic interactions. Examples on protein having quaternary structure: – Collagen is a fibrous protein of three polypeptides (trimeric) that are supercoiled like a rope. ...
... polypeptide subunits held together by non-covalent interaction like H-bonds, ionic or hydrophobic interactions. Examples on protein having quaternary structure: – Collagen is a fibrous protein of three polypeptides (trimeric) that are supercoiled like a rope. ...
Hormones in action
... Natural hormones are themselves agonists and, in many cases, more than one distinct hormone binds to the same receptor. For a given receptor, different agonists can have dramatically different potencies. Antagonists are molecules that bind the receptor and block binding of the agonist, but fail to ...
... Natural hormones are themselves agonists and, in many cases, more than one distinct hormone binds to the same receptor. For a given receptor, different agonists can have dramatically different potencies. Antagonists are molecules that bind the receptor and block binding of the agonist, but fail to ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).