CELL MEMBRANE - Western Washington University
... ECF has permeant solute, ECF & ICF initially equal ...
... ECF has permeant solute, ECF & ICF initially equal ...
Document
... Length of fatty acid plays a role in its _____________________ • Usually contain _________numbers of carbons (can contain ___________, depending on how they are biosynthesized) • FA that contain C=C, are ____________________: If contain only C-C bonds, they are _______________________ ...
... Length of fatty acid plays a role in its _____________________ • Usually contain _________numbers of carbons (can contain ___________, depending on how they are biosynthesized) • FA that contain C=C, are ____________________: If contain only C-C bonds, they are _______________________ ...
6-9_IonChannelsPatchClamp_TasiBenedekJozsef
... The „patch clamp” is a technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in a wide variety of cells. It is technically a refinement of the Voltage clamp, an experimental method which measures the ion currents through cell membranes. The patch clamp was developed ...
... The „patch clamp” is a technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in a wide variety of cells. It is technically a refinement of the Voltage clamp, an experimental method which measures the ion currents through cell membranes. The patch clamp was developed ...
Isabel Hoyt Membrane
... 1. What does selective permeability mean and why is that important to cells? The plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability, it allows some substances to cross it more easily than others. This ability of the cell to discriminate in its chemical exchanges with its environment is fundamental to l ...
... 1. What does selective permeability mean and why is that important to cells? The plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability, it allows some substances to cross it more easily than others. This ability of the cell to discriminate in its chemical exchanges with its environment is fundamental to l ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important in some reflexes - chemical synapses do have a significant delay ie slow - commo ...
... - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important in some reflexes - chemical synapses do have a significant delay ie slow - commo ...
Topic 1.4 Membrane Transport
... The axons of nerve cells transmit electrical impulses by translocating ions to create a voltage difference across the membrane. ...
... The axons of nerve cells transmit electrical impulses by translocating ions to create a voltage difference across the membrane. ...
Molecular dynamics simulations of membrane
... The aim of this laboratory practice is to get familiar with the tools for molecular dynamics, possibilities to set on models and graphical presentation of atomistic models. EXPERIMENT Due to the limited time and large resources needed to generate MD trajectories of membranes, the latter will be prov ...
... The aim of this laboratory practice is to get familiar with the tools for molecular dynamics, possibilities to set on models and graphical presentation of atomistic models. EXPERIMENT Due to the limited time and large resources needed to generate MD trajectories of membranes, the latter will be prov ...
Cell Membrane Diffusion
... The Special Case of Water Movement of water across the cell membrane ...
... The Special Case of Water Movement of water across the cell membrane ...
Lipids and Membranes, Fall 12—Worksheet - KEY
... influenced by extracellular signals (like the chemical cues from bacteria!) causing them to group in on region of the membrane. So the reality is more complex. ...
... influenced by extracellular signals (like the chemical cues from bacteria!) causing them to group in on region of the membrane. So the reality is more complex. ...
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of
... Potassium ions are present in higher concentrations inside the cells through a pumping mechanism that requires energy to work against the concentration ...
... Potassium ions are present in higher concentrations inside the cells through a pumping mechanism that requires energy to work against the concentration ...
1. Given the molecule: a. What type of molecule is this? b. Give the
... g. Would you expect concentrations of this type of molecule to be higher in animals living in the arctic or in the tropics? Explain why in 40 words or fewer. 5. Multiple choice. Which one of the following statements is correct? a. Transbilayer diffusion of lipids is slow because of the flexibility o ...
... g. Would you expect concentrations of this type of molecule to be higher in animals living in the arctic or in the tropics? Explain why in 40 words or fewer. 5. Multiple choice. Which one of the following statements is correct? a. Transbilayer diffusion of lipids is slow because of the flexibility o ...
ATP-sensitive potassium channels in capillaries isolated from
... vasoactive substances such as adenosine, calcitonin generelated peptide and angiotensin II (Dart & Standen, 1993; Quayle et al. 1994; Kubo et al. 1997) and by numerous intracellular factors such as pH, lactate, protein kinase A and protein kinase C (Han et al. 1993; Kleppisch & Nelson, 1995; Bonev & ...
... vasoactive substances such as adenosine, calcitonin generelated peptide and angiotensin II (Dart & Standen, 1993; Quayle et al. 1994; Kubo et al. 1997) and by numerous intracellular factors such as pH, lactate, protein kinase A and protein kinase C (Han et al. 1993; Kleppisch & Nelson, 1995; Bonev & ...
Channels active in the excitability of nerves and skeletal muscles
... nels have different degrees of delayed rectification when their voltage-sensing segment detects that the neuron is depolarized. They open after short depolarization but eventually close with long depolarization. It is likely that cytoplasmic ball-and-chain portions of these protein channels from eit ...
... nels have different degrees of delayed rectification when their voltage-sensing segment detects that the neuron is depolarized. They open after short depolarization but eventually close with long depolarization. It is likely that cytoplasmic ball-and-chain portions of these protein channels from eit ...
Figure 8-9
... What if the reversal potential for an ion channel that is selective for “univalent” cations so both Na+ and K+ are permeable? (e.g., the Ach muscarinic receptor in the motor end plate of skeletal muscle.) • If ACh were to open an ion channel permeable only to K+, then the reversal potential of the ...
... What if the reversal potential for an ion channel that is selective for “univalent” cations so both Na+ and K+ are permeable? (e.g., the Ach muscarinic receptor in the motor end plate of skeletal muscle.) • If ACh were to open an ion channel permeable only to K+, then the reversal potential of the ...
Tutorial Vm
... • Initial diffusion of K+ down concentration gradient from I to II • This causes + charge to accumulate in II because + and - charges are separated – Remember that Cl- can’t cross the membrane ! • Therefore II becomes positive relative to I ...
... • Initial diffusion of K+ down concentration gradient from I to II • This causes + charge to accumulate in II because + and - charges are separated – Remember that Cl- can’t cross the membrane ! • Therefore II becomes positive relative to I ...
Domains and Kingdoms Taxonomy Notes 2
... bacteria by that they are – Smaller than bacteria – Non-‐living with a strand of gene
... bacteria by that they are – Smaller than bacteria – Non-‐living with a strand of gene
Test Your Knowledge!
... summation response. C. chemical synapses rely on neurotransmitters for signaling. D. electrical synapses have an all or none response. E. All the above are correct ...
... summation response. C. chemical synapses rely on neurotransmitters for signaling. D. electrical synapses have an all or none response. E. All the above are correct ...
Channels active in the excitability of nerves and skeletal muscles
... nels have different degrees of delayed rectification when their voltage-sensing segment detects that the neuron is depolarized. They open after short depolarization but eventually close with long depolarization. It is likely that cytoplasmic ball-and-chain portions of these protein channels from eit ...
... nels have different degrees of delayed rectification when their voltage-sensing segment detects that the neuron is depolarized. They open after short depolarization but eventually close with long depolarization. It is likely that cytoplasmic ball-and-chain portions of these protein channels from eit ...
DIFFUSION, OSMOSIS AND CELLULAR TRANSPORT
... specific for one chemical; binding of substrate causes shape change in transport protein ...
... specific for one chemical; binding of substrate causes shape change in transport protein ...
Membrane structure, I
... Membrane structure, I Selective permeability Amphipathic~ hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions 1935 Davson Danielli sandwich model Singer-Nicolson: 1972 fluid mosaic model ...
... Membrane structure, I Selective permeability Amphipathic~ hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions 1935 Davson Danielli sandwich model Singer-Nicolson: 1972 fluid mosaic model ...
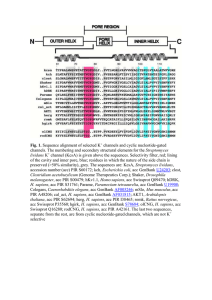
Fig. 1. Sequence alignment of selected K+ channels and cyclic
... chain affects both agitoxin2 and TEA binding from the extracellular solution (14). This residue is the external TEA site. The mustard-colored side chain at the base of the selectivity filter affects TEA binding from the intracellular solution [the internal TEA site (15)]. The side chains colored gre ...
... chain affects both agitoxin2 and TEA binding from the extracellular solution (14). This residue is the external TEA site. The mustard-colored side chain at the base of the selectivity filter affects TEA binding from the intracellular solution [the internal TEA site (15)]. The side chains colored gre ...
Interaction of small* molecules with membranes.
... 2) Types of molecules interacting with the membrane 3) Membrane permeability to nonelectrolytes 4) Water permeability 5) Membrane potential at the surface 6) Transmembrane potential. Permeability to protons and other ions. Measuring the transmembrane potential ...
... 2) Types of molecules interacting with the membrane 3) Membrane permeability to nonelectrolytes 4) Water permeability 5) Membrane potential at the surface 6) Transmembrane potential. Permeability to protons and other ions. Measuring the transmembrane potential ...
Chapter 5
... kinetic energy. • Molecules are in constant motion because they have kinetic energy. ...
... kinetic energy. • Molecules are in constant motion because they have kinetic energy. ...
Bio-261-chapter-3
... are covalently linked to the NAM molecules of the glycan chain. Some are linked to the cytoplasmic membrane and are called lipoteichoic acids. • These polymers consists of ribitol-phosphates and glycerol phosphates molecules joined together. Sugars and D- alanine may be attached to these polymers pr ...
... are covalently linked to the NAM molecules of the glycan chain. Some are linked to the cytoplasmic membrane and are called lipoteichoic acids. • These polymers consists of ribitol-phosphates and glycerol phosphates molecules joined together. Sugars and D- alanine may be attached to these polymers pr ...
Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments
... Peripheral proteins attach to its surface by ionic bonds. • The association of protein molecules with lipid molecules is not covalent; both are free to move around laterally, according to the fluid mosaic model. ...
... Peripheral proteins attach to its surface by ionic bonds. • The association of protein molecules with lipid molecules is not covalent; both are free to move around laterally, according to the fluid mosaic model. ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.