Protect Your Hearing!
... The outer ear consists of the ear canal and eardrum. Sound travels down the ear canal, striking the eardrum and causing it to move or vibrate. The middle ear is a space behind the eardrum that contains three small bones called ossicles. This chain of tiny bones is connected to the eardrum at ...
... The outer ear consists of the ear canal and eardrum. Sound travels down the ear canal, striking the eardrum and causing it to move or vibrate. The middle ear is a space behind the eardrum that contains three small bones called ossicles. This chain of tiny bones is connected to the eardrum at ...
Lesson 2.1: Critical Reading Name___________________
... Boyle. Boyle placed a ticking clock in a sealed glass jar. The clock could be heard ticking through the air and glass of the jar. Then Boyle pumped the air out of the jar. The clock was still running, but the ticking could no longer be heard. That’s because the sound couldn’t travel away from the cl ...
... Boyle. Boyle placed a ticking clock in a sealed glass jar. The clock could be heard ticking through the air and glass of the jar. Then Boyle pumped the air out of the jar. The clock was still running, but the ticking could no longer be heard. That’s because the sound couldn’t travel away from the cl ...
effects of loud music on hearing
... perceived echo or ‘boomy’ quality of the wearer’s own voice (which may be related to an ‘occlusion effect’). A special filter is placed in the earpiece to attenuate the frequencies more evenly. The resulting sound has a better balance of low and high frequency components, so that only the volume (in ...
... perceived echo or ‘boomy’ quality of the wearer’s own voice (which may be related to an ‘occlusion effect’). A special filter is placed in the earpiece to attenuate the frequencies more evenly. The resulting sound has a better balance of low and high frequency components, so that only the volume (in ...
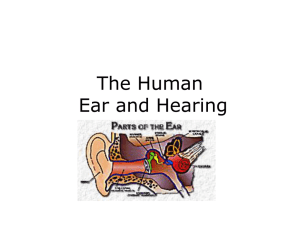
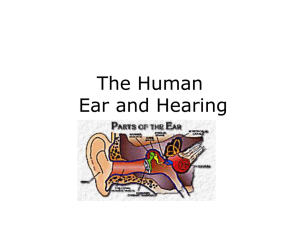
The Human Ear and Hearing
... Initial experiments on the frequency sensitivity of the human ear. ...
... Initial experiments on the frequency sensitivity of the human ear. ...
The Human Ear and Hearing - Baldwin County Public Schools
... Initial experiments on the frequency sensitivity of the human ear. ...
... Initial experiments on the frequency sensitivity of the human ear. ...
A Simplified Solid Mechanical and Acoustic Model for
... EARING is a branch of science concerned with the physiology of sound, perception and relates with the field of processing and interpreting the sound signals and their disorders. Hearing is the second most important sensible part that will make more perception and awareness with other people [1]. Hum ...
... EARING is a branch of science concerned with the physiology of sound, perception and relates with the field of processing and interpreting the sound signals and their disorders. Hearing is the second most important sensible part that will make more perception and awareness with other people [1]. Hum ...
Ear [screen displays a model of the ear] [voice of Dr. Barbara
... [screen displays a model of the ear] [voice of Dr. Barbara Davis, Instructor, Biology, speaking] Welcome to the sensory lab. In this video we’ll be looking at the ear. The outside portion of the ear is called the auricle. The opening into the external auditory canal is called the external auditory m ...
... [screen displays a model of the ear] [voice of Dr. Barbara Davis, Instructor, Biology, speaking] Welcome to the sensory lab. In this video we’ll be looking at the ear. The outside portion of the ear is called the auricle. The opening into the external auditory canal is called the external auditory m ...
File
... the outer ear and the middle ear. It vibrates as soon as it receives the sound waves and transforms the sound energy into the mechanical energy. Hammer - It is a tiny bone, located next to the eardrum. Since it lies adjacent to the eardrum, the vibrations from the eardrum cause the hammer to vibra ...
... the outer ear and the middle ear. It vibrates as soon as it receives the sound waves and transforms the sound energy into the mechanical energy. Hammer - It is a tiny bone, located next to the eardrum. Since it lies adjacent to the eardrum, the vibrations from the eardrum cause the hammer to vibra ...
Abstract
... Shoulder’, M.B.) The physiological levels of Ldp are easily programmed and we use them as reference values for the dB-DP-Loss presentation in our DP-grams. For clinical application on has to confine the number of registrations to 6 to 10 per ear and frequency. Now, as a side result we can read and ...
... Shoulder’, M.B.) The physiological levels of Ldp are easily programmed and we use them as reference values for the dB-DP-Loss presentation in our DP-grams. For clinical application on has to confine the number of registrations to 6 to 10 per ear and frequency. Now, as a side result we can read and ...
Course Guide
... 1203 - Grado de Logopedia - Students must have acquired knowledge and understanding in a specific field of study, on the basis of general secondary education and at a level that includes mainly knowledge drawn from advanced textbooks, but also some cutting-edge knowledge in their field of study. ...
... 1203 - Grado de Logopedia - Students must have acquired knowledge and understanding in a specific field of study, on the basis of general secondary education and at a level that includes mainly knowledge drawn from advanced textbooks, but also some cutting-edge knowledge in their field of study. ...
Answers to Assignments
... 1. Students’ answers should include the following: a. An accurate health history of the ears, nose, mouth, and throat includes questions concerning: Past and recent injuries or surgeries Acute or chronic pain/tenderness Lumps Drainage Difficulty swallowing b. The physical examination techn ...
... 1. Students’ answers should include the following: a. An accurate health history of the ears, nose, mouth, and throat includes questions concerning: Past and recent injuries or surgeries Acute or chronic pain/tenderness Lumps Drainage Difficulty swallowing b. The physical examination techn ...
A quick tour of the auditory system
... analyzer • Basilar membrane is wide and stiff at base by oval window, and narrow and less stiff at apex • Mechanical properties cause selective amplification of waves of high and low frequencies at particular places along membrane • Preserved along auditory pathway, provide tonotopy mapping, a place ...
... analyzer • Basilar membrane is wide and stiff at base by oval window, and narrow and less stiff at apex • Mechanical properties cause selective amplification of waves of high and low frequencies at particular places along membrane • Preserved along auditory pathway, provide tonotopy mapping, a place ...
Introduction to Health Science
... Eustachian (auditory) tubes to become blocked, inflamed or irritated. • Examples include colds, sinus infections, allergies, tobacco smoke or other irritants, babies who spend a lot of time drinking on his or her back. ...
... Eustachian (auditory) tubes to become blocked, inflamed or irritated. • Examples include colds, sinus infections, allergies, tobacco smoke or other irritants, babies who spend a lot of time drinking on his or her back. ...
THE PSYCHOACOUSTIC BASIS AND IMPLEMENTATION
... The psychoacoustic response to directional sounders has been shown in numerous exercises and research studies with human subjects to lessen the time required for evacuation and to effectively assist occupants searching for egress routes and exits. A summary of several scenarios is presented in Table ...
... The psychoacoustic response to directional sounders has been shown in numerous exercises and research studies with human subjects to lessen the time required for evacuation and to effectively assist occupants searching for egress routes and exits. A summary of several scenarios is presented in Table ...
primary somatosensory cortex
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of touch? (continued) • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive touch information subsequently project the information to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary ...
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of touch? (continued) • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive touch information subsequently project the information to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI). Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary ...
Noise Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
... hear are at safe levels that do not affect our hearing. However, when we are exposed to harmful noise - loud sounds that last a long time or extremely loud sounds – hair cells in our inner ear can be damaged. These small sensitive structures make hearing possible by converting sound energy into elec ...
... hear are at safe levels that do not affect our hearing. However, when we are exposed to harmful noise - loud sounds that last a long time or extremely loud sounds – hair cells in our inner ear can be damaged. These small sensitive structures make hearing possible by converting sound energy into elec ...
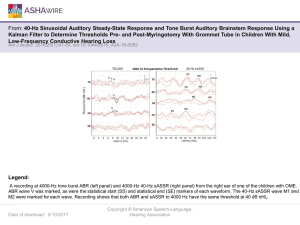
40-Hz Sinusoidal Auditory Steady-State Response and Tone Burst
... From: 40-Hz Sinusoidal Auditory Steady-State Response and Tone Burst Auditory Brainstem Response Using a Kalman Filter to Determine Thresholds Pre- and Post-Myringotomy With Grommet Tube in Children With Mild, Low-Frequency Conductive Hearing Loss Am J Audiol. 2016;25(1):41-53. doi:10.1044/2015_AJA- ...
... From: 40-Hz Sinusoidal Auditory Steady-State Response and Tone Burst Auditory Brainstem Response Using a Kalman Filter to Determine Thresholds Pre- and Post-Myringotomy With Grommet Tube in Children With Mild, Low-Frequency Conductive Hearing Loss Am J Audiol. 2016;25(1):41-53. doi:10.1044/2015_AJA- ...
Hearing and the Ear
... Cochlea: cavity of the inner ear filled with liquid and Lined with thousands of tiny hairs. The vibrations are passed from stirrup to membrane to liquid to hairs (which sway back and forth). The hairs are attached to nerve cells that detect movement and send messages to the brain. ...
... Cochlea: cavity of the inner ear filled with liquid and Lined with thousands of tiny hairs. The vibrations are passed from stirrup to membrane to liquid to hairs (which sway back and forth). The hairs are attached to nerve cells that detect movement and send messages to the brain. ...
Cochlear Implants - Electrical, Computer & Biomedical Engineering
... Fluid movement stimulates hair cells Hairs move back and forth sending electrical signals to auditory nerve Carried to the brain ...
... Fluid movement stimulates hair cells Hairs move back and forth sending electrical signals to auditory nerve Carried to the brain ...
Signal Transmission in the Auditory System
... modulation frequencies in that range, and are therefore likely to perform temporal processing relevant to musical consonance. To test this hypothesis, we recorded responses of single units in the inferior colliculus (IC, the principal auditory nucleus in the midbrain) of anesthetized cats to pairs ...
... modulation frequencies in that range, and are therefore likely to perform temporal processing relevant to musical consonance. To test this hypothesis, we recorded responses of single units in the inferior colliculus (IC, the principal auditory nucleus in the midbrain) of anesthetized cats to pairs ...
Sound and Hearing
... The first cymbal experiment gives an estimate for the speed of sound as 294 m/s. Use the average of your results to calculate another estimate for the speed of sound. 1. How does this calculation for the average speed of sound compare with the real speed? 2. What errors could have affected the resul ...
... The first cymbal experiment gives an estimate for the speed of sound as 294 m/s. Use the average of your results to calculate another estimate for the speed of sound. 1. How does this calculation for the average speed of sound compare with the real speed? 2. What errors could have affected the resul ...
Ear Care Guidance
... It is a mixture of cerumen (a sweat-like substance) and sebum (an oily substance) both secreted by glands in your ear canal which combines with dust, debris, hair etc to form ear wax. It is normal to have ear wax and it only usually becomes a problem when it has been pushed deeper into the ear canal ...
... It is a mixture of cerumen (a sweat-like substance) and sebum (an oily substance) both secreted by glands in your ear canal which combines with dust, debris, hair etc to form ear wax. It is normal to have ear wax and it only usually becomes a problem when it has been pushed deeper into the ear canal ...
The Evolution of Mammalian Sound Localization
... between the ears. Thus, the smaller the animal, the higher it must hear in order to use the binaural intensity cue. Finally, mammals evolved external ears, or pinnae, that alter the spectrum of a sound as a function of the location of the sound source (Figure 1B); monaural pinna cues enable an anim ...
... between the ears. Thus, the smaller the animal, the higher it must hear in order to use the binaural intensity cue. Finally, mammals evolved external ears, or pinnae, that alter the spectrum of a sound as a function of the location of the sound source (Figure 1B); monaural pinna cues enable an anim ...



![Ear [screen displays a model of the ear] [voice of Dr. Barbara](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011552985_1-3bf3ff483c5a0491f00193de7607703b-300x300.png)